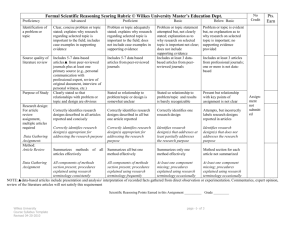
Science Kindergarten SC K 050 Given a particular classification of
advertisement

Science Kindergarten SC K 050 and Given a particular classification of animals such as farm, pet, zoo, jungle, reptile, each student names three animals belonging to the group. SC K 060 Given a stimulus picture or real object, each student classifies the animals that are common to the seashore or not common to the seashore. SC K 061 and In his own words, each student names the three components of the earth practice good stewardship in caring for the environment. SC K 240 Given a shell, each student verbally describes how the shell functions as a home and protection for an animal. SC K 241 bears Given appropriate materials, each student chooses one of the types of studied and creates a den representing its habitat. SC K 260 Orally, each student describes two ways insects are helpful and two ways that insects are harmful to man. SC K 261 Given project materials, each student creates a representation of metamorphosis. SC K 270 Given a model or a picture of a spider, each student verbally describes two characteristics of the spider's body and habits. SC K 335 From memory, each student describes three characteristics of dinosaurs. SC K 400 Given an oral stimulus, each student correctly identifies the corresponding body parts to include hands, arms, legs, hips, elbows, heart, stomach, lungs, head, neck, and feet. SC K 411 Given a stimulus item, each student uses the appropriate sense to identify the item and states which senses were used in the process. SC K 450 Given the name of a sense organ, each student describes the safety precautions necessary to maintain good health. SC K 600 Through experimentation, each student identifies three objects that float and three objects that sink. SC K 610 Given magnets and various items to manipulate, each student verbally identifies three items a magnet will pick up and three items a magnet will not pick up. SC K 800 Given a season, each student describes three common weather conditions, describe three environmental changes, and choose appropriate clothing. Revised 7/2003 Science First Grade SC 01 052 When given pictures of living and non-living organisms, each student classifies the pictures into the two categories. SC 01 131 Given different seeds, each student identifies the association of the seed to the plant it will become and identifies the stages of development from seed to root, stem, and leaf. SC 01 355 Given a picture of a hibernating animal, each student verbally presents an explanation of hibernation. SC 01 412 From memory, each student identifies the five senses and matches the senses to the corresponding body part. SC 01 451 Given a variety of pictures of different situations, the student differentiates between correct and incorrect manners and etiquette. SC 01 454 Given a teacher-directed simulation, each student demonstrates an application of the concept of height and weight. SC 01 620 Given a group of pictures of household items, each student correctly classifies the items as electrical or non-electrical. SC 01 801 Given the descriptive data, each student produces a chart representing the various types of weather. SC 01 860 In his own words, each student identifies where rocks are found and how people use rocks. SC 01 870 Given pictures of different water forms, each student correctly identifies two forms of water (liquid and solid) and verbalizes the importance of water to our bodies. Revised – 7/2003 Science Second Grade SC 02 010 When given a picture of a fossil or the actual fossil, each student explains how fossils help people learn about the past. SC 02 109 Given a picture of a plant, each student correctly labels the flower, leaf, stem, and roots. SC 02 262 Given a picture of an insect, each student identifies the insect’s head, thorax, and abdomen. SC 02 336 the As a homework assignment, each student constructs a diorama showing natural habitat of a specific dinosaur. SC 02 337 Using a Biblical foundation, each student explains the reasons why dinosaurs are extinct. SC 02 413 When given a diagram of the ear, each student labels the parts of the outer ear, inner ear, and middle ear. SC 02 460 Using pictures of foods, each student constructs a model of the Food Guide Pyramid and classifies each item correctly. SC 02 461 In his own words, each student describes his conceptualization of why people need different kinds of food to stay healthy and that God expects us to take care of our bodies. SC 02 470 When given a model or shown a picture of a tooth, each student identifies the three major parts (enamel, gum, & root) and demonstrates the proper care of teeth. SC 02 610 When given 10 objects, each student classifies each object according to whether it is or is not attracted to a magnet. SC 02 611 When given a magnet, each student identifies the position of the pole, describes the function of the poles, and describes the relationship between similar and opposite poles. SC 02 613 and When