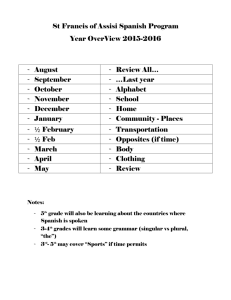
Chap 15. Interest Rate Derivative Markets

Chap. 1. Financial Markets and Institutions
*Financial Markets: surplus units and deficit units, governments
-Money vs Capital Markets
-Primary vs Secondary Markets, liquidity
-Organized vs OTC Markets
*Securities Traded in Financial Markets
- Money Market Securities
- Capital Market Securities
- Derivatives
Hedging vs Speculation
*Valuation of Securities
-Importance
-Factors
-Formulae/Process (Exh)
-Market Efficiency
*Financial Market Regulation
-Disclosure
Securities Act of 1933, Enron & Worldcom
-Other Regulations
Fed, SEC, FDIC, NASD, --- many banking and securities laws and rules
*Financial Market Globalization
-Recent Trends privatization, liberalization, integration, tech improvement
-FX Markets
*Financial Institutions
- Depository Institutions
Commercial Banks, S&Ls, Credit Unions
-Non-depository Institutions
Finance Companies, Mutual Funds, Securities Firms, Insurance
Companies, Pension Funds, --
-Recent Trends liberalization, more competition, consolidation, global expansion
Chap. 2. Interest Rate Determination
-Loanable Funds Theory
-Economic Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Economic Growth
Inflation (Fisher Effect)
Money Supply
Budge Deficit
Foreign Funds Flows
- Evaluation of Interest Rates over Time and Forecasting
Chap 3. Structure of Interest Rates
*Factors causing varying yields
1. Credit (default) risk
2. Liquidity
3. Tax status
4. Term to maturity, term structure of interest rates, yield curve
5. Special provisions
1) Call
2) Convertibility
3) Sinking fund
4) Put
5) Collateral
6) Senior vs. junior
*Explaining yield differentials ( www.ratecurve.com
)
- Money market securities
- Capital market securities
- Estimating the appropriate yield
*Term structure hypotheses
1. Pure expectations hypothesis
See illustration
2. Liquidity premium hypothesis
3. Market segmentation & Impact of debt management on term structure
- Historical Review
- International structure
Chap 4. Functions of the Fed
* Organization
- 12 Federal Reserve District Banks
- Member Banks: Some commercial banks by meeting “certain” requirements, all national banks chartered by the C of C and some state banks (35% of all)
- Board of Governors (Federal Reserve Board)
- FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee)
- Advisory committees
- Integration
* Monetary Policy Tools
- Open Market Operations
- (Federal) Discount Window: discount rate set by Board of Governors
cf) Federal Fund Rates: market determined rates
- Reserve Requirement Ratio: 8~12% to see How,
- Summary
- Monetary Control Act of 1980
* Fed Control of the Money Supply
- Money Supply Measures
* Global Monetary Policy
- Euro
- Global Central Bank Coordination, BIS
Chap 5. Monetary Theory and Policy
* Monetary Theory
- Keynesian
- Quantity Theory
- Rational Expectation
- Which one?
* Tradeoff and Priorities: Phillips Curve
* Economic Indicators Monitored by the Fed, see the Web
- Growth
- Inflation
* Lags in Monetary Policy and Assessing the Impact
* Integrating Monetary and Fiscal Policies
* Global Effects of Monetary Policy, Global Crowding Out?
Debt Security Markets: p.129
Chap. 6: Money Markets
*Money Market Securities
-T Bills: Auction, Estimating the Yield & T-bill Discount
-CP, Estimating the Yield p.140, Inverse relationship between funds rasied and yield
-NCDs, yiled higher than T-bills
-Repos, reverse repos, Estimating the Yield
-Fed Funds
-BAs, L/Cs
*Institutional Use of Money Markets
*Valuation of Money Market Securities
-Explaining Money Market Price Movements, Pm?
-eg., 911
*Risk of Money Market Securities, becomes risky=>T-Bills or higher pm
- Illustration
*Interaction among Money Market Yields, competitive yields!
-WSJ
*Globalization
-Exh
-Eurodollar deposits
-Euro-CP
-$ yield (effective yield)
*www.Bloomberg.com/markets for yield curve for major countires.
Chap. 7: Bond Markets
*Yield (YTM)
*T-Bonds
-Auction, The Salomon Brothers Scandal
-Trading
-Quotations
-Stripped, Inflation-Indexed, Brady
*Federal Government Agency Bonds
-Ginne Mae, Fannie Mae, Fredie Mac, -- Securitization: pooling and repackaging loans into securites.
