Comparison info
advertisement
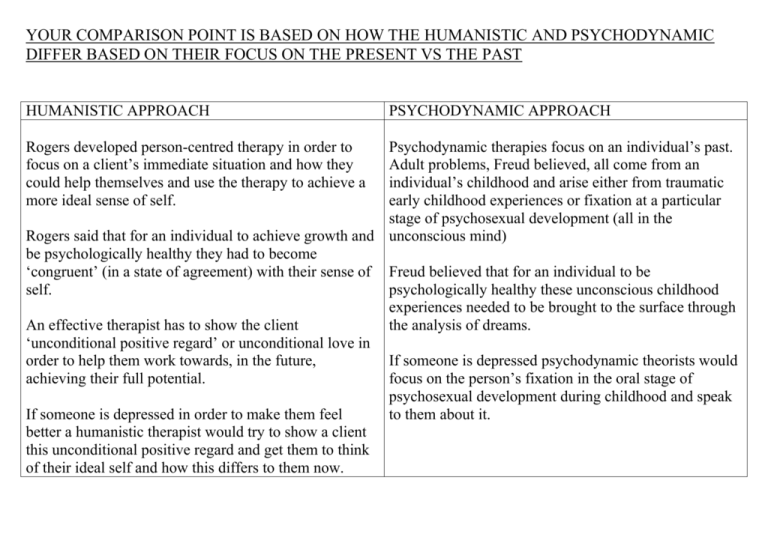
YOUR COMPARISON POINT IS BASED ON HOW THE HUMANISTIC AND PSYCHODYNAMIC DIFFER BASED ON THEIR FOCUS ON THE PRESENT VS THE PAST HUMANISTIC APPROACH PSYCHODYNAMIC APPROACH Psychodynamic therapies focus on an individual’s past. Adult problems, Freud believed, all come from an individual’s childhood and arise either from traumatic early childhood experiences or fixation at a particular stage of psychosexual development (all in the Rogers said that for an individual to achieve growth and unconscious mind) be psychologically healthy they had to become ‘congruent’ (in a state of agreement) with their sense of Freud believed that for an individual to be self. psychologically healthy these unconscious childhood experiences needed to be brought to the surface through An effective therapist has to show the client the analysis of dreams. ‘unconditional positive regard’ or unconditional love in order to help them work towards, in the future, If someone is depressed psychodynamic theorists would achieving their full potential. focus on the person’s fixation in the oral stage of psychosexual development during childhood and speak If someone is depressed in order to make them feel to them about it. better a humanistic therapist would try to show a client this unconditional positive regard and get them to think of their ideal self and how this differs to them now. Rogers developed person-centred therapy in order to focus on a client’s immediate situation and how they could help themselves and use the therapy to achieve a more ideal sense of self. YOUR COMPARISON POINT IS BASED ON HOW THE HUMANISTIC AND PSYCHODYNAMIC DIFFER BASED ON THEIR FOCUS ON THE CONSCIOUS OR UNCONSCIOUS MIND HUMANISTIC APPROACH Humanism studies the conscious mind and how our thoughts influence our behaviour. PSYCHODYNAMIC APPROACH The psychodynamic approach mainly focuses on the unconscious mind and how this influences our behaviour. Humanism focuses on the fact that human beings are intentional, this means that they seek meaning, value The psychodynamic approach believes that the and creativity. majority of our behaviour is determined by things which we are unaware of e.g. repressed childhood Rogers believed that an individual is capable of experiences in our unconscious mind, our fixations thinking about their sense of self and how that could through the psychosexual development. change in the future to be more like their ‘ideal’ self. Freud believed that an individual is incapable of Rogers said that individuals are aware of and able to accessing these unconscious thoughts without speak about the lack of positive regard that they therapy. We are unaware of what is in our received from mothers as children. If people were unconscious mind and how it influences our brought up under ‘conditions of worth’ then they behaviour as adults e.g. we don’t know if some may not feel worthy as an adult. traumatic event in our unconscious mind influences our behaviour because we cannot access it. YOUR COMPARISON POINT IS BASED ON HOW THE HUMANISTIC AND PSYCHODYNAMIC DIFFER BASED ON THE IDEA OF INTERNAL DRIVES HUMANISTIC APPROACH Humanistic psychologists believe that we have an innate (built-in) drive to reach self-actualisation. Self actualisation is the motive to achieve one’s potential and it occurs once an individual has met all of their deficiency needs (these are the lower levels in the hierarchy – esteem, love, safety and physiological needs). Self-actualisation is at the top of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Maslow said that progression through the hierarchy depended on an individual’s situation. For example, if an individual had reached self-actualisation but then lost their job so that one of the deficiency needs was unsatisfied e.g. physiological because they couldn’t afford food they would move back down the hierarchy. PSYCHODYNAMIC APPROACH Psychodynamic psychologists believe that we have an innate (built-in) drive to progress through the psychosexual stages of development. The psychosexual stages of development represent the different stages an individual gets pleasure from at the different stages of their childhood. E.g. the oral stage is where an individual gains pleasure from between 0-18 months of age. Freud said that progression