given the appropriate materials, each student generates a magnet summarizes the applications of magnets in the home and in the industry. SC 02 630 Given several different sets of sounds, each student differentiates between high and low pitch, and between loud and soft tones. SC 02 631 When generating sound with an object, each student states in his own words the cause and effect relationship of sound production. SC 02 640 When given a source of light and an opaque item, each student explains how shadows are made and associates each shadow with its corresponding source. SC 02 641 When given a set of ten icons of light each student classifies each as an artificial or a natural source of light. SC 02 642 Given icons of shadows and a choice of sources, each student associates each shadow with its corresponding source. SC 02 643 When given an object to cause a shadow, each student manipulates the object to change the size and shape of the shadow to demonstrate the relationship between the sun's position and the object forming the shadow. SC 02 650 When given an iconic representation or a thermometer, each student reads the thermometer and interprets the given temperature. SC 02 651 In his own words, each student explains that heat is a form of energy that moves from one place to another. SC 02 652 Given a type of heat, each student identifies and describes the different sources of heat. SC 02 910 Given the name of the celestial body, each student classifies the body as a star, a moon, or a planet and describes the attributes of each classification. Revised 7/2003 Science Third Grade SC 03 001 Given an icon, each student correctly matches the numbers of the days of creation with the things created on the corresponding day. SC 03 002 In a group setting, each student recites Psalm 139:14 and Genesis 1:25 SC 03 051 Given an appropriate set of questions, each student lists two major classifications of animals. SC 03 052 Using size, food storage, extinction, and unusual functions or habits as attribute markers, each student states the major characteristics of eight animal classifications and classifies animal icons correctly. SC 03 062 Given a set of choices, each student identifies bathing, washing and combing hair, using deodorant, cleaning ears and nails as elements of personal hygiene. SC 03 063 In a group setting, each student describes the word community as it relates to life in a given environment. SC 03 100 Upon request, each student accurately lists the four basic needs of plants as water, soil, sunlight, and oxygen. SC 03 101 Given a list of plants, each student accurately classifies each as edible or non-edible. SC 03 110 In his own words, each student accurately describes the function of each of the root, stem, leaf, and flower. SC 03 355 In his own words, each student accurately defines environment, hibernation, and migration. SC 03 410 In a group setting and in a testing format, each student recognizes eight of the nine body systems, describes the function of each, and orally describes how to care for and protect each major body system. SC 03 412 Given diagrams of body organs, each student correctly labels each and explains three of the five senses our bodies use. SC 03 450 In his own words, each student properly explains the importance of personal hygiene. SC 03 500 Upon request, each student defines the states of matter. SC 03 510 In his own words, each student correctly identifies matter as being all things and identifies the smallest part of matter as the molecule. SC 03 621 When given a concrete example of static electricity, each student correctly describes how static electricity is produced. SC 03 622 an Given a series of pictures, each student correctly identifies a conductor, insulator, and a set of safety precautions. SC 03 623 Given the need to reduce electricity consumption, each student describes how individuals can conserve electricity. SC 03 802 Given the verse Nahum 1:3, each student recites the verse and applies its meaning to describe the Biblical view of God's creation of the weather. SC 03 803 Orally, each student defines "weather" and lists the main elements of weather as heat, water, and wind. SC 03 810 From memory, each student recalls three kinds of storms and which weather condition creates each. SC 03 830 Given a diagram, each student labels the stages of the water cycle and explains the function of each stage. SC 03 903 Given an accurate drawing of the food chain, each student describes how plants and animals are dependent upon each other. Science Fourth Grade SC 04 011 Upon request, each student explains how fossils are made and how they can be located in unusual places due to the Great Flood described in the Genesis account. SC 04 261 Upon request each student lists the stages of development of insects in both complete and incomplete metamorphosis and the criteria for determining what characteristics are common to all insects. SC 04 262 When given a stimulus list of insects, the student identifies each social insect and explains