points, lines, & planes
advertisement
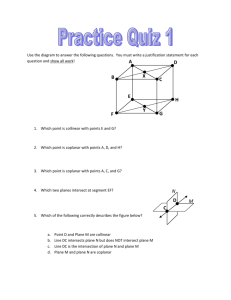
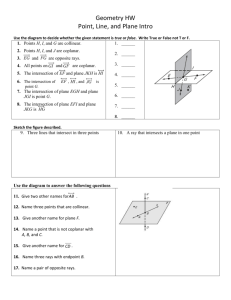
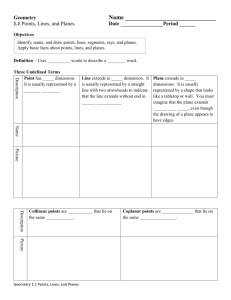
Name _________________________________________ 8/28 – 9/7 Period ____ GEOMETRY UNIT 1 - LOGIC AND SEGMENTS Vocabulary Terms: Plane Point Ray Line Segment Endpoint Opposite rays Postulates Collinear Coplanar Noncollinear Noncoplanar 8/26 Opening Day 9/2 Intersection Inductive reasoning Conjecture Analyze Given information Patty paper Midpoint Congruence Bisector Tick Mark Prove Postulate 8/27 Naming Basic Geometric Structures 9/3 Holiday 9/9 Segments Notation Compass Straight Edge Distance Length Construction Intersection Conditional Hypothesis Conclusion Inverse Converse 8/28-29 Relationships of points, lines, and planes 9/4-5 Inductive reasoning/Deductive Reasoning Contrapositive Truth Value Biconditional Counterexample Negation Logically equivalent p→ q Deductive Reasoning Law of Syllogism Valid deductive argument (conclusion) 8/30 QUIZ 9/6 Conditionals 9/10 Review Test Tuesday, 8/27 Chapter 1 Section 1: Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes I can recognize and use the markings used in geometry. I know the differences between Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry ASSIGNMENT: Pg. 9 (#1 – 10, 28, 30, 33-34, 36, 43) 16 problems Completed: Wednesday-Thursday, 8/28-29 Chapter 1 Section 1: Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes I can use geometric patterns to make valid conjectures. I know the relationships between points, lines, and planes. ASSIGNMENT: Pg. 9 (#11, 12, 20, 21, 25-27, 29, 31-32, 38 – 42, 46) 16 problems And “Geometric Structures Model” Completed: Friday, 8/30 Chapter 1 Section 1: Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes I can recognize and use the markings used in geometry. I know the differences between Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry I can use geometric patterns to make valid conjectures. I know the relationships between points, lines, and planes. ASSIGNMENT: Quiz Completed: Tuesday, 9/3 Chapter 1 Section 2: Measuring and Constructing Segments I can solve problems using Segment Addition Postulate, midpoints, or bisectors. I can recognize the markings used in geometric constructions. I can recognize the markings used in geometric symbolism. ASSIGNMENT: Pg. 17 #1-10, 19, 24-27, 36-39, 44 (20 problems) Completed: Wednesday-Thursday, 9/4-5 Chapter 2 Section 1: Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Chapter 2 Section 3: Using Deductive Reasoning to Verify Conjectures I can use geometric patterns and inductive reasoning to formulate a rule or make generalizations. I can make valid conjectures given information in various forms. I can provide and recognize a valid deductive argument. I can make valid conjectures given information in various forms. ASSIGNMENT: Pg. 77 – 79 #1, 4, 5, 7, 13, 16, 23, 28, 30, 39 (10 questions) and Supplemental Worksheet (5 questions) ASSIGNMENT: Pg. 91 #1, 6-10, 12-13, 15-18, 23, 27 (14 questions) Completed: Friday, 9/6 Chapter 2 Section 2: Conditional Statements I can write the converse, inverse, and contrapositive. I can determine the validity of a conditional, converse, inverse, or contrapositive and provide a counterexample when it is false. I can tell when statements are logically equivalent. ASSIGNMENT: Pg. 84 #1-4, 9-12, 16-19, 22, 38, 41, 53 (16 questions) Completed: Monday, 9/9 Review Day Completed: ASSIGNMENT: Review for Test IN CLASS ASSIGNMENT: Review for Test AT HOME Completed: Tuesday, 9/10 Test Day Unit 1 Test: Logic and Segments Grade: If you miss the review day, you are still expected to take the test on the test day. For more help BEFORE the test: 1. Use the indicated chapters in your book 2. Use the book online (it has videos and a homework help