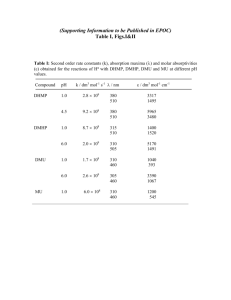
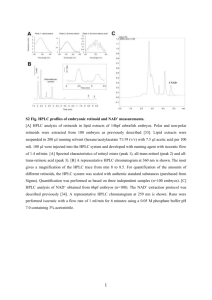
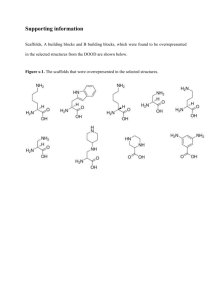
Chem 360 March Quiz
advertisement

Chem 360 March Quiz, 2004 [2] 1. When running GC, what parameter is most important in controlling retention times? [2] 2. When running HPLC, what parameter is most important in controlling retention times? [2] 3. In GC, what are the disadvantages of using too low a temperature? [2] 4. In GC, what are the disadvantages of using too high a temperature? [4] 5. In GC, what are the disadvantages of using too low a flow? In terms of the resulting chromatogram: AND the reason in terms of Rate-kinetic theory: [4] 6. In GC, what are the disadvantages of using too high a flow? In terms of the resulting chromatogram: AND the reason in terms of Rate-kinetic theory: [10] 7. State the van Deemter equation. What factors control mass transfer in the stationary phase? What factors control longitudinal diffusion? [10] 8. What column parameters can be optimized for HPLC? For each parameter, do you want it big or small or? . Give a typical value for each. [6] 9.What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a gradient? Think about both GC and HPLC. [2] 10.Why is an interface necessary between a chromatograph and a mass spectrometer? [6] 11.Describe one interface used between HPLC and MS. [3] 12.What information can be obtained by using MS as a chromatography detector? [5] 13. If a cell is at equilibrium, what is the cell voltage? [3] 14. Distinguish between a reversible electrochemical cell and an irreversible electrochemical cell. [6] 15. Indicate whether the following cell would act as an anode or cathode when coupled with a standard hydrogen electrode in a galvanic cell. Ag ׀AgI (sat’d), KI(0.0922 M) AgI + e- Ag(s) + I- Eo = -0.151 V [8] 16.What is a junction potential? Draw a diagram showing how it arises. Why do we want to minimize it? How can we minimize it?