HIDRAL 25 mg tablets
advertisement

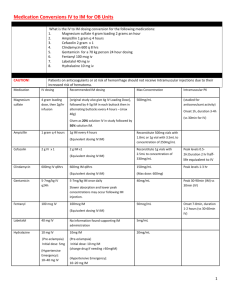
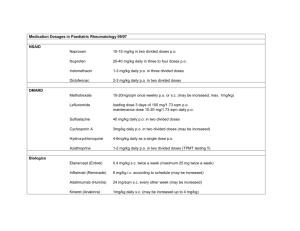
HIDRAL 25 mg tablets HIDRAL 50 mg tablets HIDRAL 20 mg 1ml ampoules Hydralazine hydrochloride Made in Argentina Sale under prescription Hidral 25mg tablet formula: Hydralazine hydrochloride 25 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 150.84 mg, croscarmellose sodium 1.8 mg, magnesium stearate 1.44 mg, quinoline yellow 0.36 mg. Hidral 50mg tablet formula: Hydralazine hydrochloride 50 mg, microcrystalline cellulose 125.84 mg, croscarmellose sodium 1.8 mg, magnesium stearate 1.44 mg, ponceau 4R 0.36 mg. Hidral 20mg injection formula: Hydralazine hydrochloride 20 mg, methylparaben 0.65 mg, propylparaben 0.35 mg, propyleneglycol 104 mg, water for injection e.f. 1 ml. PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION: The hydralazine’s pharmacological action mechanism is not yet completely known, but its main effects take place on the cardiovascular system. The hydralazine produces peripheric vasodilatation by altering the cellular calcium metabolism and relaxing the vascular musculature, causing a fall in the arterial pressure. This peripheric vasodilatation produces a drop in the arterial blood pressure (more diastolic than systolic), a decrease on the peripheric vascular resistance, a heart’s expenditure increase and a raise on the heart beat frequency. After the administration of hydralazine it normally occurs an increase of the renin’s secretion into the blood, as a sympathetic reflex response, because of which the aldosterone gets stimulated and the sodium consequently reabsorbed. The hydralazine also maintains or increases the brain and kidney blood flow. PHARMACOKINETICS – TABLETS: The hydralazine is rapidly absorbed after the oral administration, and peaks maximum plasmatic levels after 1 or 2 hours. The bind to serum proteins reachs to 87%. The hydralazine serum levels declines after 3 to 7 hours from the administration. The hydralazine suffers polymorphic acetylation, because of which the serum levels might vary from a slow acetylator patient to a rapid one. The slow acetylators get higher hydralazine serum levels, and require smaller doses to maintain their blood pressure under control than the rapid acetylators, which will require higher doses. The hydralazine has an extended hepatic metabolism and is excreted in the form of metabolites through the urine. INJECTION: The maximum fall of the blood pressure occurs usually between 10 and 80 minutes after the parenteral administration of hydralazine. INDICATIONS: Congestive cardiac failure refractory to diuretic and digital conventional treatment. It might be administered alone or in combination with nitrites. Treatment for the hypertension on its different forms (benign or malignant). It is administered as unique treatment or in combination with other antihypertensive agents, such as betablockers, in order to increase the efficiency and reduce the cardioaccelerative effect. Treatment of the Pregnancy Preeclamptic Syndrome. POSOLOGY – TABLETS Adults: The dosage must be adjusted to the individual requirements of the patient and be increased gradually. It is recommended to initiate the treatment with ½ 25 mg tablet, 2-4 times per day the first 2-4 days, and then increasing to 1 tablet of 25 mg 4 times per day on the first week, and then to 1 tablet of 50 mg 4 times per day on the second week of treatment, and so on. On the maintenance period the dosage must be adjusted to the lowest effective level. Children: The safety and efficiency on children has not yet been determined, but there is some clinical experience. The usual dosage on this patients is that of 0.75mg/kg/day oral, divided in four doses. The dosage might be increased gradually on the next 3-4 weeks, not surpassing 7.5mg/kg/day or 200mg per day. POSOLOGY and ADMINISTRATION TECHNIQUES FOR THE INJECTABLE SOLUTION ADULTS: Severe hypertension and/or hypertensive emergency: I.V.: 10 to 20 mg initially, increasing then to a dose of 5 to 20 mg every 15 to 30 minutes, according to physician’s criteria. I.M.: initial doses between 10 and 50 mg. It is recommended to use low initial doses in order to determine the further doses with base on the patient’s clinical response. Pregnancy Hypertensive Emergency (Preeclampsy): I.V.: 5 mg initially, increasing then to 5 to 20 mg every 20-30 minutes, according to physician’s criteria. CHILDREN: I.V.: initiate with 0.15 to 0.80 mg/kg (not surpassing 20 mg), increasing then to the same dose every 6 hours or 1.5 mcg/kg/minute I.V.. The dosage for children must suit to 1.7 mg/kg/day, divided between 4 to 6 doses. Administration Techniques: IV Bolus, not exceeding 1 ml per minute. We recommend to use this administration technique only for emergency situations. Drip or continuous infusion: 7.5 to 45 ml/hour (50 to 300 mcg per minute). The hydralazine is incompatible with glucose parenteral solutions, and must not be injected together with aminophillyn, ampicillyn, diazoxide, calcium disodium edetate, nifedipine, glycerol trinitrate and methohexital sodium. