Using Permutation Tests to Study Infant Handling by Female Baboons
advertisement
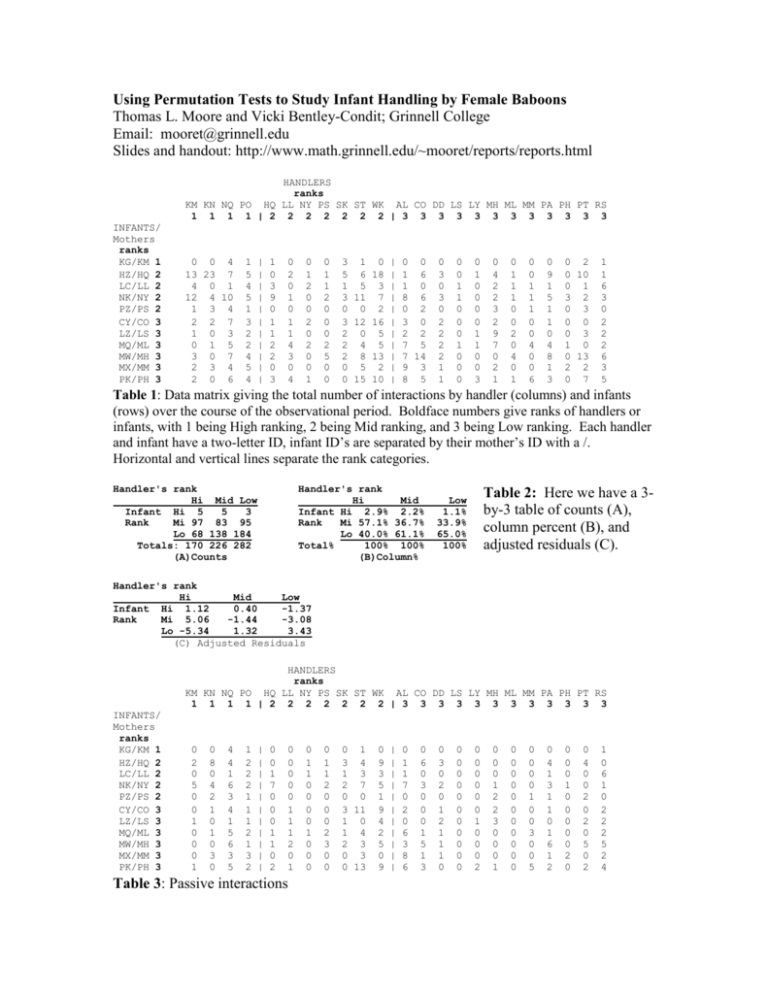
Using Permutation Tests to Study Infant Handling by Female Baboons Thomas L. Moore and Vicki Bentley-Condit; Grinnell College Email: mooret@grinnell.edu Slides and handout: http://www.math.grinnell.edu/~mooret/reports/reports.html HANDLERS ranks KM KN NQ PO HQ LL NY PS SK ST WK AL CO DD LS LY MH ML MM PA PH PT RS 1 1 1 1 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 INFANTS/ Mothers ranks KG/KM 1 HZ/HQ 2 LC/LL 2 NK/NY 2 PZ/PS 2 CY/CO 3 LZ/LS 3 MQ/ML 3 MW/MH 3 MX/MM 3 PK/PH 3 0 0 4 13 23 7 4 0 1 12 4 10 1 3 4 2 2 7 1 0 3 0 1 5 3 0 7 2 3 4 2 0 6 1 5 4 5 1 3 2 2 4 5 4 | | | | | | | | | | | 1 0 3 9 0 1 1 2 2 0 3 0 2 0 1 0 1 1 4 3 0 4 0 1 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 1 2 0 0 0 2 5 0 0 3 1 0 | 0 0 5 6 18 | 1 6 1 5 3 | 1 0 3 11 7 | 8 6 0 0 2 | 0 2 3 12 16 | 3 0 2 0 5 | 2 2 2 4 5 | 7 5 2 8 13 | 7 14 0 5 2 | 9 3 0 15 10 | 8 5 0 3 0 3 0 2 2 2 2 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 3 0 4 2 2 3 2 9 7 0 2 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 2 0 4 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 4 0 0 6 0 9 1 5 1 1 0 4 8 1 3 0 2 0 10 0 1 3 2 0 3 0 0 0 3 1 0 0 13 2 2 0 7 1 1 6 3 0 2 2 2 6 3 5 Table 1: Data matrix giving the total number of interactions by handler (columns) and infants (rows) over the course of the observational period. Boldface numbers give ranks of handlers or infants, with 1 being High ranking, 2 being Mid ranking, and 3 being Low ranking. Each handler and infant have a two-letter ID, infant ID’s are separated by their mother’s ID with a /. Horizontal and vertical lines separate the rank categories. Handler's rank Hi Mid Low Infant Hi 5 5 3 Rank Mi 97 83 95 Lo 68 138 184 Totals: 170 226 282 (A)Counts Handler's rank Hi Mid Infant Hi 2.9% 2.2% Rank Mi 57.1% 36.7% Lo 40.0% 61.1% Total% 100% 100% (B)Column% Table 2: Here we have a 3by-3 table of counts (A), column percent (B), and adjusted residuals (C). Low 1.1% 33.9% 65.0% 100% Handler's rank Hi Mid Low Infant Hi 1.12 0.40 -1.37 Rank Mi 5.06 -1.44 -3.08 Lo -5.34 1.32 3.43 (C) Adjusted Residuals HANDLERS ranks KM KN NQ PO HQ LL NY PS SK ST WK AL CO DD LS LY MH ML MM PA PH PT RS 1 1 1 1 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 INFANTS/ Mothers ranks KG/KM 1 HZ/HQ 2 LC/LL 2 NK/NY 2 PZ/PS 2 CY/CO 3 LZ/LS 3 MQ/ML 3 MW/MH 3 MX/MM 3 PK/PH 3 0 2 0 5 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 8 0 4 2 1 0 1 0 3 0 4 4 1 6 