*Munis
-General Obligation Bonds vs. Revenue Bonds (see Illustration)
-Tax exempt
-websites
*Corp Bonds
-Maturities
-Private Placements (vs. Public Offering)
-Characteristics and Indenture Provisions
-websites
-Quotations; in eighths, current yield=annual coupon payment/current price, WSJ
-Junk Bonds
-Institutional Use of Bonds (Restructuring and Exh)
-Globalization, Eurodollar Market, Tax Effects
Chap. 8: Bond Valuation and Risk
*PV
*Relationship Between Coupon Rate, Required Return, and Bond Price
-Implications for Financial Institutions,
*Excel Spreadsheet Exercises
*Bond Price Movements
-Factors
*Sensitivity of Bond Prices to Interest Rates
-Duration
-Modified Duration
*Bond Investment Strategies
-Matching
-Laddered
-Barbell
-Interest Rate
*International Bonds
-Exchange Rate Effects
-International Diversification
Equity Security Markets: p.251
Chap. 10: Assessment of Stock Markets
*Background on Stock
-Ownership and Voting Rights
-Preferred Stock
*IPO: Best Effort vs. Firm Commitment
-Process, Types, Timing, Initial and Long-term performance
*Seasoned Public Offering
-Shelf-Registration
*Stock Exchange
- Exchanges (organized markets), Listing Requirements
-OTC (NASDAQ), OTC Bulletin Board, Pink Sheets, Penny Stocks
-Stock Quotations
-Stock Index
*Investor Participation in the Secondary Market
*Monitoring
*Corporate Control
-Stock Repurchase, LBOs
-Barriers to Corporate Control
*Globalization
Chap. 11. Stock Valuation and Risk
*Stock Valuation Methods
-PE Method, Illustration V=(Exp EPS)*(Average Industry P/E)
-Dividend Discount Model/Adjusted
*Computer Exercise
-CAPM
-APT
*Factors Affecting Stock Prices
-Economic: Economic Growth, Interest Rates, Exchange Rates, ---
-Market-Related: (Small Firm in) January Effect
-Industry: IT, Oil, ---
-Firm-Specific: Strikes, M&A,---
*Role of Analysts in Valuing Stocks
-Conflicts of Interest
-Disclosure
-Unbiased
*Stock Risk
-How to measure
Individual Volatility (standard deviation, or total risk) -> In
Portfolio Context?: Systematic (undiversifiable, beta) vs unsystematic (idiosyncratic)
* PORTFOLIO exercise
-Volatility/Beta/VAR
*Forecasting Stock Price, Volatility and Beta
*Stock Performance Measurement
-Sharpe
-Treynor
-Jensen
*Stock Market Efficiency
*Foreign Stocks
-International Diversification
Chap. 12. Market Microstructure and Strategies
*Stock Market Transactions
-Placing an order: market order, limit order, stop loss, order via online
-Margin trading: initial, maintenance, margin call, impact on returns
-Short selling
-Stock indexes
*How Trades Are Executed
-Floor brokers, Specialists, ECNs, Program Trading
*Regulation of Stock Trading
-Circuit breakers, SEC,
*Barriers to International Stock Trading
-Transactions costs
-Information costs
-Exchange rate risk
Chap 15. Interest Rate Derivative Markets
1. Interest Rate Swap
1) Definition
2) Examples
Co. A: Funding a fixed-rate investment (yielding 13.25%) by a floating-rate loan
(Libor+ .5%)
Co. B: Funding a floating-rate inv. (Libor + .75%) by a fixed-rate loan (11%)
BOTH MAY BE INTERESTED IN A SWAP DEAL THAT RESULTS IN POSITIVE
LOCK-IN SPREADS. SINCE BOTH COs. ARE INTERESTED IN EXCHANGING
LIBOR + .5% WITH A FIXED RATE LOAN (IN OPPOSITE DIRECTIONS), WE CAN
FIND THAT BOTH PARTIES MAY ENTER INTO A SWAP DEAL AS LONG AS THE
POSITIVE LOCK-IN SPREADS CONDITION IS TO BE MET.
For example, Co. A offers LIBOR+.5% for say 12%. Then,
1) Co. A'S COST OF FUNDS,
2) Co. B'S
*A FI (a swap bank) may engage in the swap deal.
3) Participation by FIs
2. Types of Interest Rate Swaps
1) Plain vanilla
2) Forward
3) Callable
4) Putable
5) Extendable
6) Zero-coupon-for-floating
7) Rate-capped
8) Equity
3. Risks of Interest Rate Swaps
1) Basis
2) Credit
3) Sovereign
4. Pricing
5. Caps, Floors, and Collars