Citing and referencing: a practical guide
advertisement

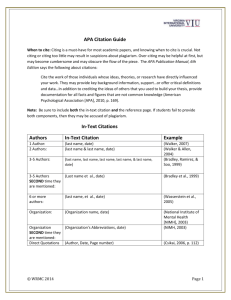
Citing and referencing: a practical guide This short guide explains how you cite some of the major types of materials you are likely to use when writing your thesis and dissertation. It is recommended that you consult one of the style guides listed in the bibliography for specific details about a particular bibliographic style. This guide is based on the Harvard method of citation (i.e.: author-date in-text citation with a reference list or bibliography) in conjunction with the American Psychological Association (APA) bibliographical style (5th edition, pp. 207- 281). a) Writing directly: Using the author’s name explicitly : Citing a book In-text: Ref. list: Travel writer Bill Bryson (1995, p.12) says that “London is a great place.” Bryson, B. (1995). Notes from a small island. London: Black Swan. b) Writing indirectly: Not including the author’s name : Citing a book In-text: A leading travel writer has recently praised London. (Bryson, 1995). In-text (specific part/quote): A leading travel writer has recently called London “a great place” (Bryson, 1995, p.12) Ref. list.: Bryson, B. (1995). Notes from a small island. London: Black Swan. Citing an edited book In-text: Ref. list: (Garafalo, 1992) Garafalo, R. (Ed.). (1992). Rockin' the boat: mass music and mass movements. Boston: South End Press. Citing a book with two authors (and a translator + editor) In-text: Ref. list: (Marx and Engels, 1965) Marx, K., & Engels, F. (1965), The Communist manifesto (S. Moore, Trans.; J. Katz, Ed.). New York: Washington Square Press (Original work published 1848). Citing a chapter from a book In-text: (Ullestad, 1992) In-text (specific part/quote): (Ullestad, 1992, p.31) Ref. list: Ullestad, N. (1992). Diverse rock rebellions subvert mass media hegemony. In R. Garofalo (Ed.). Rockin' the boat: mass music and mass movements (pp.23-45). Boston: South End Press. Citing a journal article In-text: Ref. list: (Patton, 1997) Patton, M. (1997). Evaluation as a tool. Journal of Social Science, 18 (3), 345-356. Citing a newspaper article In-text: Ref. list: (Smith, 2003, p.16) Smith, T. (2003, June 23). University tuition fees: the debate. The Guardian. p.16. Citing a conference paper In-text: Ref. list: (Secker, 2005) Secker, J. (2005). Current Issues in Information Literacy: are we making all the wrong assumptions? In A. Martin (Ed.). Proceedings of the 4th eLiteracy Conference, June 15-17, 2005 (pp.23-25) Glasgow, Scotland. University of Strathclyde. Citing a website (& corporate author) In-text: First citation (The London School of Economics and Political Science [LSE], 2005, para.12) In-text: Later citations (LSE, 2005, para.12) Ref. list: The London School of Economics and Political Science. The Identity Card Bill debate: what model might work? Retrieved 9 June, 2005, from http://www.lse.ac.uk/collections/pressAndInformationOffice/newsAndEvents/ archives/2005/ID_Card_update.htm add page or chapter number if available on the web site. see: http://www.apastyle.org/manual/related/electronic-sources.pdf for more examples of electronic references using APA. Citing a thesis In-text: Ref. list: and (Secker, 1999) Secker, J. (1999). Newspapers and historical research: a study of historians custodians in Wales. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University of Wales, Aberystwyth. Citing a research report In-text: Ref. list: (Mullineux, 1997) Mullineux, N. (1997). The world tyre industry: a new perspective to 2005. (Research Report 348). London: Economist Intelligence Unit. Citing Legislation (refer to the OSCOLA or Bluebook guides): Ref. list: For older acts: Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1987 Crown Debts Act 1801 (14 Geo 3 c 90) Citing indirect sources (author A cites author B) See the University of Manitoba examples for APA, MLA and Chicago here: http://www.umanitoba.ca/student/u1/lac/media/Citing-Secondary-or-Indirect-Sources-07.pdf Parliamentary Papers When citing parliamentary papers include the following information: Abbreviation of the House – HC or HL Paper number Date of Parliamentary Session – in brackets For example: Report from the Select Committee on Citations HC (1990-91) 7 Law reports and cases The correct referencing method for Case Reports is commonly referred to as ‘accepted legal citation’. This is not part of the Harvard system but it is the preferred method used by the legal profession. Cases, therefore, are usually cited in this way: Names of the parties (plaintiff and defendant) – underlined, in bold, or in italics and followed by a full stop Year the case was reported – in square brackets Number of the volume in which it was reported Name of the series of law reports (in abbreviated form) Page number at which the report starts For example: In-text: (Smith v. Smith, 1988) Ref. list: Smith v. Smith [1988] 5 All E.R. 3 Films, sound recordings and off-air broadcasts Spielberg, S. (Director). (1981). Raiders of the Lost Ark. [Motion picture]. New York: Warner. Panorama. (2003, June 23). Global warming: the inside story. [Television broadcast]. London: BBC . [video: VHS]. Children, language and literature. (1982). [Sound recording : audiocassette]. Milton Keynes, Open University Press. Example of order of references in list (= alphabetical, letter- by- letter): Alleyne, R.L. (2001) … Alleyne, R.L., & Evans, A.J. (1999) … Baheti, J.R. (2001a) … Baheti, J.R. (2001b) … Cabading, J.R., & Wright, K. (2000) … Cabading, J.R., & Wright, K. (2001) … Garofalo, R. (1992). …. Garofalo, R. (Ed.). (1988). …. The London School of Economics and Political Science. (2005). … Mathur, A.L., & Wallston, J. (1999) … Mathur, S.E., & Ahlers, R.J. (1998) … Panorama, (2003). … February 2010. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.5 License.