bit_22619_sm_suppldata
advertisement

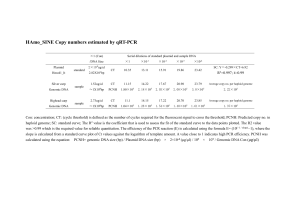
An Accumulative Site-Specific Gene Integration System Using Cre Recombinase-Mediated Cassette Exchange Yujiro Kameyama, Yoshinori Kawabe, Akira Ito and Masamichi Kamihira Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Sequence analysis for loxPs associated with recombination reactions in the plasmids (P1232Cmr and P12323Kmr) after the third and fourth reactions. (Upper) The genetic sequences of loxP[wt] and the first loxP3 (upstream of an IRES/DsRed cassette) in P1232Cmr were analyzed. The loxPs were sequenced using Pr1 (for loxP[wt]) or Pr5 (for loxP3) as the sequencing primer. (Lower) The genetic sequences of loxP[wt] and the first loxP6 in P12323Kmr were analyzed. The loxP[wt] was sequenced using Pr1 as the sequencing primer. The first loxP6 was sequenced using Pr6 as the sequencing primer for a DNA fragment generated from PstI-digested P12323Kmr to distinguish from another loxP6. Supplementary Figure 2. Sequence analysis for loxPs associated with the recombination reaction in the genome of CHO cells after the first and second reactions. The genetic sequences of loxP sites residing on the genome of CHO cells were analyzed using DNA fragments amplified from genomic DNA of CHO cell clones (CHO/P12 and CHO/P123Neor) by PCR. (Upper) DNA fragments amplified from genomic DNA of CHO/P12 cells using the Pr1 and Pr3 (for loxP[wt] and loxP4), or the Pr4 and Pr2 (for loxP3) as the primers were applied for sequencing analysis of loxPs generated in the genome of cells after the first RMCE reaction. (Lower) DNA fragments amplified from genomic DNA of CHO/P123Neor cells using the Pr1 and Pr7 (5’-ACACCGGCCTTATTCCAA-3’) (for loxP[wt] and loxP1), or the Pr6 and Pr3 (for loxP6) as the primers were applied for sequencing analysis of loxPs generated in the genome of cells after the second RMCE reaction.