3 4 1 5 6 3 5 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 | | | | | | | | | | | 0 0 1 7 0 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 0 1 Table 3: Passive interactions 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 0 0 0 2 3 0 0 0 1 3 4 1 3 2 7 0 0 3 11 1 0 1 4 2 3 0 3 0 13 0 9 3 5 1 9 4 2 5 0 9 | | | | | | | | | | | 0 1 1 7 0 2 0 6 3 8 6 0 6 0 3 0 0 0 1 5 1 3 0 3 0 2 0 1 2 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 2 2 3 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 3 0 0 5 0 4 1 3 1 1 0 1 6 1 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 4 0 0 2 0 2 0 5 0 2 1 0 6 1 0 2 2 2 5 2 4 HANDLERS ranks KM KN NQ PO HQ LL NY PS SK ST WK AL CO DD LS LY MH ML MM PA PH PT RS 1 1 1 1 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 INFANTS/ Mothers ranks KG/KM 1 HZ/HQ 2 LC/LL 2 NK/NY 2 PZ/PS 2 CY/CO 3 LZ/LS 3 MQ/ML 3 MW/MH 3 MX/MM 3 PK/PH 3 0 0 4 10 2 0 5 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 3 0 2 0 1 0 0 3 0 4 1 3 2 0 1 1 0 0 3 1 3 0 1 1 0 3 2 0 | | | | | | | | | | | 1 0 1 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 3 1 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 4 0 1 0 0 5 2 2 0 7 0 2 1 5 0 3 7 1 0 | | | | | | | | | | | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 4 1 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 1 2 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 3 4 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 3 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 3 0 1 0 0 0 0 6 2 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 Table 4: Unsuccessful interactions. HANDLERS ranks KM KN NQ PO HQ LL NY PS SK ST WK AL CO DD LS LY MH ML MM PA PH PT RS 1 1 1 1 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 INFANTS/ Mothers ranks KG/KM 1 HZ/HQ 2 LC/LL 2 NK/NY 2 PZ/PS 2 CY/CO 3 LZ/LS 3 MQ/ML 3 MW/MH 3 MX/MM 3 PK/PH 3 0 7 2 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 | | | | | | | | | | | 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 3 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 1 0 1 1 1 | | | | | | | | | | | 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 2 7 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 2 2 1 0 0 3 3 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 3 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 3 1 1 1 0 1 0 2 0 4 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Table 5: Successful interactions. KM KN NQ PO 1 3 1 3 INFANTS/ Mothers ranks KG/KM 1 HZ/HQ 3 LC/LL 3 NK/NY 2 PZ/PS 2 