Ecology & Biomes
advertisement

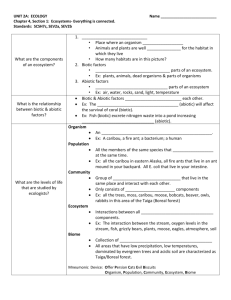
4th Nine Weeks Study Guide Ecology & Biomes 1. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic? Biotic = living; abiotic = nonliving 2. Water is lost to the abiotic parts of the biosphere from the biotic parts in what process? evaporation 3. How is water lost through the biotic parts of the environment? (plants) transpiration 4. Name 2 ways nitrogen is returned to the atmosphere (by denitrification). Death and decay by bacteria or fungi 5. How much energy (as a percentage) is lost as you move up each trophic level? 90% 6. What happens to the amount of energy? It decreases (lost) 7. Name 2 types of decomposers. Fungi (mushroom) & bacteria 8. What are the steps of the water cycle? In which step are plants involved? TRANSPIRATION Seepage into the ground transpiration Precipitation runoff into bodies of waterevaporation 9. In an energy pyramid, which level has the smallest number of organisms? Tertiary consumers (or highest level) 10. What is a terrestrial biome? An aquatic biome? Land based; water based 11. Compare and contrast density-independent factors and density-dependent factors. Density-independent Alike Density-dependent Happens regardless of the Both have an impact on a Impact depends on the pop pop size pop size 12. Density-dependent or independent: a) drought, b) food, c) competition, and d) disease. indep; dep; dep; dep 13. A cold, dry, and mostly treeless biome that has a layer of soil called permafrost. tundra 14. A type of grassland that has alternating wet and dry seasons. savannah 15. The biome that is dominated by annual trees that lose their leaves each year. Temperate deciduous forest 16. This biome is characterized by evergreen coniferous trees. taiga 17. Compare and contrast habitat and niche. A habitat is where an organism lives and a niche is the organism’s way of life (how they get their food, etc) 18. What happens if two niches overlap? Competition Animals Write the letter only: 19. Which beak is used to scoop things? C 20. Which beak is used to drill into trees for insects? D 21. Which beak is used to tear meat? B Write the letter only: 22.Which animal is a filter feeder? B 23.Which organism is the most complex? A 24.Which organism may be parasitic? C 25.Which organism has an exoskeleton and bilateral symmetry? D 26.Name a protective structure found in turtles. shell 27.What kind of symmetry do the following animals have: a) sponge, b) flatworm, c) echinoderm, & d) amphibian; asymmetrical; bilateral; radial; bilateral 28.Name the 2 endothermic animal classes. Aves and Mammals 29.What is the main advantage of the following structures: a) claws-defense/ protection, b) hair/fur-warmth/conserving heat, c) scales- protection 30. What is the difference between estivation and hibernation? Estivation is when the metabolism slows down in response to heat while hibernation is the same but in response to cold weather. 31.Name 3 adaptations animals and plants in the desert may have. Thick leaves, waxy-leaf plants, animals burrowing during the day Plants 32. Create a chart to show how plants are classified. 33.Create a chart to compare and contrast monocots and dicots in terms of: a) # of seed leaves, b) veins, c) flower parts, & d) arrangement of vascular bundles. 34. Are the following vascular or non-vascular: a) ferns-vasc, b) mosses-nonvasc, c) liverworts-nonvasc, and d) club mosses-vasc. 35. List the functions of: a) leaf-traps light energy for photosynthesis, b) cuticle-prevents water loss, c) stem-support during growth & food storage, d) xylem-transports water, and e) phloem-transports dissolved food/nutrients. 36. What are the 2 parts of the stamen? Anther & filament; 37. The 3 parts of a pistil? Style, stigma, & ovary