Steinman_Howard_M - Department of Biochemistry
advertisement

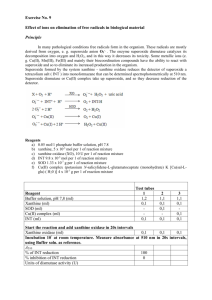
Principal Investigator/Program Director (Last, First, Middle): Steinman, Howard M. BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the key personnel and other significant contributors in the order listed on Form Page 2. Follow this format for each person. DO NOT EXCEED FOUR PAGES. NAME POSITION TITLE Steinman, Howard M. Professor of Biochemistry eRA COMMONS USER NAME howardsteinman EDUCATION/TRAINING (Begin with baccalaureate or other initial professional education, such as nursing, and include postdoctoral training.) INSTITUTION AND LOCATION Amherst College Yale University DEGREE (if applicable) YEAR(s) B.A. Ph.D. 1965 1970 FIELD OF STUDY Biophysics Mol Biophy & Biochem A. Positions and Honors Professional Positions: 1970 to 1976 Post-doctoral Fellow (Laboratory of Robert L. Hill, PhD), Department of Biochemistry, Duke University, Durham, NC 1975 to 1976 Assistant Medical Research Professor of Biochemistry, Duke University, Durham, NC 1976 to 1981 Asst Professor of Biochemistry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY 1981 to 1991 Assoc Professor of Biochemistry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY 1991 to present Professor of Biochemistry, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY Awards and Other Professional Activities: 1978 to 1981 Sinsheimer Scholar Award 1982 to 1987 Editorial Board, The Journal of Biological Chemistry 1989 to 1994 Editorial Board, The Journal of Biological Chemistry 1998 to present Member, General Medical Science Subcommittee, Merit Review, Department of Veterans Affairs 1982 Invited speaker, 3rd International Symposium on Superoxide and SOD, Ellenville, NY 1985 Invited speaker, 5th International Symposium on Superoxide and SOD, Rome, Italy 1987 Invited speaker, 4th International Conference on Oxygen Radicals, San Diego, CA 1988 Invited speaker, Oxy-Radicals in Molecular Biology and Pathology, Park City, UT 1989 Invited speaker, 5th International Conference on Superoxide and SOD, Jerusalem, Israel 1995 Invited speaker, Symposium on Structure, Function and Evolution of Glycoproteins and Related Molecules, Eastsound, WA 1996 Invited speaker, Microbial Stress Gordon Conference, Holderness, NH 1996 Organizing Committee for Oxygen ’96, Miami Beach, FL 1981 to 2000 teaching awards: Albert Einstein College of Medicine (3 awards), the Sue Golding Graduate Division of Medical Sciences of Albert Einstein College of Medicine (1 award), and American Association for Clinical Chemistry (1 award) B. Selected Peer-reviewed Publications Steinman, H.M. (1978) The Amino Acid Sequence of Mangano Superoxide Dismutase from Escherichia coli B. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 8708-8720. Steinman, H.M. (1980) The Amino Acid Sequence of Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase from Baker's Yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 6758-6765. PHS 398/2590 (Rev. 09/04, Reissued 4/2006) Page 5 Biographical Sketch Format Page Principal Investigator/Program Director (Last, First, Middle): Steinman, Howard M. Weissborn, A., Steinman, H.M., and Shapiro, L. (1982) Characterization of the Proteins of the Caulobacter crescentus Flagellar Filament: Peptide Analysis and Filament Organization. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 20662074. Keiser, H.D., Adlersberg, J.B., and Steinman, H.M. (1982) Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of the Tryptic Fragments of Bovine Nasal-Cartilage Proteoglycan Monomer of High Buoyant Density. Biochem. J. 203, 683-689. Steinman, H.M. (1982) Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase from Caulobacter crescentus CB15. Bacteriocuprein Form of the Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 10283-10293. A Novel Steinman (1985) Bacteriocuprein Superoxide Dismutases in Pseudomonads. J. Bacteriol. 162, 1255-1260. Dunlap, P.V. and Steinman, H.M. (1986) Strain Variation in the Bacteriocuprein Superoxide Dismutase from Photobacterium leiognathi. J. Bacteriol. 165, 393-398. Steinman, H.M. (1987) Bacteriocuprein Superoxide Dismutase of Photobacterium leiognathi: Isolation and Sequence of the Gene and Evidence for a Precursor Form. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 1882-1887. Carlioz, A., Ludwig, M.L., Stallings, W.C., Fee, J.A., Steinman, H.M., and Touati, D. (1988) Iron Superoxide Dismutase: Nucleotide Sequence of the Gene from E. coli K12 and Correlations with Crystal Structure. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 1555-1562. Steinman, H.M., and Ely, B. (1990) Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase of Caulobacter crescentus. Gene Cloning, Sequencing, and Mapping, and Periplasmic Location of the Enzyme. J. Bacteriol. 172, 2901-2910. Steinman, H.M. (1992) Construction of an Escherichia coli K-12 Strain Deleted for Manganese and Iron Superoxide Dismutase Genes and Its Use in Cloning the Iron Superoxide Dismutase Gene of Legionella pneumophila. Mol. Gen. Genet. 232, 427-430. Hopkin, K.A., Papazian, M.A., and Steinman, H.M. (1992) Functional Differences Between Manganese and Iron Superoxide Dismutases in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 24253-24258. Steinman, H.M. (1993) Analysis of the Function of Periplasmic Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase in Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 175, 1198-1202. Sadowsky, A.B., Wilson, J.W., Steinman, H.M., and Shuman, H.A. (1994) The Iron Superoxide Dismutase of Legionella pneumophila is Essential for Viability. J. Bacteriol. 