4 Create “SQL Select Query” Data Set
advertisement

How to Use SQL Select Query Data Set in BIRT
Keywords
BIRT,Data Source,Data Set,JDBC,SQL,JavaScript
Version Control
Version
Date
Description of Changes
Draft 1
Oct 29 2008
First draft
-1-
Index
1
Introduction ........................................................................................................... 3
2
Create JDBC Data Source .................................................................................... 3
3
Configure JDBC Data Source Dynamically ........................................................ 4
4
Create “SQL Select Query” Data Set ................................................................... 5
5
Configure “SQL Select Query” Data Set Dynamically ....................................... 8
6
Run SQL Select Query Containing Parameters .................................................. 9
7
Other Configurations for “SQL Select Query” Data Set................................... 10
8
Add JDBC Driver Search Paths ......................................................................... 11
9
References ........................................................................................................... 12
-2-
1
Introduction
In BIRT, JDBC data source is used to define how to connect a database with
JDBC protocol. Based on a JDBC data source, you can create:
“SQL Select Query” Data Set
For the case that your report consumes data from the result set of a SQL
select query.
“SQL Stored Procedure Query” Data Set
For the case that your report consumes data from the result set of a SQL
stored procedure query.
This tutorial provides an overview on the common usage of JDBC data source
and “SQL Select Query” data set in BIRT 2.3.0. For “SQL Stored Procedure
Query”
data
set,
please
refer
to
http://www.birt-exchange.com/devshare/designing-birt-reports/588-create-data
-source-on-stored-procedure-in-birt/
2
Create JDBC Data Source
First, let’s create a JDBC data source. The property input dialog is shown as
Figure 1:
Figure 1 create JDBC data source
Each property is explained in the following list:
Driver Class
-3-
JDBC
driver
class
name.
There
are
initially
“org.apache.derby.jdbc.EmbeddedDriver (Apache Derby Embedded
Driver)” and “org.eclipse.birt.report.data.oda.sampledb.Driver (Classic
Models Inc. SampleDB Driver)” items in that list, which individually
correspond to Derby database and the sample database shipped with
BIRT. User can add/remove JDBC driver packages (Jar or Zip) through
“Manage Drivers…” button. All the JDBC driver class names scanned from
the added JDBC driver packages will be added to the list for user to
choose. The added JDBC driver packages are placed into
“\\plugins\org.eclipse.birt.report.data.oda.jdbc_xxx\drivers” directory (”xxx”
represents version number).
Driver URL
JDBC connection URL. Refer to the specific JDBC driver document for its
URL format.
User Name
User name to login database.
Password
Password to login database.
JNDI URL
If JDBC connection information is configured as a JNDI data source in the
application server where the report is to be deployed, this parameter is the
URL of that JNDI data source in the application server. For example, the
JNDI data source URL in Tomcat looks like ”java:/comp/env/jdbc/xxx”
(“xxx” represents the name of JNDI data source).
Attention:If “JNDI URL” is provided, It takes effect only if the report is
deployed in the application server. The <Driver Class, Driver URL, User
Name, Password> compound is always used during design time.
Click “Test Connection…” button to test whether the database can be
connected with <Driver Class, Driver URL, User Name, Password> compound.
3
Configure JDBC Data Source Dynamically
Each property of a created JDBC data source in fact can be configured during
running the report. In “Edit Data Source” dialog, choose ”Property Binding” tab
which is shown as Figure 2:
-4-
Figure 2 Configure JDBC data source dynamically
For the property to be configured dynamically, input corresponding JavaScript
expression, whose value will be evaluated during running the report and
assigned to the property, in its text box. Take Figure 2 as an example, the
JavaScript expression for “JDBC Driver URL” is:
params["driverURL"].value
So, during run time,the value of report parameter “driverURL” will be assigned
to the “JDBC Driver URL” property of that data source.
User can click ”fx” button to open “Expression Builder” dialog which helps build
JavaScript expression.
4
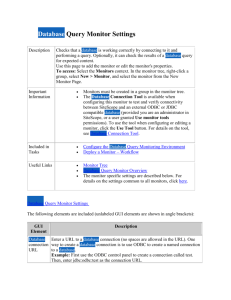
Create “SQL Select Query” Data Set
In dialog as Figure 3 shows, input data set name, choose “SQL Select Query”
as data set type and choose a data source:
-5-
Figure 3 Create“SQL Select Query”data set
Click “Next>” button to enter Figure 4:
Figure 4 SQL Select Query input dialog
The main elements are explained in the following list:
Available Items
The tables/views/stored procedures read from database are listed here.
They are grouped by schema name if schema is supported by the
database. User can double click a node which is not the root of that tree
or just drag it into the SQL input textbox to append its corresponding SQL
-6-
text.
In fact, it can still be configured that how items in “Available Items” are
displayed. Choose “Report Design”->”Data Set Editor”->”JDBC Data Set”
in the left area of the dialog which is opened through ”Window”
->”Preferences” in the main menu and shown as Figure 5:
Figure 5 JDBC data set editor configuration
Each option in Figure 5 is explained in the following list:
Prefetch all Schemas from database: takes effect only for the database
that supports schema. If checked, all schemas are listed in the “Available
Items” initially; Otherwise “Available Items” is empty by default until user
inputs some query conditions then clicks “Apply Filter” button.
Maximum number of schemas to display: the maximum number of
schemas to display in “Available Items”. Only makes sense for the
database supporting schema.
