Physics 50 workshop
advertisement

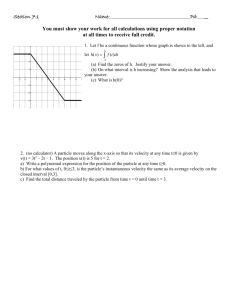
Physics 50 workshop problem set for Week 2. Chapter 2: Motion along a straight line. Please do not try to cram all of your answers on this page. Use your notebook or the paper provided in the room. 1. Convert 35.0 m3 to cubic feet, given 39.37 inches per meter. 2. This graph describes the position of a particle along the x-axis as a function of time. The position is in units of meters and the time is in seconds. a. In which time interval does the particle have its maximum speed? b. What is the average velocity in the time interval from -5 to +5 seconds? c. What is the average speed in the time interval between -5 to +5 seconds? d. At what time is the particle’s velocity zero? (There may be more than one.) 3. The position of a particle is given by x(t) = 3.0t - 2.0t , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. a. What is the velocity as a function of time? b. What is the velocity at 10.0 seconds? c. What is the acceleration as a function of time? d. What is the position of the particle when it reaches its maximum speed in the positive x direction? 2 3 4. A bank robber in a getaway car approaches an intersection at a speed of 45 mph. Just as he goes through the intersection, he realizes he needed to turn. So he steps on the brakes, comes to a complete stop, and then accelerates driving straight backwards. He reaches a speed of 22.5 mph going backwards. The total driving time is 12.4 seconds. What is the average acceleration during this time? 5. A motorcycle starts from rest and accelerates along the x axis as shown in the figure below. a. Determine the motorcycle’s speed at t = 4 seconds, and t = 14 seconds b. Find the total distance traveled in the first 14 seconds. 6. A car slows down from a speed of 31.0 m/s to a speed of 12.0 m/s over a distance of 380.0 m. a. Assuming the acceleration is constant, how much time does this take? b. What is the magnitude of the acceleration? 7. A car starts from rest and accelerates at 10.0 m/s2. How far does it travel in 2.00 seconds? 8. An object is thrown upwards with a speed of 28 m/s. You may assume it starts from a height of zero. The acceleration due to gravity on earth is -9.8 m/s2. a. What is the maximum height that it reaches? b. How long does it take to reach its maximum height? c. How high is it, 1.0 second after it is thrown? 9. An object is thrown vertically and has a speed of 25 m/s when it reaches ¼ of its maximum height above the ground (assume it starts from ground level). What is the original launch speed of the object? 10. Answer question #9, except now you are on the Moon, whose acceleration due to gravity is 1/6 that of the Earth’s. 11. Add these two vectors together: Vector A has a magnitude of 34.0 m and points at an angle of 67.0o measured counterclockwise from the x axis. Vector B has a magnitude of 22.0 m and points at an angle of 45.0o as measured counterclockwise from the y axis. Express your answer both in component form, and also as a magnitude and direction. Answers: 1. 1240 ft3 . 2. a) The maximum speed occurs during the time interval from -1 to +1 second. b) – 0.2 m/s c) 1.4 m/s. d) the particle velocity is zero when the slope of x vs. t is zero: from t = -5 to -4 sec, +1 to +2 sec, and +4 to +5 sec. 3. a) v(t) = dx/dt = 6t – 6t2 b) evaluate v(t) from part (a) at t = 10 seconds: v(t=10) = 6(10) – 6(10)2 = - 540 m/s c) a(t) = dv/dt = 6 – 12 t d) x = ½ m. 4. a = - 2.44 m/s2 . 5. a) 20 m/s and 12 m/s. 6. a) t = 17.7 seconds 7. b) 232 m b) a = -1.07 m/s2 20.0 meters 8. a) x = 40.0 9. 29.0 m/s. 10. 29.0 m/s b) t = 2.86 seconds. C) 23.1 m 11. Cx = -2.28 and Cy = 46.86, so the magnitude of C is 46.9 and it makes an angle of 87.2 degrees measured from the negative x axis, or 2.77o measured counterclockwise from the y axis.