PROTOTYPE DRUG: Oxytocin (Pitocin, Syntocinon)
advertisement
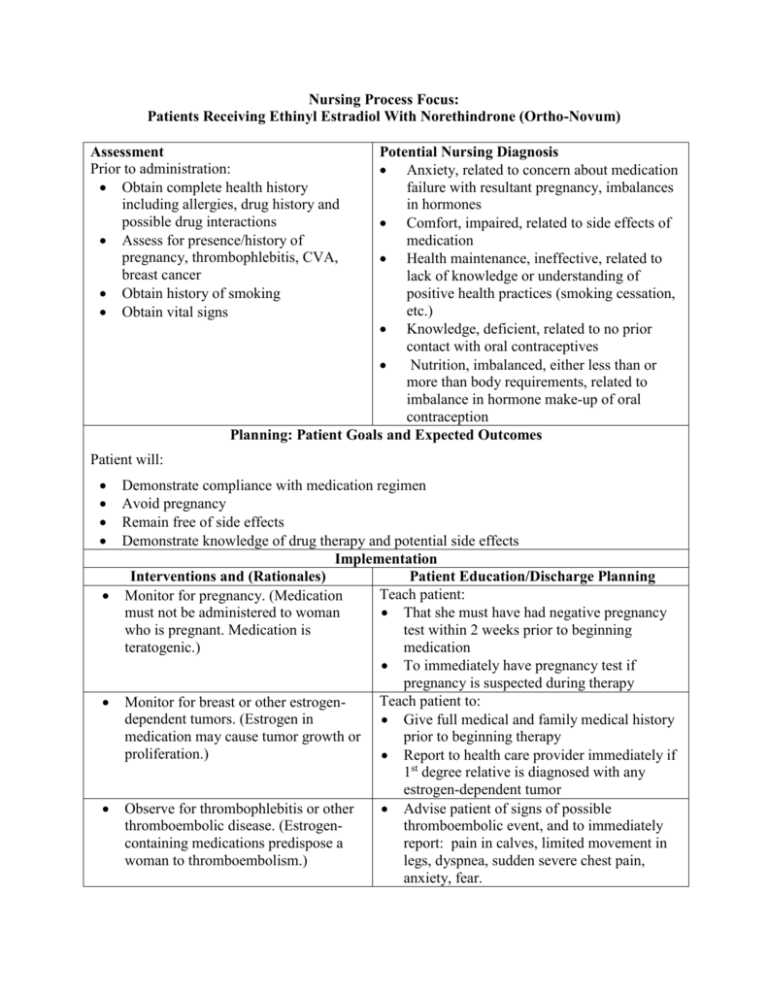
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Ethinyl Estradiol With Norethindrone (Ortho-Novum) Assessment Prior to administration: Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug interactions Assess for presence/history of pregnancy, thrombophlebitis, CVA, breast cancer Obtain history of smoking Obtain vital signs Potential Nursing Diagnosis Anxiety, related to concern about medication failure with resultant pregnancy, imbalances in hormones Comfort, impaired, related to side effects of medication Health maintenance, ineffective, related to lack of knowledge or understanding of positive health practices (smoking cessation, etc.) Knowledge, deficient, related to no prior contact with oral contraceptives Nutrition, imbalanced, either less than or more than body requirements, related to imbalance in hormone make-up of oral contraception Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will: Demonstrate compliance with medication regimen Avoid pregnancy Remain free of side effects Demonstrate knowledge of drug therapy and potential side effects Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Teach patient: Monitor for pregnancy. (Medication must not be administered to woman That she must have had negative pregnancy who is pregnant. Medication is test within 2 weeks prior to beginning teratogenic.) medication To immediately have pregnancy test if pregnancy is suspected during therapy Teach patient to: Monitor for breast or other estrogendependent tumors. (Estrogen in Give full medical and family medical history medication may cause tumor growth or prior to beginning therapy proliferation.) Report to health care provider immediately if 1st degree relative is diagnosed with any estrogen-dependent tumor Observe for thrombophlebitis or other Advise patient of signs of possible thromboembolic disease. (Estrogenthromboembolic event, and to immediately containing medications predispose a report: pain in calves, limited movement in woman to thromboembolism.) legs, dyspnea, sudden severe chest pain, anxiety, fear. Monitor for cardiac disorders. (Medication will lead to worsening of cardiac problems.) Monitor for cerebrovascular disorders. (Medication increases risk for thrombotic disorders, one of leading causes of CVA.) Obtain history of cigarette smoking. (Combination of oral contraception and smoking greatly increases risk of cardiovascular disease, especially MI Risk increases with age >35 and with number of cigarettes smoked, e.g., 15 or more/day.) Monitor mental status. (Side effects such as weight gain may cause depression in some women.) Monitor blood glucose in patients with diabetes. Use with caution in woman with diabetes or with familial history of diabetes. (Combination may upset glycemic control so patient would experience either hypo- or hyperglycemia; adjustments in dose of hypoglycemic medications may be necessary.) Monitor for side effects or adverse reactions. (If serious side effects occur, patient may need to switch to oral contraceptive with a different combination or percentage of hormones.) Advise patient of signs of possible cardiac problems which must be immediately reported: chest pain, dyspnea, edema, tachycardia or bradycardia, palpitations. Teach patient: To contact all health care providers prior to starting oral contraception so other medications can be adjusted as needed Signs of impending migraine headache or seizure, so preventative measures can be taken Advise patient to: Stop smoking prior to beginning treatment with oral contraceptives Attend smoking cessation groups. Instruct patient regarding symptoms of depression to report immediately: lack of interest in every-day activities, changes in sleeping or eating habits, stopping previously enjoyable activities, etc. Advise patient to monitor urine and blood glucose regularly, and contact health care provider if any abnormalities occur so adjustments in hypoglycemic medication can be made. Advise patient to: Be aware of edema, unexplained loss of vision, diplopia, intolerance to contact lens, nausea, gall bladder disease, diarrhea or constipation, abdominal cramps, changes in urinary function, dysmenorrhea, breast fullness, fatigue, skin rash, acne Note mid-cycle breakthrough bleeding, vaginal candidiasis, photosensitivity, changes in urinary patterns, feelings of abdominal fullness Advise patient to: Monitor whether patient understands how/when to take medication. (Only Use barrier contraceptive during 1st week of with thorough understanding will she initial cycle and for 7 days after 2 consecutive be able to take medication correctly and missed doses avoid adverse reactions, or be aware of Discontinue medication and notify health care physical changes that could be provider if bleeding