Maximum number of tables in each schema to display: the maximum
number of tables (including views) in each schema node. If that database
does not support schema, this option means the maximum number of
tables (including views) shown in the “Available Items”.
Schema
All schemas read from the database are listed here. User can choose one
schema and click ”Apply Filter” button to make “Available Items” only
display items which belong to the chosen schema.
Disabled if the database does not support schema at all.
Filter
Input something here and click “Apply Filter” button to make “Available
Items” only display the Tables/Views/Stored Procedures whose name
starts with the text user inputted.
-7-
In the inputted text, “%” represents any character sequence and “_” just
stands for any one character.
Type
Four types: “-All-“/”Table”/”View”/”Stored Procedure” are there. User can
choose one type and click ”Apply Filter” button to make “Available Items”
only display items whose type is just the chosen type.
Use identifier quoting
If checked, every part of the text, which is generated when a node in the
“Available Items” is double-clicked or dragged into the right textbox, will be
quoted with an identifier. In fact, that identifier is just read from the JDBC
driver
through
getIdentifierQuoteString()
method
in
java.sql.DataBaseMetaData interface.
Take Figure 4 as an example, this option is checked and the autogenerated text for the ”Products” node in ”Available Items” is
{ ”ROOT”.”PRODUCTS” }. If not checked, the generated text may be just
{ ROOT.PRODUCTS }.
Show system tables
To tell whether system tables are displayed in the “Available Items”. Takes
effect only after clicking “Apply Filter” button.
In the right textbox, you can input any SQL select query text as long as it’s
supported by the corresponding JDBC driver.
5
Configure “SQL Select Query” Data Set Dynamically
For a created “SQL Select Query” data set, its SQL select query text and query
time out in fact can be configured during run time. In “Edit Data Set” dialog,
choose “Property Binding” as shown in Figure 6:
Figure 6 Configure data set dynamically
-8-
Each element is explained in the following list:
Query
The string value of inputted JavaScript expression here will be evaluated
and taken as the SQL query text of the data set during running the report.
The inputted JavaScript expression in Figure 6 is:
“select * from ” + params[“tableName”].value
So, the SQL query text is constructed dynamically according to the value
of report parameter “tableName”.
Query Time Out(in seconds)
The integer value of inputted JavaScript expression here will be evaluated
and taken as the SQL query time out (in seconds) during running the report.
In fact, this integer is to be passed into the JDBC driver through
setQueryTimeOut( ) method of java.sql.Statement.
User can click ”fx” button to open “Expression Builder” dialog which helps build
JavaScript expression.
6
Run SQL Select Query Containing Parameters
If the SQL select query of a data set contains parameters as shown in Figure 7:
Figure 7 SQL query containing parameters
User should bind each parameter in the SQL query with a report parameter so
that it can be assigned with the value of its bound report parameter during run
time.
-9-
Choose “Parameters” in the left area of Figure 7, then that dialog becomes
Figure 8:
Figure 8 SQL parameter binding
Click “New…” button to open dialog as Figure 9 to bind a SQL parameter with
a report parameter or just provide a default value for it.
Figure 9 Add a SQL parameter binding
For the parameter that dose not intend to be bound with any report parameter,
user should provide a default value for it through inputting JavaScript
expression in “Default Value” textbox.
7
Other Configurations for “SQL Select Query” Data Set
Choose “Settings” in the left area of “Edit Data Set” dialog, as shown in Figure
10:
- 10 -
Figure 10 Settings for“SQL Select Qery”data set
The main elements are explained in the following list:
Data Fetch Setting
Tell how many top rows from the execution result of SQL query is taken as
the source of this data set.
In fact, if a specific value is provided, this value will be passed into JDBC
driver through setMaxRows( ) method of java.sql.Statement when
executing SQL query.
Attention: This setting takes effect both in design time and run time.
Result Set Selection
When the execution result of a SQL query, such as some SQL stored
procedure queries, contains several result sets, this parameter is used to
specify which result set is taken as the source of this data set.
The execution result of a SQL select query is always just one result set. So,
just keep it unchecked for “SQL Select Query” data set.
8
Add JDBC Driver Search Paths
As known in “2 Create JDBC Data Source”, the JDBC driver search path by
default is “\\plugins\org.eclipse.birt.report.data.oda.jdbc_xxx\drivers” directory
(“xxx” represents version number). If needed, user can add JDBC driver
search paths in using application context (AppContext). The corresponding
AppContext key is defined as Table 1:
Table 1 AppContext key to add JDBC driver search paths
Key
Description
"OdaJDBCDriverClassPath",d Its corresponding value can be a string representing
efined
as one path or a java.util.Collection instance to provide
- 11 -
org.eclipse.birt.report.data.oda multiple paths.
.jdbc.IConnectionFactory.
Each path is an absolute path of Jar/Zip or a
DRIVER_CLASSPATH
directory.
constant
The search paths user added are prior to the default search path in BIRT.
9
References
[1] BIRT official site: www.eclipse.org/BIRT
[2] JDBC 3.0 document:
http://jcp.org/aboutJava/communityprocess/first/jsr054/index.html
[3] Tomacat5.5 JNDI Resources HOW-TO:
http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-5.5-doc/jndi-resources-howto.html
[4] BIRT/FAQ/Data Access:
http://wiki.eclipse.org/index.php/BIRT/FAQ/Data_Access#Q:_How_can_I_pas
s_a_connection_object_to_BIRT.3F
- 12 -