1.4.1.g Cancer Control - Ministry of Health, Nutrition Development
advertisement

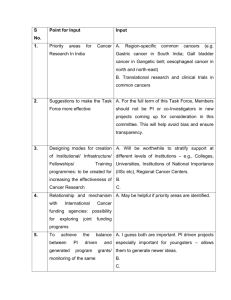
1 HEALTH SERVICES DELIVERY 1.4 DISEASE CONTROL PROGRAMME 1.4.1.g Non-Communicable Diseases Control: Cancer Control Programme (as of March 2008) A B C Focal Point Implementing Agencies Target Areas & Beneficiaries DDG/ LS National Cancer Control Programme Especially the Medical Officers of Health Areas, Plantation Sector, Rural and urban Middle and Low income population group, Migratory workers. In general, all the Groups at risk of getting cancers in Sri Lanka. Project Summary: The WHO developed Cancer Control Programs in various countries starting 1980 in order to reduce Morbidity and Mortality of cancers in the world. National Cancer Control Programme of Sri Lanka is one such organization developed with the support of the WHO by the Ministry of Health in Sri Lanka. It works under a Director and has a Field staff including Doctors. One of the main functions is Surveillance and Monitoring of the disease burden. It maintains a cancer registry data base of Pathology, Epidemiology and Public Health Related data. Times to time publications are released from these. The second aspect of cancer control is primary health care with health education, tobacco control within the island, and the Advisory committee on Tobacco control to the MoH monitors these activities and the director of the National Cancer Control Programme is the Secretary of this committee, EX - Officio. Other Health Education work is done with the collaboration of Health Education Bureau, Family Health Bureau, UNFPA, Ministry of Education, Rotary Club and other non- government organizations. Secondary prevention of early detection and screening is carried out for most common malignancies and Mobile Clinics, Local Health Personnel Training, Development of Health Care volunteers and Management of Project Based Screening Campaigns are carried out with the Plantation Health Trust, UNFPA and with other NGOO. Tertiary Care Management and Palliative Care Planning are done through the advisory committee for cancer control where the Secretary is the Director, National Cancer Control Programme. Rehabilitation work and hospice care is promoted through various NGOO. Research and development activities also are promoted by the NCCP. The following project proposal for the next 06 years will be mainly centered around the Guide lines by the WHO to increase the Monitoring and Surveillance of cancer burden in the country by developing the databases in Pathological Diagnosis, Initial Registration at Treatment, Monitoring of Follow up of cases and Mortality due to cancer. Health Education Programme will be local area based with the development of local resource personnel and volunteers. Early detection programmes will center on development of a central referral screening laboratory and clinics centre. Mobile clinics will be conducted and peripheral cancer control units will be developed to promote screening facilities. 1. Justification: 60% of the Cancers prevalent in this country are primarily preventable. Mainly through control of tobacco usage and prevention of viral infections. E.g.:- Oral and Lung cancers and Carcinoma of Cervix uteri. Other major cancers like breast cancer and colonic cancers will be controlled by early detection. The strategies for these are simple and cost effective while the increased disease burden and the late disease will need a huge amount of public health sector funds with very low quality results as the out come. The Health Education with regard to prevention of tobacco usage, healthy life styles and diet patterns, proper hygiene and the regular monitoring of health status with surveillance of occupational risks will not only result in the control of cancers but also will give significant benefits in various other disciplines too. 2. Important Assumptions/Risks/Conditions: Important Assumptions is that Medical Officers of Health will be available for dissemination of knowledge and early detection at local peripheral levels. At present, most of the funds for cancer control are obtained from various projects. To be sustainable, the flow of required funds should be from a permanent and consolidated source. 3. Project Objective: Objective To increase the knowledge with regard to prevention of cancers and increase facilities for early detection methodology, in order to reduce the cancer disease burden 4. Indicators Down staging of detected Cancers Reduction of Smokers and Tobacco usage in the country No of asymptomatic clients attending for Screening Increased detection of pre- malignant lesion Means of Verification The cancer registry database Hospital patients databases Spot surveys and periodical surveys Screening clinic databases Pathological registry database Project Output/Product: Outputs Grass root level health care workers trained in Cancer prevention and Screening Central and provincial screening clinics and reference laboratory established Mobile cancer screening programmes organized by the Central Unit as well as the peripheral organizations Smoking and Tobacco usage reduced through public awareness Indicators All Public health staff trained on awareness of cancer control A functioning central and provincial screening clinic and reference laboratory Increased early detection of asymptomatic cancer patients Means of Verification Staff assessment reports Reduction of smoking related and tobacco related Tobacco sales data, spot surveys internal Work performance of the central screening clinic and reference laboratory Screening clinic data and referral data to treatment centres and cessation work 5. cancers and other diseases Mortality and Morbidity rates Related Projects: Project No. 1 2 6. Re- Productive Health UNFPA / WWC programme Country project of Rotary Club of Colombo on Early Detection of Cancers Relevant Agencies to be Coordinated: 7. Project Title Development Programme with Ministry of Health Ministry of Education United Nations Fund for Population activity Rotary Club of Colombo Provincial Health Sector Administration Monitoring & Evaluation: 1. Who? a National Cancer Control Programme b. Family Health Bureau c. Working group on Well Women Clinics 2. When? a. Annual report b. Periodical Surveys -Quarterly c. Inspection Visits regularly d. Database Analysis- routine 3. What actions to be taken based on results of monitoring & evaluation? a. Re- Assessment and regulate the training for peripheral health staff b. Increase awareness programmes c. Using Media Campaigns for promotional work d. Further training for clinic staff e. Publications on disease burden status and preventive / preclinical diagnosis methods f. News letters to be circulated g. Health regulations to be formulated and circulated 8. Activities: Activities Expected Results 1 Appoint an advisory committee on cancer control and control of tobacco usage Health related policies developed 2 Establishment of Central and Provincial screening clinic and reference laboratory Training of peripheral health workers Good quality screening programme in place HCWs capable of 3 Process Indicators Availability of control measures of tobacco and facilities for detection of cancers Increase number of early detection Peripheral Cancer and volunteers 4 Establish tobacco control, smoking prevention and cessation units 5 Re-establish cancer registry database health education and counselling with regard to cancers developed in the peripheries Increased awareness of tobacco hazards and reduction of users Timely updated publications from the registry Control Unit / cells start functioning Number of smokers reduced tobacco removed from beetle chewing cessation unit established Accurate and timely collection of required data