resembling menstrual secondary to the medication, and take cycle occurs mid-cycle measures to prevent permanent, serious Be aware of fluid retention (teach to weigh harm.) self weekly and record, note tightening of rings, shoes, etc.) Decrease salt intake if edema occurs Contact health care provider if 2 consecutive periods are missed; pregnancy may have occurred Follow recommendations for follow-up Do self breast exams monthly Have annual PAP smears done. See health care provider at regular intervals Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Conjugated Estgrogens (Premarin) and Conjugated Estrogens with Medroxyprogesterone (Prempro) ASSESSMENT POTENTIAL NURSING DIAGNOSES Prior to administration: Body image, disturbed, related to side Obtain complete health history including effects of medication allergies, drug history and possible drug Comfort, impaired, related to effects of intgeractions medication Assess for presence/history of breast Fluid volume, excess, related to edema cancer, estrogen dependent cancer, secondary to medication abnormal genital bleeding, Noncompliance, related to unpleasant side thromboembolic disorders, cardiovascular effects, desire for pregnancy, lack of disorders, smoking history, pregnancy knowledge or understanding of proper self-administration Tissue perfusion, impaired, cardiopulmonary, related to development of thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, or cerebral, related to incidence of CVA secondary to medication PLANNING: PATIENT GOALS AND EXPECTED OUTCOMES Patient will: Demonstrate understanding of correct self administration and potential side effects Demonstrate positive body image and self-concept Remain compliance with drug regimen Remain free of symptoms of thrombophlebitis or other clot development Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Teaching/Discharge Planning Obtain history of cancer in patient or close Advise patient of importance of complete relative. (Estrogen-dependent cancer physical exam prior to beginning therapy combination of medication and estrogenwith conjugated estrogen. dependent tumors, either currently or history of, put patient at much higher risk for developing cancer.) Instruct patient to Monitor for signs of pregnancy. (Can cause serious fetal harm.) Have negative pregnancy test no more than 2 weeks prior to beginning conjugated estrogen therapy and periodically during treatment Report immediately if she suspects she is pregnant Monitor for current or past history of Advise patient of importance of complete thromboembolism. (Estrogen use disclosure of past medical history. increases chance of thromboembolism occurring.) Monitor for undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding. (Can increase bleeding, tumor size, if undiagnosed tumor present.) Monitor for cardiovascular/cerebrovascular disorders. (Must be used with caution in patients with CAD, hypertension, and cerebrovascular disease. Any of these conditions predispose woman to thromboembolic disorders. Cardiovascular side effects are the most serious side effects, and include MI, pulmonary embolism, hypertension, CVA.) Evaluate breast health. (Use with caution in patient with fibrocystic breast disease, breast nodules, or abnormal mammograms. Can cause worsening of condition. If cancer develops, it is essential to have baseline information with which to make comparisons.) Monitor for vision changes. (Medication may cause worsened myopia or astigmatism, intolerance of contact lenses.) Obtain smoking history. (Smoking increases risk of cardiovascular disease, especially when in combination with estrogens.) Monitor for diabetes mellitus. (Estrogens may alter blood glucose levels.) Monitor for seizure disorder. (Estrogeninduced fluid retention may increase incidence of seizures.) Observe for side effects. Side effects are dose dependent, and include: weight gain, edema, nausea/vomiting, abdominal cramps and bloating, acute pancreatitis, Instruct patient to have complete physical exam prior to beginning therapy. Teach patient to: Have complete physical exam prior to estrogen therapy Have routine blood pressure screening; teach that hypertension has no symptoms Inform female patients that atypical symptoms of a MI may be experienced: fatigue, dyspnea, nausea, light-headedness, palpitations, “racing” heart and to report to health care provider immediately if any of these sensations occur Advise patient of importance of complete physical exam prior to treatment and periodically during treatment. Instruct patient to: Have complete eye exam prior to beginning treatment and periodically during treatment Report if decreased vision occurs, or if intolerance to contact lenses occurs Instruct patient to: Quit smoking Attend smoking cessation programs Advise diabetic patient to monitor blood glucose frequently and report if any