SI Figure 5
advertisement

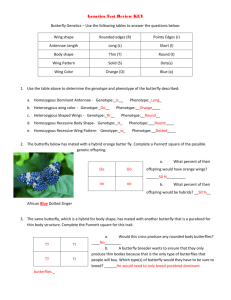
Figure S1. The stretch10477 mutant localizes to the 85E-F region of the Drosophila
third chromosome and exhibits a recessive out-stretched wing defect. We identified
a P transposable element insertion line P{PZ}l(3)10477 obtained from the Bloomington
Stock Center in which 100% of the flies in the stock held their wings out at a 45 degree
angle. The P{PZ}l(3)10477 stock was listed as containing a dominant Dichaete allele
(CxD) suggesting that there was no association of the wing phenotype with the P
transposable element insertion (flies with the CxD mutant chromosome exhibit an
outstretched wing phenotype due to the presence of the Dichaete1 allele). However, our
analysis indicated that CxD was not present in the P{PZ}l(3)10477 fly stock we obtained
from Bloomington for three reasons. First, wing structures including the alulae are
missing in flies containing CxD mutations, but the alulae were intact in the
P{PZ}l(3)10477 stock. Second, the P{PZ}l(3)10477 stock had a Stubble (Sb) appearance,
and CxD does not have Sb associated with it. Third, flies containing CxD exhibit an
outstretched wing phenotype when only one copy of CxD is present (dominant
phenotype) but the wing phenotype associated with the P{PZ}l(3)10477 stock was not
dominant (it disappeared following out-crossing to a wild-type chromosome; see the
complementation matrix).
The P element insertion position of the lethal P{PZ}l(3)10477 line had been
mapped to the 85E-85F region of the Drosophila chromosome (BDGP 1994-1999) but
was reported to be viable over deficiencies (Df(3R)by62 and Df(3R)by10) that removed
that region of the chromosome (BDGP 1994-1999). Therefore, because there was
reported to be a separation of the lethality from the location of the insertion, the
P{PZ}l(3)10477 stock was discarded from the gene disruption project (BDGP 1994-
1999). However, as seen in the complementation matrix, our genetic complementation
analysis revealed that the P{PZ}l(3)10477 line failed to complement a deficiency of the
85F region (Df(3R)by62) with respect to the outstretched wing phenotype. These results
indicated that there was a separation of the recessive lethal mutation (which we now call
l(3)10477) from the mutation causing the wing phenotype (which we now call 10477).
We have therefore re-named this fly line (P{PZ}10477, l(3)10477) to indicate the
presence of both mutations. These results reveal the association of a recessive mutant
wing phenotype with a gene in the 85E-85F region. +, viable; – , lethal; wing, wing
phenotype was exhibited in the resultant flies; blank boxes indicate that particular cross
was not performed. *, semi-lethal due to 2nd site lethality present in the P element line
(l(3)s2681) used to make the small deficiencies Df(3R)mr73 and Df(3R)mrO1 (TERMAN
et al. 2002). Fly lines were all obtained from the Bloomington Stock Center except
Df(3R)mr73, Df(3R)mrO1, Df(3R)segG16 (TERMAN et al. 2002); s13308, s103402
(Szeged Stock Center); Evar631 (kind gift from Gunter Reuter); Df(3R)B22-5 (kind gift
from Bill Chia); and P{wH}2-1 (kind gift from Jim Birchler).
LITERATURE CITED
BDGP, 1994-1999 Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project.
TERMAN, J. R., T. MAO, R. J. PASTERKAMP, H. H. YU and A. L. KOLODKIN, 2002
MICALs, a family of conserved flavoprotein oxidoreductases, function in plexinmediated axonal repulsion. Cell 109: 887-900.