Coastal Landforms Basic Concepts The Coastal Zone Coastal Zone
advertisement

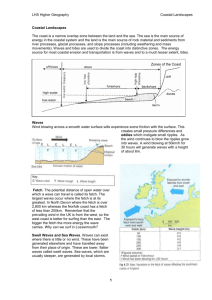
Coastal Landforms Basic Concepts The Coastal Zone Coastal Zone: General region of interaction between the land and the ocean Shoreline: Constantly changing contact between the ocean surface and the dry land. Swash: The thin sheet of water rushing towards the shoreline Backwash: The return flow of water to the ocean Eustatic Change and Submergent vs. Emergent Coastlines Coasts 1. Passive margin Coasts-Atlantic Coast Tectonic activity occurs in the middle of the ocean. Coast is tectonically passive. 2. Active margin Coast – Pacific Coast Most activity occurs around the ocean margin because of active subduction and transform plate boundaries. West Coast Coastlines of emergence: where water level has fallen, or land has risen due to tactonic activity Marine terraces, Sea Stacks, Sea cliffs Emergent Coastlines Coastlines of Submergence Sea levels rise due to retreate of Pleistocene ice sheet and many features of the former shore lie underwater Tactonic forces have lowered the level of the land- San Franscisco Bay Submergent Coastlines Rias: river valleys are drowned Fjords: Glacial Valleys drowned Submergent Coastlines COASTAL FLUVIAL PROCESSES/LANDFORMS Origin and Nature of Waves Waves : are travelling, repeating forms of alternating highs and lows called Wave crests and wave troughs Wave Height: The vertical distance between a wave trough and wave crest Wave Length: Horizontal distance between successive wave crests Tides: Two very long wavelength waves caused by the interaction between Earth, Moon and Sun Coastal Erosion Corrosion: removal of ions, rock forming minerls by solutions through chemical weathering, Hydraulic action: Sheer physical force, the pounding of waves against coastal rock material. Abrasion: The process of wearing down or rubbing away by means of friction. Beach Erosion Coastal Erosion Landforms 1. Sea Cliffs: When Waves pound directly against steep land 2. Sea Caves: Erosion, corrosion and hydraulic action along lines of weakness 3. Sea Arches: 2 caves meet from each side of hydraulic action of a headland 4. Sea Stacks: A resistant pillar is left standing the remnant is called a sea stack 5. Marine Terraces: Formed by tectonic activity uplift out of reaches of wave action Marine Terraces Point Reyes National Seashore Wave Refraction - waves change directional trend as they approach shore. Tombolo Tombolo Sand Spit Sand Spit Sea Stacks Natural Bridges and Arches Depositional Landforms 1. Beach: Landform of coastal deposition continuous with the mainland. Sandy beaches Pebble and boulder beaches White coral reef beaches Black sandy beaches- in volcanic big island Hawaii Longshore bars Spits: Coastal deposit landforms connected to the mainland at just one end Barrier beaches: long depositional feature constructed parallel to mainland, protection from direct wave attack. Lagoon Tombolo: Strip of sediment connecting mainland to an island Barrier Islands Barrier Islands Outer Banks, North Carolina Tropical Coasts Factors Correlated with Healthy Coral Reef Growth water temperature range: 18 – 29C normal seawater salinity: 32 – 35 ‰ clear, transparent water little or no sedimentation vigorous water motion Tides Tides Tides