Overcoming barriers in mathematics – Level 2 / 3
advertisement

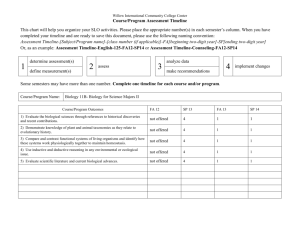
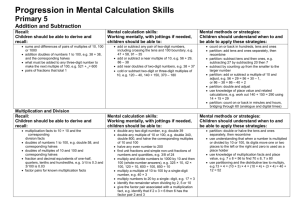
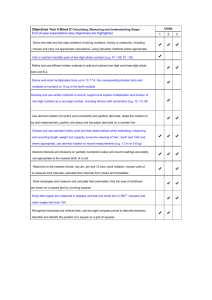
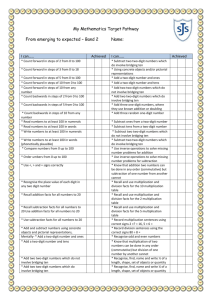
Overcoming barriers in mathematics – Level 2 / 3 Support for Year 2 teachers – Challenging more able pupils The PNS Overcoming barriers in mathematics – level 2/3 are to support Year 3 and Year 4 teachers, using Year 3 and Year 4 objectives. These materials could also be used by Year2 teachers to challenge more able pupils and support them in achieving level 3 at the end of KS1. The following guidance has been put together by leading teachers to allow this to happen. BLOCK A UNIT 1 (autumn) 2 weeks - Counting partitioning and calculating Year 2 Objectives Children’s learning outcomes in italic Present solutions to puzzles and problems in an organised way; explain decisions, methods and results in pictorial, spoken or written form, using mathematical language and number sentences I can explain to others how I solved a problem Year 3 Objectives Children’s learning outcomes in italic Overcoming barriers sequences Describe and explain methods, choices and solutions to puzzles and problems, orally and in writing, using pictures and diagrams I can explain how I solve problems Calculating (5th arrow) Can I identify the calculation needed to solve a word problem? Can I identify the stages involved in a two-step problem? Can I explain and record my methods and solutions? Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; explain what each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition two-digit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of 10 and 1 I can count objects by putting them into groups I can partition numbers Estimate a number of objects; round two-digit numbers to the nearest 10 I can round numbers to the nearest 10 Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 in different ways I can split a number into hundreds, tens and ones I can explain how the digits in a number change when I count in 10s or 100s Counting and understanding number (1st arrow) Can I round whole numbers to 1000 to the nearest 10 or 100? Can I read, write and partition whole numbers to 1000? Can I order two-digit and three-digit numbers and position these on a number line? Read and write two-digit and three-digit numbers in figures and words; describe and extend number sequences and recognise odd and even numbers I can read and write two-digit numbers I know which numbers are odd and which are even Order two-digit numbers and position them on a number line; use the greater than (>) and less than (<) signs I can write numbers in order and position them on a number line I can use the greater than and less than symbols to show that one number is larger or smaller than another Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers I can add and subtract some numbers in my head Understand that subtraction is the inverse of addition and vice versa; use this to derive and record related addition and subtraction number sentences I know that addition and subtraction ‘undo’ each other I can write three other related number sentences for 6+3=9 Read, write and order whole numbers to at least 1000 and position them on a number line; count on from and back to zero in single-digit steps or multiples of 10 I can read and write numbers to 1000 and put them in order Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20, sums and differences of multiples of 10 and number pairs that total 100 I know the sum and difference of any pair of numbers to 20 I can add and subtract multiples of 10 or 100 in my head Knowing and using number facts (1st arrow) Can I recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20? Can I find pairs of numbers that total 100? Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and twodigit numbers I can add and subtract one-digit and two-digit numbers in my head (e.g. 62 + 7, 7 + 45, 48 – 6, 60 – 8) BLOCK A Unit 2 (spring) 2 weeks Year 2 Year 3 Objectives Children’s learning outcomes in italic Objectives Children’s learning outcomes in italic Overcoming barriers sequences Present solutions to puzzles and problems in an organised way; explain decisions, methods and results in pictorial, spoken or written form, using mathematical language and number sentences I can explain how I solved a problem and say why I did it that way Describe and explain methods, choices and solutions to puzzles and problems, orally and in writing, using pictures and diagrams I can explain how I solve problems Calculating (5th arrow) Can I identify the calculation needed to solve a word problem? Can I identify the stages involved in a two-step problem? Can I explain and record my methods and solutions? Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in Partition three-digit numbers into multiples of 100, 10 and 1 Counting and understanding number (1st arrow) tens, fives or twos; explain what each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition two-digit numbers in different ways, including into multiples of 10 and 1 I can explain what each digit in a two-digit number stands for I can partition numbers in different ways in different ways I can split a number into hundreds, tens and ones I can explain how the digits in a number change when I count in 10s or 100s Can I round whole numbers to 1000 to the nearest 10 or 100? Can I read, write and partition whole numbers to 1000? Read and write two-digit and three-digit numbers in figures and words; describe and extend number sequences and recognise odd and even numbers I can read and write