why it is classified as such. SC 04 632 Upon request, each student demonstrates how vibrations produce sounds and how changes in the vibrations affect pitch and volume. SC 04 633 Upon request, each student names materials which affect the way sounds are absorbed and reflected. SC 04 644 Upon request, the student explains how color and texture of a material can either reflect or absorb light. SC 04 645 When given a set of stimulus objects for experimentation, each student categorizes each as either transparent, translucent, or opaque. SC 04 646 When given a prism, the student demonstrates how each of the colors of the spectrum is found in white light. SC 04 660 When given a simple machine, each student demonstrates how it makes work easier. SC 04 661 When given a set of common household tools, each student identifies which simple machine(s) each applies. SC 04 861 When given a stimulus set of rocks, the student classifies each as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic rock. SC 04 862 Upon request, each student recalls the composition of igneous rocks and explains why the crystals in the rocks vary in size. SC 04 872 Upon request, the student explains how water acts as a constructive force in the creation of deltas and as an erosive force. SC 04 920 When given a depiction of the solar system, each student correctly labels the nine planets in order. SC 04 930 Upon request, each student explains how the moon reflects light from the sun rather than producing its own light, causing the different phases. Revised 2003 Approved _______ Science Fifth Grade SC 05 110 Given a diagram of the structure of a flowering seed plant, each student identifies and describes the function of each part. SC 05 132 Given a diagram of the parts of a monocot and a dicot seed, each student identifies the seed type, labels its parts, and describes the function of each part. SC 05 150 Given a list of plants, each student classifies each as green or non-green. SC 05 410 Given a diagram of the human body, each student identifies each of the nine systems and summarizes the function and inter-relatedness of each. SC 05 455 Given a solid foundation of knowledge from a Christian viewpoint, each student applies Biblical principles to science concepts, articulates the relationships, and transfers the precepts to decisions which are made in conjunction with the changes of adolescence. SC 05 501 Given diagrams showing the molecular motion and position in a solid, a liquid, and a gas, each student identifies which diagram depicts each of the three states of matter. SC 05 670 Given an essay question, each student defines the Law of Conservation of Energy and gives an example illustrating that law. SC 05 671 Given a variety of examples showing mechanical, heat, chemical, and nuclear energy, each student classifies the examples according to the type(s) of energy being used. SC 05 820 After building weather instruments and using these instruments to observe and record weather changes, each student predicts the direction and speed of the wind, humidity, precipitation, and air pressure. SC 05 821 Given a weather map, each student interprets symbols for cold, warm, and stationary fronts, and explains the direction each air mass is moving. Science Sixth Grade SC 06 511 Given a diagram of an atom, each student labels it correctly. SC 06 520 Given a periodic chart with symbols, each student correctly identifies at least fifteen of the elements, identifies the atomic number and mass of each element, and defines the meaning of each descriptor used to classify each element. SC 06 647 Given a diagram of a sound wave, each student correctly defines a wave; identifies the crest and trough; and explains the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and pitch. SC 06 Given a diagram of a light wave, each student correctly replicates the wave pattern for reflection,refraction, and dispersion. SC 06 662 From memory, each student defines "work", gives an example of work, and describes an example of an activity that is not work by scientific definition. SC 06 663 Given pictures of several simple machines, each student correctly classifies the machines by type. SC 06 664 Given the formula for work, mechanical advantage, and horsepower, each student identifies each and accurately applies the formula for each in a problem solving situation. SC 06 672 Given the six kinds of energy, each student defines and describes each type. SC 06 804 After a study of God's structure for the earth's atmosphere, each student describes the "greenhouse effect" and its theoretical impact on life on earth. SC 06 850 Given a diagram of the earth, each student names the four layers of the earth correctly. SC 06 863 In his own words, each student correctly explains that many varied kinds of gems and metals are found in the earth and cites three examples of each. SC 06 864 In his own words, each student identifies coal and petroleum as two important fuels mined or taken from the earth and describes two basic mining processes. SC 