176, 3790-3799. Steinman, H.M., Weinstein, L.W., and Brenowitz, M. (1994) The Manganese Superoxide Dismutase of Escherichia coli K12 Associates with DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 28629-28634. Steinman, H.M. (1995) The Bcl-2 Oncogene Functions as a Pro-Oxidant. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 3487-3490. Schnell, S. and Steinman, H.M. (1995) Function and Stationary Phase Induction of Periplasmic Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase/Peroxidase in Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 177, 5924-5929. St. John, G. and Steinman, H.M (1996) Periplasmic Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase of Legionella pneumophila. A Role in Stationary Phase Survival. J. Bacteriol. 178, 1578-1584. Bourne, Y., Redford, S.M., Steinman, H.M., Lepock, J.R., Tainer, J.A., and Getzoff, E.D. (1996) Novel Dimeric Interface and Electrostatic Recognition in Bacterial Cu, Zn Superoxide Dismutase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 93, 12774-12779. Steinman, H.M., Fareed, F. and Weinstein, L. (1997) Catalase-Peroxidase of Caulobacter crescentus: Function and Role in Stationary-Phase Survival. J. Bacteriol. 179, 6831-6836. Jacono, A.A., Hu, B., Kopke, R.D., Henderson, D., Van De Water, T.R. and Steinman, H.M. (1998) Changes in Cochlear Antioxidant Enzyme Activity After Sound Conditioning and Noise Exposure in the Chinchilla. Hearing Res. 117, 31-38. Bandyopadhyay, P. and Steinman, H.M. (1998) Catalase-Peroxidases Legionella pneumophila. Cloning of the katB Gene and Studies of KatB Function. J. Bacteriol. 180, 5369-5374. PHS 398/2590 (Rev. 09/04, Reissued 4/2006) Page 6 Continuation Format Page Principal Investigator/Program Director (Last, First, Middle): Steinman, Howard M. Rava, P.S., Somma, L. and Steinman, H.M. (1999) Identification of a Regulator that Controls Stationary-Phase Expression of Catalase-Peroxidase in Caulobacter crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 181, 6152-6159. Bandyopadhay, P. and Steinman, H.M. (2000) Catalase-Peroxidases of Legionella pneumophila: Cloning of the katA Gene and Studies of KatA Function. J. Bacteriol. 182, 6679-6686. Jacob, C., Courbot, M., Brun, A., Steinman, H.M., Jacquot, J.P., Botton, B., Chalot, M. (2001) Eur. J Biochem. 268, 3223-32. Molecular cloning, characterization and regulation by cadmium of a superoxide dismutase from the ectomycorrhizal fungus Paxillus involutus. Bandyopadhyay, P., Byrne, B., Chan, Y., Swanson, M., and Steinman, H. M. (2003) The Legionella pneumophila catalase-peroxidases are required for proper trafficking and growth in primary macrophages. Infection and Immunity, 71, 8, 4526-4535. Bandyopadhyay, P., Xiao, H., Coleman, H.A., Price-Whelan, A. and Steinman, H.M. (2004) Icm/Dotindependent entry of Legionella pneumophila into amoeba and macrophage hosts. Infection and Immunity, 72, 8, 4541-4551. [This article was selected for the “Journal Highlights” section of September, 2004 ASM News] Bandyopadhyay, P., Liu, S., Gabbai, C.B., Venitelli, Z. and Steinman, H.M. (2006) Environmental mimics and the Lvh Type IVA secretion system contribute to virulence-related phenotypes of Legionella pneumophila Infection and Immunity, Ms No. 00956-06, accepted for publication. C. Recent Invited Talks ASM 105th General Meeting. Atlanta, GA. June, 2005. ‘Stress and the Acquisition of Virulence Traits by Legionella pneumophila” Microbial Pathogenesis & Host Response. Cold Spring Harbor, NY. September, 2005. “A second Type IV secretion system functions in virulence traits of Legionella pneumophila”. D. Research Support On going research on virulence mechanisms of Legionella pneumophila PI: Howard M. Steinman Agency: Institutional support from Albert Einstein College of Medicine, 09/30/2001 to 07/31/2007 Current Period 08/01/2006 to 07/31/2007: salary/fringe for one post doctoral fellow, Dr. Purnima Bandyopadhyay, $12,000 for supplies/other. An Einstein PI must have external funding to recruit graduate students,. During this time, we demonstrated that the Dot/Icm Type IV secretion system (T4SS), generally thought to be required for virulence phenotypes of Legionella, is dispensable under certain culture conditions. Specifically, we showed that defective virulence phenotypes of dotA and dotB mutants are reversed when Legionella cultures are exposed to mimics of the aquatic and amoebae cyst environments encountered in the spread of Legionnaires’ disease. Our working hypothesis is that a second T4SS, encoded by the lvh locus of L. pneumophila, contributes to virulence phenotypes under conditions relevant to the etiology of Legionnaires’ disease. These observations resulted in one publication (Bandyopadhyay et al. 2004), invitations to speak in 2005 at ASM and the Cold Spring Harbor meeting on Microbial Pathogenesis and Host Response and an Infection and Immunity manuscript being revised following review. Elucidating the mechanism by which defective virulence phenotypes of dot/icm mutants are reversed, in particular the role of the Lvh T4SS and the role of tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) proteins in this reversal, is a goal of this proposal. PHS 398/2590 (Rev. 09/04, Reissued 4/2006) Page 7 Continuation Format Page