section) 3. Use Moodle to find more resources 4. Come to tutoring (with assignment) GEOMETRY UNIT 1 - LOGIC AND ANGLES Day 1 - Chapter 1 Section 1: Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Objectives: I can recognize and use the markings used in geometry. I know the differences between Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometry Term Plane Definition has two dimensions. It is represented by a shape that looks like a floor or wall, but it extends without end. Point has no dimension. It is represented by a dot. Ray AB consists of the endpoint A and all points on AB that lie on the same side of A as B. Line has one dimension. It is represented by a line with two arrowheads, but it extends without end. Endpoint is a point at the end of a segment or beginning of a ray. Opposite Rays have a common endpoint and form a line. Collinear are points that lie on the same line. Coplanar are points that lie in the same plane. Noncollinear Two or more geometric figures intersect if they have one or more points in common. The intersection of the figures is the set of points the figures have in common. Noncoplanar Two figures that are not in Picture the same plane Practice: Pg. 9 (#1 – 10, 28, 30, 33-34, 36, 43) 16 problems Notation MORE POINTS, LINES, & PLANES Important facts about points, lines, and planes. Two points determine a _______________. Three NON-COLLINEAR points determine a ________________. Four NON-COPLANAR points determine _____________. The intersection of two lines is a ________________. The intersection of a line and a plane is a _______________. The intersection of two planes is a _________________. If two points are in a plane, then the line that contains them is _________________________. S EXAMPLE 2 T U L Q N R M O a) Are points S, O, Q, and M coplanar? Why or why not? b) Name the intersection of planes LON and NQM: Explain: c) Name the intersection of plane LNO and MN. Explain: d) Do S and M determine a line? Why or why not? e) Name the intersection of UO and MN. Explain: X EXAMPLE 3 J U V K W Y Z a) Name three points that determine plane J. Points: b) Name a set of collinear points, and a set of non-collinear points. Collinear: Noncollinear: c) Name a set of points, other than those in a) that are coplanar. Points: Plane Activity Lesson: Points, Lines, & Planes 1. Are points R, H, and F coplanar to plane N? Explain. ___________________ 2. Are points A, B, and D in plane M? Explain. ___________________ 3. Are points A, B, and D in plane N? Explain. ___________________ 4. Are points F, A, R, and T coplanar? Explain. ___________________ 5. Are points F, S, and G coplanar to plane N? Explain. ___________________ 6. Are points F, S, and G coplanar to plane M? Explain. ___________________ 7. Are points F, S, and G coplanar? Explain. ___________________ 8. Are points C, S, and E coplanar? Explain. ___________________ 9. Name 3 points that are coplanar, but not coplanar to plane M or plane N? Explain. ___________________ 10. Name 4 points coplanar to M. Explain. ___________________ 11. Write 2 questions of yur own using this intersection of planes M and N. ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ Vocabulary- Segment Addition & Bisectors 1) Segment- (line segment) part of a line consisting of two endpoints and all points between them 2) Distance- absolute value of the difference of the points (coordinates). It can also be called length. (Think of number line) 3) Congruence- same length or measure 4) Midpoint- point that bisects, or divides, the segment into two congruent segments. 5) Perpendicular Bisector- a line perpendicular to a segment at the segment’s midpoint. Segment Addition If B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC. Example: If AB = 5, BC = 10, find AC. Solution HINT: Draw a picture & label.