06 880 In his own words, each student correctly describes a volcano and labels the parts of the formation. SC 06 881 Given pictures and descriptions of volcanoes, each student correctly classifies each in terms of formation, activity, and type of eruption. SC 06 900 Using shape as criterion, each student identifies the name of the galaxy in which we live, classifies it, and describes the three basic types of galaxies, SC 06 901 In his own words, each student identifies and defines astronomy, astronautics, geology, chemistry, and physics. SC 06 910 From memory, each student compares and contrasts the apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude of stars. SC 06 911 Given a picture of the constellations, each student correctly identifies each of the following; Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, Cassiopeia, Orion, and Scorpius. SC 06 921 From memory, each student correctly lists the planets in order from the sun outward. SC 06 922 Given a set of three characteristics of each planet, each student correctly identifies the planet being described. SC 06 923 In his own words, each student compares and contrasts comets, meteoroids, and asteroids using elements of the definition of each. SC 06 931 Given pictures of the phases of the moon, each student labels each phase correctly. SC 06 950 Given a list of names and a list of accomplishments, each student matches scientists and astronauts with the corresponding accomplishment. SC 06 951 Given a set of descriptions of satellites and types of satellites, each student correctly matches the satellite with what each does. Science Seventh Grade SC 07 003 After a study of Biblical creation, each student lists and explains the seven creationistic theories or models and gives the rationale for each theory's existence. SC 07 020 When given an experiment to do or to watch, each student lists in order the steps of the scientific method and describes what takes place in each step. SC 07 021 When given a series of true statements, each student classifies and labels each statement as historical fact, scientific fact, universal statement, or value judgement. SC 07 053 After a study of the modern classification system each student lists in order the seven levels of the system, lists and describes the five kingdoms, and gives examples of the organisms that belong in each of the kingdoms. SC 07 054 Given the set of common characteristics, each student classifies a group of organisms according to the kingdom and compares the characteristics of some common animals within the group. SC 07 064 In his own words, each student explains the carbon-oxygen cycle and the water cycle using a self-generated illustration. SC 07 065 Given a set of ecosystems, each student defines ecology, describes each ecosystem, and lists the two main components of each ecosystem. SC 07 066 In an essay format, each student identifies and describes each of the following relationships: independent, social, competition, commensalism, mutualism, and parasite-host. SC 07 067 In his own words, each student compares and contrasts camouflage, warning coloration, and mimicry. SC 07 068 Given the order of dominance, each student explains the sequence of a food chain model. SC 07 069 Given a list of major biomes and a descriptions of the relationships between organisms, each student analyzes a data chart to predict probable habitat locations of different animals and explains the animals adaptation to the environment. SC 07 102 Using observation skills in an experimental format, each student explains transpiration, translocation, and photosynthesis. SC 07 103 After a study of the reactions of organisms, each student differentiates between positive and negative tropisms (phototropism, geotropism, photoperiodism) in plants. SC 07 104 Given a simulation of plant growth, each student determines which factor must be varied in order to reach a conclusion. SC 07 111 Given a stimulus of a flower, each student describes the process of cell division, sexual and asexual reproduction, pollination, and fertilization. SC 07 112 In his own words, each student determines and explains the relationships between pollinators and the different kinds of flowers produced. SC 07 200 Given a listing of a jellyfish, an earthworm, an octopus, a clam, or a starfish each student describes the body covering, the method of support, and the forms of movement of each organism. SC 07 201 When given a listing of planarian, a grasshopper, an earthworm, and a plant as a stimulus, each student defines and describes the processes of circulation, respiration, and excretion in each organism. SC 07 210 Given a diagram, each student identifies, labels, and describes the primary functions of the eight cytoplasmic organelles and lists the four functions common to all cells. SC 07 211 In his own words, each student explains the difference between passive and active transport of a substance through a membrane and differentiates between osmosis and diffusion. SC 07 212 After hands-on experience