Cloze Sentence Flood Plains and Levee
advertisement

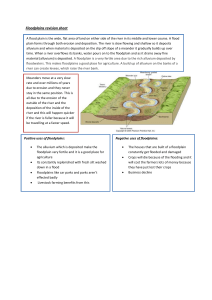
Floodplain formation The floodplain is an area of relatively _____ land on either side of the channel. It is formed by downstream ________ migration of __________. This occurs because the point of maximum erosion is just downstream of the centre of the meander bend. As well as meander deposits, the floodplain consists of ________ deposits from times of _______. As the river overflows its channel, there is a reduction in __________ (due to the sudden increase in wetted perimeter and the hydraulic radius which in turn will produce an increase in _______ and a corresponding decrease in velocity) and any coarse sediment will be quickly _______. overbank flat velocity meanders deposited lateral flood friction Levee formation When a river _______ its banks the _________ produced by the flood plain cause material to be ________. The ______ material is dropped first to form a small, natural __________ alongside the channel. These deposits form distinct ridges on the floodplain, called _________. The finer sediment load is slowly deposited from the flood waters as they sit on the floodplain and forms a fertile deposit called ________. If, later on, the river bed is raised by deposition of material, these embankments are sometimes _________ strengthened and heightened to try to contain the river. Some rivers flow above the level of their flood plains which means that if the levees collapse there can be serious danger to life and property. Levees sometimes have a ________ structure due to a series of flood events with the ________ material nearest the channel due to sorting. deposited artificially Overflows alluvium largest layered embankment friction coarsest levees Floodplain formation The floodplain is an area of relatively _____ land on either side of the channel. It is formed by downstream ________ migration of __________. This occurs because the point of maximum erosion is just downstream of the centre of the meander bend. As well as meander deposits, the floodplain consists of ________ deposits from times of _______. As the river overflows its channel, there is a reduction in __________ (due to the sudden increase in wetted perimeter and the hydraulic radius which in turn will produce an increase in _______ and a corresponding decrease in velocity) and any coarse sediment will be quickly _______. overbank flat velocity meanders deposited lateral flood friction Levee formation When a river _______ its banks the _________ produced by the flood plain cause material to be ________. The ______ material is dropped first to form a small, natural __________ alongside the channel. These deposits form distinct ridges on the floodplain, called _________. The finer sediment load is slowly deposited from the flood waters as they sit on the floodplain and forms a fertile deposit called ________. If, later on, the river bed is raised by deposition of material, these embankments are sometimes _________ strengthened and heightened to try to contain the river. Some rivers flow above the level of their flood plains which means that if the levees collapse there can be serious danger to life and property. Levees sometimes have a ________ structure due to a series of flood events with the ________ material nearest the channel due to sorting. deposited artificially Overflows alluvium largest layered embankment friction coarsest levees