Fossils and Correlation
advertisement

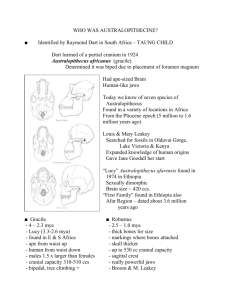
Science 8 Lab: Fossils II: Geologic Time and Fossil Identification Direction Sheet Purpose: You are a paleontologist with an unknown fossil to describe. Use what you know about geologic time and fossils to develop a hypothesis as to the origin of an unknown fossil. Remember that all the fossils in a layer are the same age. Materials: “rock” slab sample containing fossils, fossil reference sheet, stratigraphic column sheet, geologic time scale sheet, paper, pencil Procedure: A. Compare the fossils on the stratigraphic column sheet to the fossils on the fossil reference sheet. Note that the geologic time periods are in parentheses, for example: (Ordovician) 1. List the time periods that are represented in the stratigraphic column. Layer 1Layer 2Etc. B. Use the geologic time scale sheet to determine the order of the periods and which are missing. 2. What time periods are missing from the stratigraphic column? Only count time periods missing between the eight layers. 3. Why do you think some time periods are missing? C. The fossil slabs represent one of the layers from the stratigraphic column. Look closely at the fossils and determine which layer is represented. The fossil that is not on the sheets is your “unknown” fossil. 4. What time period does the unknown fossil come from? 5. How many years ago did the unknown organism live? 6. What do you thing the fossil is? 7. Is it an entire organism or is it part of a larger creature? 8. As best as you can, describe the organism. What size was it? (Estimate with numbers and units). How did it eat? Where did it live? Give your discovery a name. Provide evidence to support for your answers and draw a sketch of your creature. 9. Is the fossil organism related to anything alive today? Lab: Fossils 2 ver. 2.0 2/12/2016 Page 1 of 4 Lab: Fossils 2 ver. 2.0 2/12/2016 Page 2 of 4 Lab: Fossils 2 ver. 2.0 2/12/2016 Page 3 of 4 Geologic Time Scale mya = millions of years ago Phanerozoic Eon (543 mya to present) Cenozoic Era (65 mya to today) Quaternary (1.8 mya to today) Holocene (10,000 years to today) Pleistocene (1.8 mya to 10,000 yrs) Tertiary (65 to 1.8 mya) Pliocene (5.3 to 1.8 mya) Miocene (23.8 to 5.3 mya) Oligocene (33.7 to 23.8 mya) Eocene (54.8 to 33.7 mya) Paleocene (65 to 54.8 mya) Mesozoic Era (248 to 65 mya) Cretaceous (144 to 65 mya) Jurassic (206 to 144 mya) Triassic (248 to 206 mya) Paleozoic Era (543 to 248 mya) Permian (290 to 248 mya) Carboniferous (354 to 290 mya) Pennsylvanian (323 to 290 mya) Mississippian (354 to 323 mya) Devonian (417 to 354 mya) Silurian (443 to 417 mya) Ordovician (490 to 443 mya) Cambrian (543 to 490 mya) Tommotian (530 to 527 mya) Precambrian Time (4,500 to 543 mya) Proterozoic Era (2500 to 543 mya) Neoproterozoic (900 to 543 mya) Vendian (650 to 543 mya) Mesoproterozoic (1600 to 900 mya) Paleoproterozoic (2500 to 1600 mya) Archaean (3800 to 2500 mya) Hadean (4500 to 3800 mya) This geologic time scale is from: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/help/timeform.html Lab: Fossils 2 ver. 2.0 2/12/2016 Page 4 of 4