Glossary - Research Services
advertisement

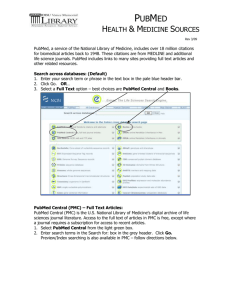
NIH Public Access Policy Glossary of Terms Final peer-reviewed manuscript: The author’s final manuscript of a peer-reviewed article accepted for journal publication, including all modifications from the peer review process. Final published article: The journal’s authoritative copy of the article, including all modifications from the publishing peer review process, copyediting and stylistic edits, and formatting changes. Mandated OA – open access archiving mandated by a funding agency, a publisher, or other body. MyNCBI – A personal account for users of PubMed, PubMed Central, NIHMS, and other NCBI databases to customize NCBI web services. Registration is free. NIHMS – NIH Manuscript Submission System. NIHMS manages your manuscript submissions to PubMed Central. NIHPA Policy – NIH Public Access Policy Open Access – Open Access involves the use of a copyrighted document under a Creative Commons or similar license-type agreement that allows more liberal use (including redistribution) than the traditional principles of Fair Use. Only a subset of the articles in PMC is available under such Open Access provisions PMC - PubMed Central. The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) free digital archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature developed and managed by NIH's National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) in the National Library of Medicine (NLM). A subject based repository of life sciences journal literature, as well as materials deposited by individual authors. This is an extensive and expansive resource for researchers in the bioscience, biotech and biomedical related disciplines. The citations database, PubMed, links to full-text materials within PMC. Thanks to a National Library of Medicine digitization activity, older journal content is being made freely available, back to the early 1900s in some cases. Currently 250 journal titles are included within the site. It is possible to register for an update email to ensure notification when new journals are added to the PMC collections. PMCID – PubMed Central reference number, a unique identifier assigned to each manuscript at the point of submission to PubMed Central, included in the records of all articles published in PMC. For example, the PMCID for this manuscript is PMC2169055: Requirement of RAD52 Group Genes for Postreplication Repair of UV-Damaged DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Venkateswarlu Gangavarapu, Satya Prakash, and Louise Prakash Mol Cell Biol. 2007 November; 27(21): 7758–7764. Published online 2007 September 4. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01331-07. PMCID: PMC2169055 | Abstract | Full Text | PDF–367K | PMID – PubMed unique identifier for each record, included in the records of all externally published articles indexed by PubMed. For example, the PMID for this article is 17785441: Gangavarapu V, Prakash S, Prakash L. Requirement of RAD52 group genes for postreplication repair of UV-damaged DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(21):7758-64. Epub 2007 Sep 4. PMID: 17785441 [PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE] Public Access – The Policy of NIH for its funded research. The policy ensures that the public has access to the peer reviewed and published results of all NIH-funded research through PubMed Central (PMC). United States and/or foreign copyright laws protect most of the articles in PMC; PMC provides access to them at no cost, much like a library does, under the principles of Fair Use. SHERPA RoMEO – Securing a Hybrid Environment for Research Preservation and Access. A partnership, begun in 2002, of research-led universities in the United Kingdom with an active interest in establishing an example of the 116101879 4/8/2008 concept of an open access. The SHERPA/RoMEO service site is maintained by SHERPA staff and provides a listing of 377 publishers' copyright conditions as they relate to authors archiving their work on-line. SPARC - Scholarly Publishing and Academic Resources Coalition, an international alliance of more than 800 academic and research libraries working to create a more open system of scholarly communication. SPARC’s advocacy, educational and publisher partnership programs encourage expanded dissemination of research. SPARC is on the Web at http://www.arl.org/sparc/ . 116101879 4/8/2008