Genetics Vocabulary Worksheet for Science 9
advertisement

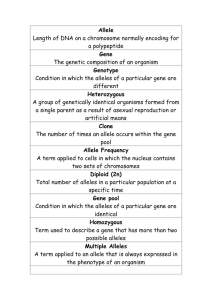
Name____________________ Science 9 Genetics Vocabulary Date:____________ Genetics Vocabulary characteristic Definition: A distinguishing quality Context: A pair of factors determines each inherited characteristic. chromosomes Definition: Rod-shaped structures contained in a cell made up of a molecule of DNA threaded around proteins Context: In females, the gene responsible for red eyes on one of the X chromosomes might be overshadowing the gene for white eyes on the other chromosome. dominant Definition: An allele that produces the same phenotype whether inherited with a homozygous (pure dominant) or heterozygous (hybrid) allele; exercising the most influence or control. Context: Certain genes are dominant and others are recessive. recessive Definition: An allele that produces a recessive trait phenotype. It can only be homozygous (pure recessive) because heterozygous (hybrid) alleles only show the dominant trait . Context: The genotype for all recessive traits is pure recessive. enzymes Definition: Any of several complex proteins produced by cells that act as catalysts in specific biochemical reactions Context: Genes direct the production of enzymes. genes Definition: Basic, functional units of heredity, each occupying a specific place on a chromosome. Genes are represented by a pair of letters. Heterozygous or Homozygous Context: In 1909 a Danish botanist coined the term “genes” to describe Mendel’s factors in inherited traits. heredity Definition: Genetic transmission of characteristics from parent to offspring Context: Fixed laws of nature govern heredity. Transcription: Definition: Copying individual DNA strands to create RNA (a genetic blueprint for a single DNA strand) Translation: Definition: Used with the ribosome the mRNA(messenger RNA) is then used to create a protein, which is the building block for most organisms. The mRNA carries specific codes each form certain types of proteins. Codon Definition: A sequence of three nucleotides in messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid (the building blocks of life for most organisms). Context: This codon sequence will produce a certain protein that will form a specific amino acid Heterozygous Definition: A genotype consisting of two different alleles for the same gene on a pair of chromosomes. The individual has received a different allele for the given gene from each parent. Homozygous Definition: A genotype consisting of two identical alleles for the same gene on a pair of chromosomes. The individual has received the same allele for the given gene from each parent. Allele Definition: One of the alternate forms of a single gene. Different traits Genotype Definition: The genetic makeup of an organism. Often used to refer to a specific genetic allele which is responsible for specific observable trait (phenotype). A set of alleles which is responsible for a particular phenotype. Phenotype Definition: An observable, measurable characteristic of an organism. The physical manifestation of the genotype as a particular trait. For example, some peas can have a phenotype of roundness while others have a phenotype of roughness. Hybrid: Definition: An offspring of two pure recessive parents, containing two different alleles, though only one may be seen in the organism. Trait: Definition: visible characteristic based on genetic make-up. Co-dominant Definition: a gene that causes the homozygous form to look different than the wild-type and the heterozygous form to have traits of both.