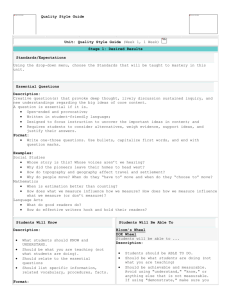
Zoologist Notes: Animals: Bald Eagle: carnivore Badger: carnivore
advertisement

Zoologist Notes: Animals: Bald Eagle: carnivore Badger: carnivore Bobcat: carnivore Coyote: omnivore Prairie Dog: omnivore Swift Fox: omnivore Blue Planet Buffalo: herbivore Antelope: herbivore Mice: herbivore Kids do ecology Outdoor Nebraska Worm: decomposer Outdoor Nebraska Australia - dingo, emu, kangaroo, wallaby, wombat, and many other animals. Many non-native animals have been introduced, including the camel, donkey, goat, horse, rabbit, and sheep. North America - American toad, badger, black-footed ferret, bison, black-tailed jack rabbit, bumble bee, burrowing owl, California condor, carrion beetle, common snipe, coyote, deer, dragonfly, eagles, eastern cottontail, elk, ferruginous hawk, fox snake, golden owl, gopher snake, grasshopper, gray wolf, ground squirrels, killdeer, lady beetle, larks, long-billled curlew, meadow vole, monarch butterfly, northern grasshopper mouse, prairie chicken, prairie dog, prairie rattlesnake, prairie skink, pronghorn antelope, red fox, red-tailed hawk, shrew, skunk, stink bug, tiger beetle, western meadowlark, western tiger swallowtail, white-tailed jack rabbit, and many other animals. South America - armadillo, opossum, fox, jaguar, llama, puma, rhea, tapir, many rodents, and many other animals. Eurasia - golden pheasant, leopard gecko, snow leopard, vole, and many other animals. Enchanted learning Biotic Factores that effect animals: Biotic: living like plants A large variety of grasses growing in prairies encourages grass eating animals like antelope. All grasslands share a lack of shelter from predators, and an abundance of grass for food; therefore, grassland animal populations are similar throughout the world. The dominant vertebrates in grasslands are herbivorous or plant-eating grazers called ungulates. Ungulates are mammals with hoofs, like horses and deer. Their long legs help them run fast to escape grassland predators. The temperate grassland does not have much animal diversity, especially compared to the Savannah. Some animals that inhabit temperate grasslands in North America are bison, antelope, birds, gophers, prairie dogs, coyotes, and insects. On the steppes you’ll find similar animals to the Great Plains including lynx, antelopes, falcons, and fox. Kids do ecology Abiotic: Landscape: The grasslands are large and open with lots of grass. The animals that live there like antelope can run quickly with their long legs and hooves. This is because the prairie is large and open, meaning fast running predators as well. Climate: The white tailed jackrabbit, which lives in the prairie, turns white in winter Adaptations: The dominant vertebrates in grasslands are herbivorous or plant-eating grazers called ungulates. Ungulates are mammals with hoofs, like horses and deer. Their long legs help them run fast to escape grassland predators. The prairies have seasons whcih include cold and snowy winters. Because of this, bison and buffalo have thick, furry, well insulated coats. National Geographic The swift fox is much faster and smaller that other foxes for a few reasons. This will help them catch their fast running prey, running across the open prairie, and run from thier predators which include the eagle and coyote. The swift fox has large ears. This could be for the fact that thier main prey is prairie dogs, and they will need to hear them both about in the grass and in their burrows. Blue Planet Biomes Kids do ecology The grasslands are large and open areas, meaning they are good for fast running animals.