consistent changes. Teach patient to Disclose information if seizure disorder present Consult health care provider of anti-seizure medication prior to beginning estrogen therapy Be extra alert for possibility of seizures occurring Advise patient of common side effects and to be alert to occurrence of them. appetite changes, skin eruptions, mental depression, decreased libido, headache, fatigue, nervousness. Monitor for GU changes. (Can be caused by estrogens: breakthrough bleeding, spotting, changes in amount and/or duration of menstrual flow, amenorrhea during and after use, candida vaginitis.) Advise male patient that he may develop feminine characteristics or become impotent; teach him these will resolve when treatment completed Advise female patient to report any of GU changes. Instruct patient: Evaluate patient’s understanding and proper self-administration. (To ensure Regarding dose, form and frequency of patient safety) medication To take with food to decrease GI irritation To take daily dose at HS to decrease occurrence of side effects That if cyclic therapy ordered, to take medication for 3 weeks and then omit for 1 week To document menstruation and any problems that occur To report immediately if pregnancy suspected To take lowest effective dose for shortest time period, to decrease chances of side effects developing Risks associated with supplemental estrogens Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Medroxyprogesterone (Provera) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Health maintenance, ineffective, related to Obtain complete health history including lack of knowledge or understanding of allergies, drug history and possible drug positive health practices, such as smoking interactions. cessation Assess for presence/history of: Nausea, related to side effects of Pregnancy medication Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Nutrition, imbalanced, less than or more Metastatic endometrial or renal cancer than body requirements related to Endometrial hyperplasia imbalance in hormone make-up Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic Sexual dysfunction, relate to hormonal disease imbalance Breast cancer Sleep pattern disturbed, insomnia, related Decreased liver or kidney function to effects of medication Depression Therapeutic regimen management, Epilepsy ineffective, related to knowledge deficit or Asthma planned failure of therapy Migraine headache Cardiac disorders PLANNING: PATIENT GOALS AND EXPECTED OUTCOMES Patient will: Follow medication regime exactly as recommended Remain free of sleep disturbances Remain free of side effects or adverse reactions Demonstrate understanding of side effects and adverse reactions to report Maintain usual sexual function Maintain nutrition at expected level Demonstrate understanding of appropriate lifestyle changes Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Monitor for pregnancy. (Medication must Instruct patient that she must have not be administered to woman who is negative pregnancy test within 2 weeks pregnant; will cause serious fetal prior to beginning medication. damage.) Advise patient: Monitor for seizure disorder. (Fluid retention secondary to medication may Of importance of consulting health care increase seizure activity. Use with provider who ordered anticonvulsants caution in women with seizure disorders.) before beginning this medication Regarding life-style changes that may decrease chances of triggering seizure activity Advise patient to: Have regular lab studies performed Increase fluids as way to decrease chance of hypercalcemia occurring Note signs of hypercalcemia and report immediately: deep bone and flank pain, anorexia, nausea/vomiting, thirst, constipation, lethargy, psychoses) Monitor mental status. (Use with caution Advise patient and caregivers regarding in women with history of depression. symptoms of depression to note and Medication may cause nervousness, report: changes in eating and sleeping insomnia, worsening of depression.) habits, disinterest in every-day activities, failure to perform ADLs, etc. Instruct patient: Evaluate patient’s knowledge level. (Informed patient will comply more fully How and when to take medication, and with importance of taking exactly as ordered if being used for contraception administration regime, and be more aware of and alert to adverse reactions.) Proper self-administration if being taken as cancer therapy Regarding symptoms of hypercalcemia Instruct patient to: Monitor for side effects: amenorrhea, nausea, jaundice, dizziness, headache, Monitor for side effects and to report to signs of pulmonary embolism (sudden health care provider if they occur severe chest pain and dyspnea), edema, Monitor for edema or weight gain by weight gain. Report immediately weighing self weekly and recording; noting if rings or shoes become tight Instruct patient: Observe foreskin changes caused by reactions to medication. To monitor for pruritis, urticaria, acne, rash, hirsutism, alopecia That these changes are temporary and will improve upon discontinuation of this medication Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Monitor for hypercalcemia. (Medication may cause increased serum calcium levels, especially if in conjunction with a low daily fluid intake.) Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Oxytocin Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnosis Prior to administration: Comfort, Impaired related to strong uterine contractions Obtain complete health history including complete past and present Excessive fluid volume gynecological and obstetric history Injury, Risk for to fetus related to effect of Obtain drug history to determine drug on uterine contractions possible drug interactions and allergies Obtain vital signs Asses fetal monitoring Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will Demonstrate increase in force and frequency of uterine contractions and/or let down of milk for breastfeeding. Demonstrate understanding of the drug’s action by accurately describing drug side effects and precautions. Demonstrate need to report effects such as listlessness, headache, confusion, anuria, hypotension, nausea, vomiting, and weight gain. Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Administer IV medication through Inform patient regarding the need for infusion device (To maintain accurate equipment. dosing) Monitor fetal heart rate. (Increase in force Instruct patient about the purpose and and frequency of uterine contractions may importance of fetal monitoring. cause fetal distress.) Monitor maternal status including BP, Instruct patient about the importance of pulse, and frequency, duration and monitoring maternal status. intensity of contractions and pain. (Initial administration of mediation may cause a drop in blood pressure. High doses may increase duration and intensity of contractions and increase pain level) Monitor fluid balance. (Prolonged IV Instruct patient to report symptoms of water infusion may cause water intoxication.) intoxication including drowsiness, listlessness, headache, confusion, anuria, or weight gain. Instruct patient: Monitor for post partum/post abortion hemorrhage. About the importance of being monitored frequently after delivery or after abortion To report severe vaginal bleeding or increase in lochia Evaluation Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Testosterone Base (Andro and Others) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnosis Prior to administration: Body image, disturbed, related to lack of Obtain complete health history including normal sexual development, impotence, allergies, drug history and possible drug decreased sperm count, growth interactions. retardation, gynecomastia, Assess for presence/history of virilism in females hypogonadism, secondary sex Coping, ineffective, related to delayed characteristics, increased or decreased sexual development and inability to libido, low sperm count, impotence accept this Monitor history of cardiovascular disease Family processes, interrupted, related to male’s inability to function sexually and/or inability to impregnate partner Identity, disturbed personal, related to lack of secondary sex characteristics expected in pubertal boy Sexual dysfunction, related to lack of normal amounts of androgen Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will: Experience improvement of underlying condition for which testosterone ordered, without worsening of underlying condition, with few side effects and no adverse reactions Demonstrate understanding of how/why he/she is taking medication and desired effects Demonstrate improved body image as effectiveness of medication is established Experience return of usual sexual function Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Instruct patient to: Monitor for prostatic or male breast cancer. (Testosterone will worsen either Have complete medical exam including condition.) PSA tests prior to taking testosterone and periodically during therapy Note and report any symptoms of altered urinary function: retention, hesitancy, nocturia, hesitancy, frequency, dribbling Monitor for serious renal disease. (Edema Instruct patient to: caused by testosterone and added stress Have renal function tests, BUN, creatinine placed on the kidneys.) performed prior to testosterone therapy and periodically during therapy Report immediately any symptoms of kidney dysfunction: decreased urination, edema, uremic frost, confusion, etc. Instruct patient to: Monitor for decreased cardiac function. (Edema caused by testosterone stresses Have cardiac function tests performed prior the heart.) to and periodically during therapy Immediately report