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity to hydralazine. Patients with tachycardia and/or heart failure background. Myocardic disease and/or mitral valve disease. PRECAUTIONS and WARNINGS: It has been rarely described, on patients treated with hydralazine, a syndrome similar to the Lupus Erythematosus Disease with glomerulonephritis. On this cases the treatment must be interrupted, unless the potential risk/benefit relationship advises to continue the antihypertensive therapy with this product. It must be administered with caution on patients with coronary artery disease, on patients with brain vessel stroke or with end stage renal disease. The circulatory stimulation caused by the hydralazine may increase some cardiovascular insufficiency, such as rising the blood pressure on the lungs on patients with mitral valve disease. On prolonged treatments it is advisable to perform a complete blood analisys and determination of antinuclear factors. On the parenteral treatment with hydralazine vital signs must be monitored during and after the administration. The administration of hydralazine and diazoxide can produce severe hypotension. INTERACTIONS: The hydralazine must be used with caution on patients treated with monoaminooxidase inhibitors. On concomitant treatments with other potent antihypertensive medications, such as diazoxide, the patient’s blood pressure level must be continuosly controlled to avoid a severe hypotension. The hydralazine has antipyridoxine action, and might reduce the epinephrine vasopressant response. The injectable hydralazine is incompatible with solutions containing glucose and must not be infunded concomitantly with aminophillyn, ampicillyn, diazoxide, calcium disodium edetate, nifedipine, glycerol trinitrate and methohexital sodium. PREGNANCY: Even when the clinical experience with hydralazine on pregnant women has not shown any theratogenic effect at therapeutic doses, it must only be used during pregnancy when the physician’s criteria advises that the possible benefit justifies the potential risk. The hydralazine has shown wide clinical efficiency on the treatment of the preeclamptic syndrome, and this dysfunction may be of considerable risk both for the mother and the fetus, because of which the physician should evaluate the necessity of indicating the treatment in consideration of the disease’s gravity, as well as its lenght, dose to administer and possible undesirable effects. NURSING: The hydralazine is excreted trough the breast milk, because of which its use during breast-feeding is not recommendable. EFFECTS ON THE ABILITY TO DRIVE AND OPERATE MACHINES: Hidral does not affect the mental alert state, but in the possibility of driving automobiles and operate machines it is recommendable to verify certainly that the patient does not present orthostatic hypotension and/or dizziness. In case of presenting orthostatic hypotension and/or dizziness the patient should not drive automobiles or operate machines. UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS: There might arise tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, headaches, palpitations, anorexy, nauseas, dizziness, sweating, dyarrea and tremor; all this effects disappear with the decrease of the dosage, and are less frequent when the dose is increased slowly. Rarely there might appear edema, depression, anxiety, hypersensitivity, constipation, urinary retention and hemorrhage. The chronic administration of high doses (more than 400 mg) might produce an acute rheumatic condition on approximately 10% of the patients, as well as a lupus erithematosus (LE) like syndrome, which might disappear by suppressing the treatment or with the use of corticosteroids on acute cases. OVERDOSE and its TREATMENT: In case of overdose, symptoms include hypotension, tachycardia, headache and blushing, which might worsen with myocardic ischemia, cardiac arrithmias and deep shock. There is not specific antidote, because of which adequate measures to gastric lavage must be performed. It is fundamental to sustain the cardiovascular system, avoiding the administration of vasopressant medications, and if its use is of total need, there must be used a product which won’t worsen the cardiac arrhythmia. The tachycardia responds to betablockers. In case of necessity on digitalizing the patient, the renal function must be tightly controlled. IN CASE OF OVERDOSE REFER TO THE NEAREST TOXICOLOGICAL CENTER: Ref. DR. RICARDO GUTIERREZ Children Hospital – Toxicology Unit Tel. (011) 4962-6666/4962-2247 Presentations: HIDRAL 25mg & 50mg – 30 tablets bottle. HIDRAL 20mg – 5 & 100 1ml ampoules boxes. Keep out of the reach of children Store between 15ºC to 30ºC Protect from light inside the box BioControl S.A. Laboratorios Fraga 1504 (1427) Buenos Aires – Rep. Argentina Tel. (54-11) 4555-7585 / 4552-2684 e-mail: biocontrolsa@yahoo.com.ar Technical Director: María Fernanda Filia – Pharmacist – M.N. 13.747. Medication authorized by the Ministry of Health. Certified Nº 48.489 Lot and expiry date: see the bottom of the box.