Grammar II Oral Exam Items
advertisement

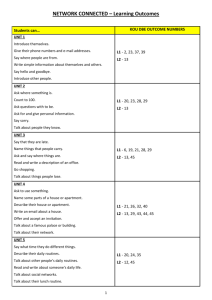
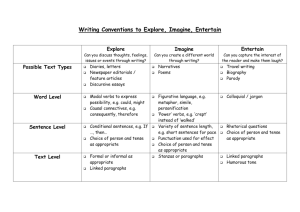
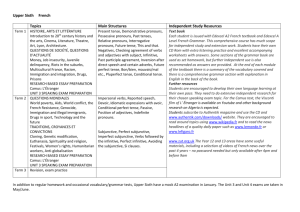
Grammar II Oral Exam Items 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. Auxiliary verbs: primary vs. modal auxiliaries Enumerate and give examples of non-finite verbal forms The all-inclusive present vs. the real/actual and the general present The Indefinite Present Tense used to indicate the all-inclusive present time The Indefinite Present Tense used for the real present The Indefinite Present Tense used for a past action The Indefinite Present Tense used for a future action The Progressive Present Tense used for the real/actual present The Progressive Present Tense used for the general present The Progressive Present Tense used for repeated activities The Progressive Present Tense used with always and its synonyms The Progressive Present Tense used for developing situations and for future actions The difference between the indefinite and progressive form Verbs not used in the progressive form: stative verbs The Indefinite Past Tense The Progressive Past Tense used a) for actions in progress at a given moment of past time, b) at the time when another past action happened The Progressive Past Tense used: a) for coextensive actions, b) with: between ... and ...; from ... to/till ..., etc. c) with: last night, last year, etc. The Progressive Past Tense used a) to indicate a more casual, less deliberate action, b) to make something seem less important, c) to indicate the beginning of an activity. The Progressive Past Tense used a) to indicate alternate activities, b) in polite enquiries, c) for repeated actions, d) explain the difference between Did you hear about ...? – Yes, Jane was telling me/told me about it. The Modal Past Tense: a) in conditional clause, b) after the verb wish and after if only. The Modal Past Tense after: a) as if and as though, b) it is (high/about time). The Modal Past Tense: a) after the phrase would/had rather/sooner, b) in main clauses, c) the modal past tense and the sequence of tenses The meaning of the subjunctive; the form of the present and the past subjunctive; the form of the negative subjunctive The Present Subjunctive: a) the form, b) time reference, c) in poetry and in elevated prose The Present Subjunctive in set/fixed phrases The Present Subjunctive in that clauses The Present Subjunctive in adverbial clauses The Past Subjunctive Other ways of expressing the subjunctive mood The Imperative: the form The Imperative: uses Uses of the imperative with DO The subject in imperative sentences The imperative with question tags The perfect tenses: form and time reference The Indefinite Present Perfect The Progressive Present Perfect The Present Perfect vs. The Past Tense with regard to time expressions The Indefinite Past Perfect The Progressive Past Perfect The Modal Past Perfect The Indefinite Future Tense The Progressive Future Tense The BE + TO-INFINITIVE structure The GOING TO + INFINITIVE structure The Indefinite Future Perfect and The Progressive Future Perfect The Passive Voice: form and the uses of the tenses in the passive voice Verbs used in the passive voice The passive for focus and the use of by + agent after a passive 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. The Passive Voice with verbs denoting knowledge, judgement, belief ... The Passive Voice with modal verbs, with the –ing form and the to-infinitive The use of the passive voice The use of abbreviated passive constructions: wishes, preferences, headlines, advertisemnets, notices; the use of the passive in formal notices and announcements The get-passive The causative have/get Question tags: form (basic information); negatives: full forms; meaning and intonation; requests Question tags (advanced points): the question tag for I am; let’s; there; negative words; this and that Question tags: nothing, nobody, somebody; non-auxiliary have; ellipsis ’Same-way’ question tags (see additional comments)