File - Jonathon Males E
advertisement

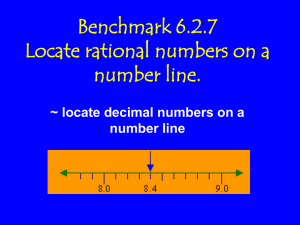
GRADE: 3 Mathematics Program-Focus: Decimals: Week: 1 Term 4 PoLT Principle to be focused on: PoLT Principle 5-Assessment practises are an integral part of teaching and learning Particularly concentrating on: 5.1 - Assessment practices reflect the full range of learning program objectives 5.2 - The teacher ensures that students receive frequent constructive feedback that supports further learning 5.5 - The teacher uses evidence from assessment to inform planning and teaching Aim to fulfil these recommendations through implementing both summative and formative assessment. Immediate feedback will be provided where possible. Skills and concepts that are not understood by the majority of students will be easily identified in the anecdotal log and these concepts will be retaught. OUTCOMES Links to VELS Knowledge-concepts and understanding Standards and progression points come under discipline-based learning, mathematics domain, number dimension Concept of a decimal-what it is, how a decimal is written Understand tenths, hundredths and their relationship to each other and 1 Progression Point 2.75 (progressing towards achieving Level 3 standard) Ordering decimals based on their knowledge of place value use of place value (as the idea that ‘ten of these is one of those’) to Skills /behaviours: determine the size and order of decimals to hundredths -Sharing materials -Co-operative skills in working with a partner this progression point is the focus for this week. Students will be using -Good listening skills -Turn-taking skills when working with others LAB as their concrete material in order to achieve this focus. -Communication skills -Skills in reflecting on their own learning Day Mon Outcomes -Introduce students to the concept of a decimal (Number Between Game) Lesson Play the ‘Number Between Game’ Materials -LAB Bring out the LAB that represent one and discuss cutting into 10 pieces as an introduction to tenths. -Wooden Organiser Using the LAB, construct decimals with the ones and tenths pieces on a wooden organiser. Children to say which decimals have been constructed. Link this with written notation. -Decimal cards -Allow students to explore the Place children in mixed ability pairs and give them cards with written decimals -Attached Sheet Assessment Diagnostic Assessment A pre-assessment task completed revealed that students do not have a strong understanding of decimals, so this lesson focuses on introducing decimals. Mimi Mimi performed well in the diagnostic assessment task, and Teaching strategies -Questioning (to encourage students to construct own knowledge)-Positive reinforcement -Catering for a range of different learning concept of a tenth through LAB -Link the use of LAB to written notation on them (up to the tenths place). Pairs construct these decimals out of LAB and complete the corresponding sheet mentioned doing similar maths at her previous school. The vocabulary being introduced in this unit is new to all students, so Mimi will be treated the same in regard to learning new vocabulary. Reflection Each pair create a decimal for the class. Students in the class can say the decimal that has been created. Write these decimals on the board Formative Assessment Rove, observe and complete anecdotal log (attached) for all students. styles (kinaesthetic learners-constructing decimals out of LAB, visual learnersdecimal sheet) These three strategies will be implemented each lesson Feedback Ensure feedback is immediate and specific. This may involve the teacher sitting down with the student and explaining/demonstrating a concept if the student does not seem to be grasping it. Tues -Consolidate tenths Reflect on last lesson-tenths. Using the LAB and wooden organiser, introduce hundredths. -Introduce hundredths Place children in mixed ability pairs and repeat activity that was done on Monday with decimal cards, however include cards that go up to hundredths. Complete corresponding sheet -Develop skills -LAB -Wooden Organiser -Decimal cards Formative Assessment Rove, observe and complete anecdotal log for all students. (Additional teaching strategies) -Think Pair Share Feedback Provide immediate, specific feedback -Group discussions in creating decimals out of LAB Mimi’s parnter Partner Mimi with a child who may need support in maths, however who has good language skills -Peer teaching -Attached sheet Reflection Pairs create a decimal that goes up to the hundredths place for the class. Students in the class can say the decimal. Write these decimals on the board. Wed -Consolidate understandings of tenths and hundredths -Develop skills in matching a constructed decimal with written notation -Develop the skill of ordering decimal numbers based on place value knowledge Review ideas discussed in the previous lesson. -LAB Play “guess the decimal”. -Decimal cards Mixed ability pairs given cards with decimals written on them. One child picks up a card and constructs the decimal shown. The other child to fill in the sheet – swap roles. -Attached sheet Formative Assessment Rove, observe and complete anecdotal log for all students. -Peer teaching -Group discussions Feedback Provide immediate, specific feedback Mimi’s partner If Mimi’s communication with her partner was successful, and if the partnership seems to be working well keep this the same. Reflection Discuss strategies used to determine what decimal has been constructed. Piece of string with 0 on one end and 1 on the other- each child has decimal in between these numbers to place on the number line. In groups of 3, students order a set of 10 decimals (using LAB). Complete the ordering decimals sheet Extension Group Play the hidden number game -String -LAB Formative Assessment Observe where individual children place their decimal on the number line. Question children and encourage them to explain choice. Take notes in anecdotal log. -Ordering Feedback -Decimal cards -Constructive feedback -Whole class teaching -Linking mathematics with real life scenarios Reflection Show students the long jump results of the previous athletics carnival. As a class, order these jumps from smallest to largest. Fri -Address likely THIS LESSON WILL ADDRESS ANY MISCONCEPTIONS STUDENTS MAY HAVE-(ways misconceptions to correct likely misconceptions with zero outlined below). -Through LAB, recognise the difference between decimals such as 1.5 and 1.05, 1.6 and 1.06 etc -Develop skills of ordering decimals with a zero in them Construct a decimal with a zero in the tenths place. Model filling in the decimal sheet that was introduced in lesson 1. Create 1. 05 and 1.5 and point out the differences between these decimals. Students to determine the largest decimal from a pair of decimals. Complete the attached sheet decimals sheet -Long jump results -LAB -Attached sheet ` Provide immediate, specific feedback as the students place their number on the number line. Identify misconceptions as soon as they occur and determine effective ways to address these misconceptions. Formative Assessment Observe and complete anecdotal log for support students Formative Assessment Collect the sheet students in the class completed. Mark this sheet and provide students with feedback in the following lesson. Support group Given the same decimals as those on the sheet, however work in pairs using LAB to determine which of these is largest. Reflection Share strategies used in order to determine the largest decimals. Paterson, A. (2006). Dr Edward de Bono's six thinking hats and numeracy. Australian Primary Mathematics Classroom , 26 (1), 1. -Six thinking hats during reflection time. Sequence of introducing hats: 1).Blue hat-what did we learn? 2).Green hat-are there any other different ways we could have solved the problem? 3). Yellow and Black hat-benefits and weaknesses of green hat ideas 4). Red hat-examine attitudes before and after learning (Paterson, 2006)