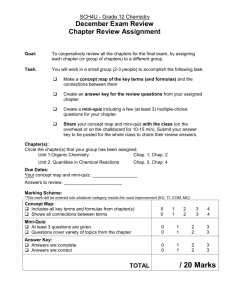
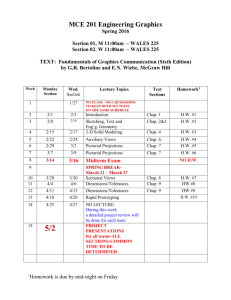
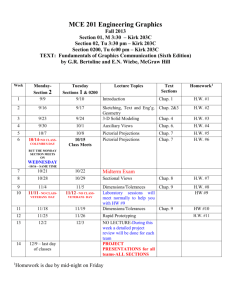
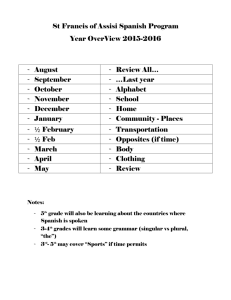
Final check list and formulas

CHEM Final Vocab./Concepts To Know A Check list
* Poly-atomic ions
* Nomenclature
* Diatomic Molecules (7)
* Coefficients
Mole Ratio
* Stoichiometry problems (mass-mass)
* Ideal vs Real Gas
* Molar mass
* Molar Volume
* Absolute Zero (the Kelvin Scale)
* Boyles Law
* Standard Pressure (Pressure conversions torr
kPa
atm)
* Charles Law
* Ideal gas Law
* Graham’s Law
* LAB Safety / Procedures
* Electrolyte vs. Non-electrolyte
* Polar vs. Non-Polar
* Molarity problem solving
* molality problem solving
* Saturated v supersaturated v unsaturated
Use a solubility chart
* Phase diagram Sublimation, melting and boiling curves meet at the triple pt.
* Van’t Hoff multiplier
* Molecules vs. compounds
* dissociation vs. ionization
* boiling & freezing point problems.
* acid vs. bases (hydrogen vs hydroxide)
* pH, pOH and indicators
Formula writing – be able to criss-cross charges.
Be able to name chemical compounds
Classify Chem equations
Balancing & predicating chem. Equation
Use the Gas laws to describe Density & why nothing sucks.
Solve problems using Colligative property concepts.
Formulas and constants for the test that you can put on a card!
Chap 7 Nomenclature
1 mol of X = Formula mass = gram atomic mass from the periodic table
% composition = mass of the element / molar mass of formula x 100
Chap 8 Balancing equations
Chemical equations
no formulas
Chap 9 Stoichiometry
% yield = actual yield (experiment) / Theoretical yield(stoichiometry) x100
Chap 10 Phase changes as temp increase = faster molecular motion Graham’s law
𝑉𝑒𝑙
𝐴
𝑉𝑒𝑙
𝐵
Chap 11 GAS LAWS
Pressure = Force/area (N/m 2 ) or (Pascal)
Standard Atmospheric pressure = 1 atm = 760 mmHg = 101.3 kPa
Standard Temperature 0 = 273 K
= √
Dalton’s Law
P total
= P
1
+ P
2
+ P
3
+…. (collected over water)
Boyle’s
P
1
V
1
= P
2
V
2
Charles
V
1
/T
1
= V
2
/T
2
Gay-Lussacs’
P
1
/T
1
= P
2
/T
2
Combined Gas Law
P
Avogadro
n
1
1
V
1
/T
1
= P
2
V
2
/T
2
/V
1
= n
2
/V
2
{ molar volume = 1 mole of gas at STP = 22.4 L
}
𝑀
𝐵
𝑀
𝐴
PV = nRT or PV = mRT/M or D = PM/RT
R= 8.31 (kPa x L)/(mol x K)
R= 0.0821 (atm x L)/(mol x K)
R= 62.4 (mmHg x L)/(mol x K)
Chap 12 Solutions
% mass = Mass of solute/mass solution x 100
Molarity = moles of solute/ L of soln.
THIS PAPER WILL NOT BE
ABLE TO BE USED AS YOU
NOTE CARD
MAKE YOUR OWN!!! molality = moles of solute / kg of solvent
∆
T b
= i K b
m
∆
T f
= i K f
m
K f H2O
= -1.86 °C/m K b H2O
= 0.512 °C/m
Chap 14 & 15 Acids and Base
[H
3
O + ]= 1x10 -14 M 2 / [OH ] pH = - log[H
3
O + ] pOH= - log[OH ]