through the stages depends on how much pleasure an individual receives at a stage. Too much or too little pleasure results in fixation (this is where part of the person’s personality remains at this stage) which can have an effect on personality. For example, fixation at the anal stage of development may lead to an individual who is very tidy. YOUR COMPARISON POINT IS BASED ON HOW THE HUMANISTIC AND PSYCHODYNAMIC DIFFER BASED ON THE APPROACH THEY TAKE TO THERAPY HUMANISTIC APPROACH Humanistic therapy is described as being ‘person centred’. PSYCHODYNAMIC APPROACH Psychodynamic therapy is described as being ‘directive’. Rogers believed that the therapist should develop a personal relationship with the client in order to help them to improve. The therapist encourages the client to discuss their inner feelings and perceptions. Psychodynamic theorists believe that the therapists main role was to uncover unconscious childhood trauma, breaking through defence mechanisms to force the person to confront the contents of their unconscious mind. Rather than suggesting how the client might wish to change the therapist becomes a ‘mirror’ listening and reflecting back a client’s thoughts and feelings. This way the client has free will to decide what changes they would like in order for them to achieve personal growth. Psychodynamic theorists believe that in order to achieve psychological health, the contents of the unconscious mind must be experienced consciously so that the individual can go through the traumatic experiences again and begin to resolve any conflicts they have with the therapist. EXTENSION – A2 level evaluation A comparison can be drawn between the psychodynamic and humanistic approach based on the debate of free will and determinism. Below is some information on free will and determinism. Can you produce an exemplified evaluative point about how the approaches differ on their stances to this debate? Free will Determinism People have the ability to choose their own course of action, Behaviour is determined by external events or stimuli or by to determine their own lives - we have the freedom to choose internal events such as hormones or unconscious drives our behaviour. People are passive responders - therefore we do not have People have responsibility for their actions - they are the freedom to choose cause of what they do Behaviour occurs in a regular, orderly manner which is totally predictable (in principle) EXTENSION (II) A2 level evaluation A comparison can be drawn between the humanistic approach and psychodynamic approach in terms of their stance on the holism and reductionist debate. The humanistic approach is clearly holistic. You need to assess in an exemplified A02 point the extent to which the psychodynamic approach is reductionist. Reductionism Behaviour can be reduced to minute units of analysis such as stimulus-response connections, neuron activity, muscle movements and any larger units of analysis are pointless. Explanations of complex wholes in terms of the units of which those “wholes” are composed are the only explanations that are worthwhile Holism Thorough knowledge of organisms cannot be gained through knowledge of nerve activity and muscle movement or through knowledge of stimulus-response connections. There is a hierarchy of levels of explanation, from the sociological to the psychological down, eventually, to the physical and chemical. No one level can account for the whole of behaviour and all levels are needed for a complete explanation A human cannot be reduced to stimulus-response connections. The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. HELPSHEET This sheet will help you to start off your perfect evaluation point! A similarity / difference is…… This is because…. (explain both humanism and psychodynamic) For example… (give an example for both humanism and psychodynamic) HELPSHEET This sheet will help you to start off your perfect evaluation point! A similarity / difference is…… This is because…. (explain both humanism and psychodynamic) For example… (give an example for both humanism and psychodynamic) HELPSHEET This sheet will help you to start off your perfect evaluation point! A similarity / difference is…… This is because…. (explain both humanism and psychodynamic) For example… (give an example for both humanism and psychodynamic)








