Hydrologic Analysis and Statistical Methods
Course Title
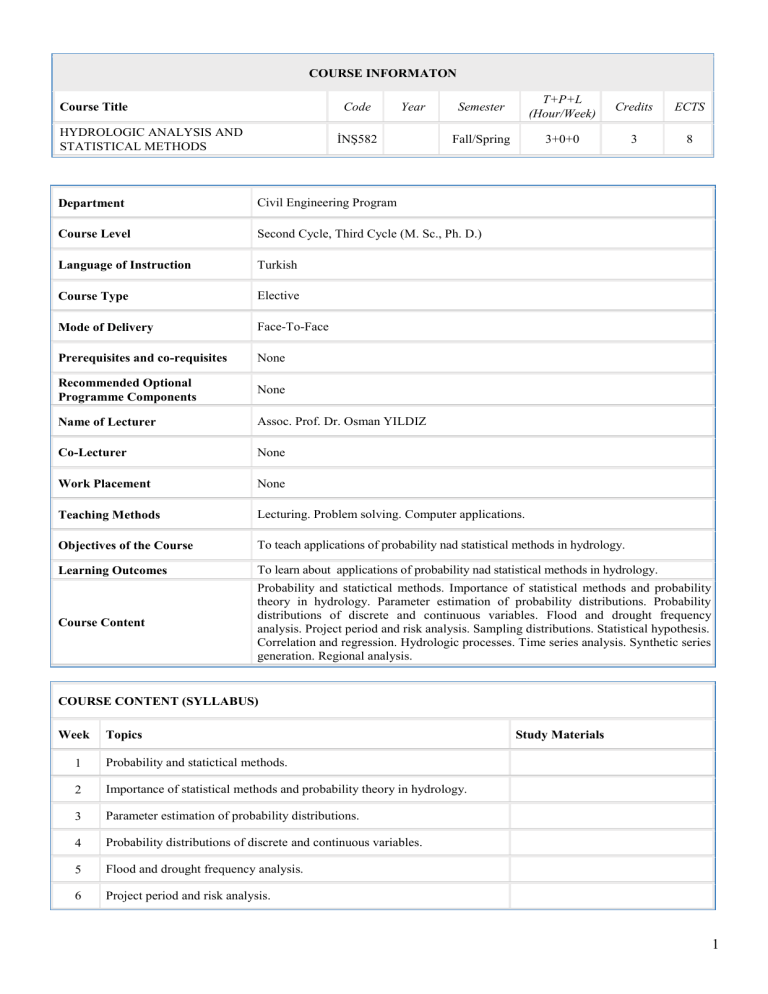
HYDROLOGIC ANALYSIS AND
STATISTICAL METHODS
Department
COURSE INFORMATON
Code
İNŞ582
Civil Engineering Program
Year Semester
Fall/Spring
T+P+L
(Hour/Week)
Credits ECTS
3+0+0 3 8
Course Level
Language of Instruction
Second Cycle, Third Cycle (M. Sc., Ph. D.)
Turkish
Course Type
Mode of Delivery
Elective
Face-To-Face
None Prerequisites and co-requisites
Recommended Optional
Programme Components
Name of Lecturer
Co-Lecturer
Work Placement
Teaching Methods
Objectives of the Course
Learning Outcomes
Course Content
None
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Osman YILDIZ
None
None
Lecturing. Problem solving. Computer applications.
To teach applications of probability nad statistical methods in hydrology.
To learn about applications of probability nad statistical methods in hydrology.
Probability and statictical methods. Importance of statistical methods and probability theory in hydrology. Parameter estimation of probability distributions. Probability distributions of discrete and continuous variables. Flood and drought frequency analysis. Project period and risk analysis. Sampling distributions. Statistical hypothesis.
Correlation and regression. Hydrologic processes. Time series analysis. Synthetic series generation. Regional analysis.
COURSE CONTENT (SYLLABUS)
Week Topics
1 Probability and statictical methods.
2 Importance of statistical methods and probability theory in hydrology.
3 Parameter estimation of probability distributions.
4 Probability distributions of discrete and continuous variables.
5 Flood and drought frequency analysis.
6 Project period and risk analysis.
Study Materials
1
7 MİDTERM EXAM
8 Sampling distributins.
9
Statistical hypothesis.
10
Correlation and regression.
11
Hydrologic processes.
12
Time series analysis.
13
Synthetic series generation.
14
Regional analysis.
RECOMMENDED SOURCES
Textbook
Additional Resources
Mühendisler İçin İstatistik, Bayazıt, M., Birsen Yayınevi.
Hydrology For Engineers, Linsley, R.K.
, McGraw-Hill ,1982.
Engineering hydrology,Usul, N., Metu Press , 2005.
Hidroloji, Bayazıt, M. İTÜ Yayınları, 1991.
Statistical Methods In Hydrology, Haan, C.T., Iowa State Press, 2002.
MATERIAL SHARING
Documents
Assignments
Exams
8 homeworks.
Midterm, Final.
ASSESSMENT
EXAMS
Contribution of Midterm Examination to Overall Grade
Contribution of Final Examination to Overall Grade
TOTAL
QUANTITY
1
1
2
PERCENTAGE
30
70
100
COURSE'S CONTRIBUTION TO PROGRAMME
1
2
3
Contribution
Nr. Programme Learning Outcomes
1 2 3 4 5
To gain the ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering to civil engineering problems.
To be able to identify, model and solve civil engineering problems in consideration with safety, economy, aesthetics and environmental factors.
To get familiar with modern techniques and computation methods in civil engineering.
X
X
X
4
To learn measurement and evaluation methods and techniques in civil engineering.
X
2
5
To gain the responsibility for work and labor safety in all civil engineering applications.
10
To take initiative and responsibility, to work independently, and to innovate.
6
To be able to identify, analyze, and synthesize civil engineering problems and applications.
X
7
To have enough knowledge about construction materials.
X
8
To be able to conduct laboratory and site experiments, to evaluate, and to interpret experimental data. X
9
To be able to work together with other people, to adapt teamwork.
X
11
To gain the ability for effective written and oral communication in Turkish and English.
12
To recognize the need for, and to gain the ability to engage in life-long learning.
X
ECTS ALLOCATED BASED ON STUDENT WORKLOAD BY THE COURSE DESCRIPTION
Activities
Course Duration (Including the exam week: 16x Total course hours)
Hours for off-the-classroom study (Pre-study, practice)
Quantity
16
16
Duration
(Hour)
3
3
Assignments
Presentation / Preparing Seminar
Mid-term
Final examination
8
4
1
1
6
12
24
24
Total Work Load
Total Work Load / 30 (h)
ECTS Credit of the Course
Total Workload
(Hour)
48
48
48
48
24
24
240
8
8
3