Midterm review
advertisement

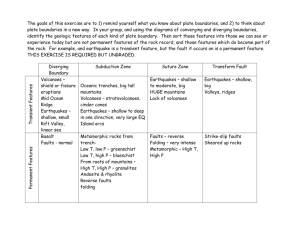
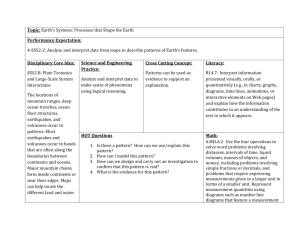
GEOG 3251 SUMMER 2010, TERM B MID-TERM REVIEW Topics to review: Importance of the mountains o Why do we care about mountains? Historical attitudes toward mountains (pre-historic to modern) Definitions of mountains o Be prepared to list criteria for defining mountains (general) vs high mountains (alpine) environments Sacred mountains: o What makes some mountains sacred o Ways to worship in different cultures o Examples of some sacred mountains o Be prepared to link the sacredness of the mountains to plate tectonics, volcanism and earthquakes in various places discussed later in class Plate tectonics: o Be able to describe the theory of plate tectonics, starting with the structure of the Earth; provide clues for this theory; continental drift theory. o Compare and contrast oceanic vs. continental crust in terms of chemical composition (felsic/basaltic vs mafic/andesitic), thickness, etc.. o Be able to explain why we find fossils on Mt. Everest o Know names and location of the plates discussed in class (N. American, S American, Juan de Fuca, Faralon, Eurasian, Indian, Nazca) and know which mountain orogenies they are involved in o Be able to define mountain orogeny in general o Define subduction zone and be able to draw a generic mountain formed at the subduction zone (incl. the crusts) o Define magma, subduction, trenches o Be able to summarize the Laramide orogeny o Know the types of plate boundaries, and the landforms associated with each (eg. cordillera mountains, hot spot volcanoes, volcanic arcs, complex mountains etc..) o Explain what a hot spot is o Examples of each landform associated with each type of plate boundary o 4 Major processes involved in mountain formation o Define/identify faults (different types – normal, low angle, high angle reverse, transform), folds; mountain ranges associated with each of these Rocks: o Know the three main rock categories, and most typical rocks discussed in class o Know what rock formations we find in the Flatirons Volcanoes o Two types of volcanoes (shield vs composite), their composition and eruption, examples of each; o Know why hot spot volcanoes differ in composition than volcanic arcs o Be able to label elements of a composite volcano Earthquakes o Where they occur, and why o Know the three types of waves associated with earthquakes o Why earthquakes are destructive Mass movement types o Rock slides o Creep o Lahars o Landslides Huascaran disaster: be able to explain the 1970 Huascaran disaster using plate tectonics, glaciers, earthquake, landslide, human elements Human sacrifice in the Andes: o What was human sacrifice and why it was performed o How were high altitudes sites chosen o Who were the Incas? o Be able to relate Inca activity in the mountains with plate tectonics, volcanism and earthquakes