numbers up to 1000 in figures and in words I know which numbers are odd and which are even Can I order two-digit and three-digit numbers and position these on a number line? Round two-digit or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and give estimates for their sums and differences I can round numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and estimate a sum or difference Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers I can add and subtract some numbers in my head Derive and recall all addition and subtraction facts for each number to 20, sums and differences of multiples of 10 and number pairs that total 100 I know the sum and difference of any pair of numbers to 20 I can add and subtract multiples of 10 or 100 in my head I know number pairs that sum to 100 Knowing and using number facts (1st arrow) Can I recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20? Can I find pairs of numbers that total 100? Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and twodigit numbers I can add or subtract one-digit and two-digit numbers in my head (e.g. 62 + 7, 7 + 45, 48 – 6, 60 – 8) Calculating (1st arrow) Can I subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers? Can I say a subtraction fact that is the inverse of an addition fact, and vice versa? I can add and subtract bigger numbers using practical equipment or by writing notes to help me Use the symbols +, –, ×, ÷ and = to record and interpret number sentences involving all four operations; calculate the value of an unknown in a number sentence (e.g. Knowing and using number facts (2nd arrow) Can I recall multiplication and division facts for the 2, ÷ 2 = 6, 30 – = 24) I know how to write number sentences using the symbols +, –, ×, ÷ and = 3, 4, 5 and 10 times-tables? Can I use understanding of multiplication and division to solve problems? I can explain what different number sentences mean Multiply one-digit and two-digit numbers by 10 or 100, and describe the effect I can multiply by 10 or 100 and say what happens to the number I multiply Derive and recall multiplication facts for the 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 times-tables and the corresponding division facts; recognise multiples of 2, 5 or 10 up to 1000 I know my tables for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 10 Calculating (2nd+3rd arrows) Can I multiply one-digit and two-digit numbers by 10 and 100? Can I multiply a two-digit number by a one-digit number? Can I divide a two-digit number by a one-digit number and explain any remainders? BLOCK A Unit 3 (summer) 2 weeks Year 2 Year 3 Objectives Children’s learning outcomes in italic Objectives Children’s learning outcomes in italic Present solutions to puzzles and problems in an organised way; explain decisions, methods and results in pictorial, spoken or written form, using mathematical language and number sentences I can show and explain clearly how I solved a problem Solve one-step and two-step problems involving numbers, money or measures, including time, choosing and carrying out appropriate calculations I can solve a problem by writing down what calculation I should do Read and write two-digit and three-digit numbers in figures and words; describe and extend number sequences and recognise odd and even numbers I can read and write numbers up to 1000 in figures and in words I can explain the pattern for a sequence of numbers and work out the next few numbers in the list Count up to 100 objects by grouping them and counting in tens, fives or twos; explain what each digit in a two-digit number represents, including numbers where 0 is a place holder; partition two-digit numbers in different ways, Overcoming barriers sequences Calculating (5th arrow) Can I identify the calculation needed to solve a word problem? Can I identify the stages involved in a two-step problem? Can I explain and record my methods and solutions? Counting and understanding number(1st arrow) Can I round whole numbers to 1000 to the nearest 10 or 100? Can I read, write and partition whole numbers to 1000? Can I order two-digit and three-digit numbers and position these on a number line? including into multiples of 10 and 1 I can use partitioning to help me to carry out calculations Order two-digit numbers and position them on a number line; use the greater than (>) and less than (<) signs I can write numbers in order and position them on a number line I can use the greater than and less than symbols to show that one number is larger or smaller than another Estimate a number of objects; round two-digit numbers to the nearest 10 I can say roughly how many there are in a group of objects Round two-digit or three-digit numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 and give estimates for their sums and differences I can use rounding to estimate a sum or difference Counting and understanding number (1st arrow) Can I round whole numbers to 1000 to the nearest 10 or 100? Add or subtract mentally a one-digit number or a multiple of 10 to or from any two-digit number; use practical and informal written methods to add and subtract two-digit numbers I can add and subtract two-digit numbers using practical equipment or written notes to help me Add or subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and twodigit numbers I can find the sum of or difference between one-digit and two-digit numbers in my head (e.g. 7 + 45, 45 – 7) I can add several one-digit numbers in my head Calculating (1st arrow) Can I subtract mentally combinations of one-digit and two-digit numbers? Can I say a subtraction fact that is the inverse of an addition fact, and vice versa?