CY/CO 2 LZ/LS 3 MQ/ML 3 MW/MH 3 MX/MM 3 PK/PH 2 0 0 4 13 23 7 4 0 1 12 4 10 1 3 4 2 2 7 1 0 3 0 1 5 3 0 7 2 3 4 2 0 6 1 5 4 5 1 3 2 2 4 5 4 HANDLERS ranks HQ LL NY PS SK ST WK 3 3 2 2 3 1 3 | | | | | | | | | | | 1 0 3 9 0 1 1 2 2 0 3 0 2 0 1 0 1 1 4 3 0 4 0 1 2 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 1 2 0 0 0 2 5 0 0 AL CO DD LS LY MH ML MM PA PH PT RS 2 2 3 3 1 3 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 1 0 | 0 0 5 6 18 | 1 6 1 5 3 | 1 0 3 11 7 | 8 6 0 0 2 | 0 2 3 12 16 | 3 0 2 0 5 | 2 2 2 4 5 | 7 5 2 8 13 | 7 14 0 5 2 | 9 3 0 15 10 | 8 5 0 3 0 3 0 2 2 2 2 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 3 0 4 2 2 3 2 9 7 0 2 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 2 0 4 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 4 0 0 6 0 9 1 5 1 1 0 4 8 1 3 0 2 0 10 0 1 3 2 0 3 0 0 0 3 1 0 0 13 2 2 0 7 Table 6: This is the original data table but with a random permutation of the infant/mother ranks and the non-mother ranks. 1 1 6 3 0 2 2 2 6 3 5 [1,] [2,] [3,] [,1] [,2] [,3] 5 1 7 85 60 119 81 117 203 Table 7: The 3-by-3 table induced by the random permutation matrix in Table 6. LTE has a value of 424 for this table. PA Pass Un Succ LTE 0.015 0.013 0.012 0.372 LT 0.038 0.071 0.119 0.017 n 678 377 189 112 ------------------------------ Table 7: Permutation test p-values for 4 data sets with the two test statistics, LTE and LT; n gives the total number of interactions in the data set. The LTE column suggests that Research Hypothesis 1 is supported for Passive and Unsuccessful interactions, but not for Successful interactions. It appears that Research Hypothesis 2 is supported only for Successful interactions. References 1. Agresti, Alan. Categorical Data Analysis, 2nd editio.. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2002. 2. Bentley-Condit, Vicki K., Thomas L. Moore, and E. O. Smith. “Infant Handling by Tana River Adult Female Yellow Baboons (Papio Cynocephalus Cynocephalu.,” American Journal of Primatology 55 (2001): 117-130. 3. Gotelli, Nicholas J. and Gary R. Graves. Null Models in Ecology. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press, 1996. 4. Lunneborg, Clifford E. “Infant Handling by Female Baboons: A Sensitivity Analysis.” STATS 31 (2001): 7-14. 5. Lunneborg, Clifford E. Data Analysis by Resampling: Concepts and Applications. Pacific Grove, CA: Duxbury (Brooks/Cole), 2000. 6. Moore, Thomas L. and Vicki Bentley-Condit. “Using Permutation Tests to Study Infant Handling by Female Baboons.” STATS 31 (2001): 7-14.