symptoms of decreased cardiac function: general weakness, fatigue, dyspnea, and edema Instruct patient: Monitor serum cholesterol levels. (Elevated cholesterol levels secondary to To have cholesterol levels measured prior to testosterone administration may increase and periodically during therapy patient’s risk of cardiovascular disease.) Regarding lifestyle modifications which may lower risk of hypercholesterolemia: low fat diet, increased exercise, decrease consumption of red meat, butter, fried foods, etc. If patient is female, monitor for pregnancy Instruct patient: or lactation. (Testosterone crosses into To have negative pregnancy test within 2 breast milk and may cause damage to weeks before initiating testosterone therapy infant, including masculinization of and monthly during therapy female infant.) Regarding the importance of reliable birth control during testosterone therapy Instruct patient: Monitor for hypercalcemia. (Hypercalcemia in patient with metastatic To have lab studies performed prior to breast cancer usually indicates bone and during therapy metastasis.) About symptoms of increased serum calcium and to report immediately if the following occurs: deep bone and flank pain, anorexia, nausea/vomiting, thirst, constipation, lethargy, psychoses Evaluate bone growth in children and Advise patient and caregivers that bone age adolescents. (Premature epiphyseal determinations should be done every 6 closing may occur, leading to growth months. retardation.) Advise patient: Monitor fluid intake. (Increased fluids will increase urine production and To consume 3,000-4,000cc fluid daily decrease chance of stone formation.) That urinary output will increase, and not to be alarmed Non-liquids that can be consumed to increase fluid intake: gelatin, popsicles, ice cream, etc. Instruct patient to: Monitor for diabetes mellitus. (Testosterone therapy may change glucose Monitor blood sugar daily and notify health tolerance.) care provider if changes occur Make needed adjustments in hypoglycemic medications and diet Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). NURSING PROCESS FOCUS: Patients Receiving Sildenafil (Viagra) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnosis Prior to administration: Body image, Disturbed related to impaired sexual function Obtain complete health history including hematologic disorders, cardiac, kidney Sexual dysfunction related to known or or liver disease, and anatomic unknown cause deformities Sensory perception, disturbed, visual related to Obtain drug history, specifically organic disease process. nitrates and nitroglycerin, to determine possible drug interactions and allergies Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will: Report more positive body image during drug therapy Report normal sexual function Demonstrate understanding of the drug’s action by accurately describing side effects and precautions, and importance of follow-up care Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Teaching/Discharge Planning Monitor cardiovascular status. (Patient Instruct patient and/or caregiver to: who has 1st attack of angina during Carry identification stating he is taking time he is taking sildenafil should not Sildenafil, so he will not be given nitrates receive any nitrate products. Recognize the importance of EKG monitoring periodically during therapy Have vital signs, including BP, checked routinely during therapy with slidenafil Recognize CV risk factors and modify: smoking, high fat/high cholesterol diet, lack of exercise, obesity, Type A personality, high stress lifestyle Instruct patient and/or caregiver to: Monitor sexual response to include: *Frequency, firmness, maintenance of Keep diary R/T use of sildenafil, sexual erections; response, any cardiovascular symptoms that *Frequency of orgasms may occur *Frequency, satisfaction and enjoyment of Report any changes to health care provider sexual activity; Seek emergency care if erection lasts longer *Satisfaction with sexual relationship that 4 hours. Instruct patient and/or caregiver to: Monitor diet. (High fat meals can delay absorption of sildenafil and Avoid administration of Sildenafil with meals, delay onset of action by 1 hour. especially high-fat meals Taking sildenafil with grapefruit juice Avoid grapefruit juice when administering may lead to increased serum sildenafil Sildenafil levels, leading to adverse effects.) Instruct patient and/or caregiver that: Sildenafil should not be taken more than once in a 24 hour period Optimum time to take Sildenafil is 1 hour prior to sexual activity, but that it can be taken for up to 4 hours prior Sildenafil will not produce erection unless he is sexually stimulated This medication should not to share medication with anyone else Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Monitor patient knowledge and understanding.