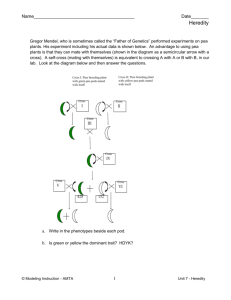
Genetics Lab Handout (Lab 5)
advertisement

Bot 106 GENETICS WORKSHEET Terms to know: 1. Genes 2. Alleles 3. Dominant and recessive genes 4. Haploid and diploid 5. True breeding parents 6. Phenotype 7. Genotype 8. Homozygous condition 9. Heterozygous condition Genetics Lab 1 10. P,F1 and F2 generations 11. Monohybrid cross 12. Dihybrid cross 13. Gametes in a cross 14. Punnett square 15. Phenotypic ratios 16. Genotypic ratios Genetics Lab 2 Problems Sets: 1. Lets study a monohybrid cross: Mendel in one of his experiments crossed a true breeding pea plant having green pods with a true breeding pea plant with yellow pods. All of the F1 population plants had yellow pods. (a). From this above result, which trait do you think is recessive? Why? (b). Set up a Punnett square to show the Parental cross, the F1 phenotypes, and the F1 genotypes, along with their respective ratios. (c). If an F1 plant is now self-pollinated, what are the phenotypes(s) produced in F2, and their ratios? Also give the F2 gentoypes and genotypic ratios. Do the Punnett squares for the F1 cross. PLEASE SHOW ALL CALCULATION: Problem 2. You cross a true breeding radish line that produces a long root with a true breeding round rooted variety. All of the F1 has long roots. (a). How many alleles are there for root shape? (b). Which allele is dominant? Why? You allow the F1 population to self-pollinate. You get 100 F2 plants. SHOW THE PUNNETT SQUARE FOR THE F1 CROSS. (c). How many plants will have long roots? (d). How many plants will have round roots? (e). Among the long rooted plants will all of them have the same genotypes? Explain. Genetics Lab 3 Bot 106 Genetic Problems 1. What are the genotypes of the spores produced by plants that have the following genotypes: XXYyZZ CcDDEEFFggHh AabbCCDd 2. You cross a true breeding radish line that produces a long root with a true breeding round rooted variety. All of the F1 have oval roots. You allow the F1 to self-pollinate. You examine the F2 and find that of the 100 plants examined 25 have long roots, 50 have oval roots, and 25 have round roots. How many genes control the shape of the fruit? What type of genetic interaction does this problem illustrate? 3. Tomato stems can be green or purple. The stems can have long or short internodes. Green (G) is dominant over purp0le (g) and long (L) is dominant over short (l). Answer the following questions about this cross: Llgg X llGg What are the phenotypes of each parent? What are the genotypes and genotypic ratios of the F1? What are the phenotypes and phenotypic ratios of the F1? Genetics Lab 4