using a microscope, each student correctly identifies, labels, and explains the function of each part of the microscope. SC 07 213 Citing a specific example of each process, each student compares and contrasts kinetic and potential energy; aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration; and external digestion, cellular digestion, and digestion within a digestive system. SC 07 300 After a study of reactions of organisms, each student lists, describes, and gives examples of the three levels of animal behavior. SC 07 410 Using animal systems as a reference, each student evaluates the relative importance or interrelationship of body organs based on a given function and identifies the function of each major body structure. SC 07 411 After a study of the reactions of organisms, each student describes the nervous system of the planarian, earthworm, and frog. Science Eighth Grade Physical Science SC 08 022 Given a scientific problem with directions to follow, each student accurately applies the basic steps of the scientific method to solve it. SC 08 502 Given a list of fifteen items, each student correctly classifies each item as a solid, liquid, or gas. SC 08 521 Given a list of thirty -five elements/symbols, each student recalls the corresponding symbol/name for each element with 100% accuracy. SC 08 530 Given a set of compounds and mixtures, the student labels each substance, specifies the type of the identified mixtures, and justifies each label by describing its composition. SC 08 531 Given twenty examples of characteristics of acids and bases, each student classifies each as an acid or a base. SC 08 540 Given a list of twenty changes or properties, each student classifies each as chemical or physical. SC 08 550 Given ten chemical equations, each student accurately identifies each as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, or double replacement. SC 08 560 Given a periodic table of elements, each student demonstrates knowledge of its arrangement by accurately classifying fifteen elements as metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. SC 08 624 Given a drawing of light bulbs and batteries, the student accurately draws lines to connect the objects as they would be arranged in a series and in a parallel circuit. SC 08 625 In his own words, each student explains the relationship between electricity and magnetism. SC 08 647 Given a drawing of a wave, each student labels the four parts. SC 08 648 Given illustrations of five waves, each student arranges them in sequence according to frequency, amplitude, and wavelength. SC 08 649 Given a drawing of the electromagnetic spectrum, each student labels the twelve parts. SC 08 663 Given ten examples of simple machines, each student correctly classifies each example. SC 08 673 Given eight types of energy, each student defines each one. SC 08 680 Given a set of formulas for speed, acceleration, force, power, and work, each student chooses the appropriate formula and correctly solves the problem. SC 08 681 Given a list of twenty situations, each student classifies them according to Newton's laws of motion with no more than four errors. SC 08 700 Given a set of six mirrors, lenses, and images, each student accurately predicts whether the image is real or virtual, upright or inverted. Science Earth Science High School SC HS 811 Given a description of an air mass, each student identifies the clouds, winds, and storms associated with the mass. SC HS 822 When given weather information, each student identifies how it was gathered, how it was processed, and how it is used to make predictions. SC HS 832 Given the description of types of water in the atmosphere, each student identifies cloud types and traces the water cycle in the atmosphere. SC HS 833 Given a diagram of the atmosphere, each student labels the layers of the atmosphere and describes the energy and conditions of each layer. SC HS 851 Given a cross sectional diagram of the earth, each student applies Biblical descriptions and geological findings to label the diagram and describe the history of the earth. SC HS 852 Given a mountain, each student describes its formation and classifies it according to its type. SC HS 853 Given weathering, mass wasting, or erosion, each student describes each process and explains the effects on the surface of the earth. SC HS 865 Using identification methods, each student identifies each of a set of minerals and classifies rocks that are produced from each. SC HS 882 Given a simulation of an earthquake or volcanic eruption, each student explains what happens during the earthquake or eruption and identifies a set of historically significant eruptions. SC HS 890 Given an ocean name, a glacier name, or the idea of ground water, each student describes the label for and the function of each part of the phenomenon. SC HS 912 Given a stellar object, each student identifies types of tools to see the object, names the constellations associated with the object, and defines various types of stars. SC HS 924 Given a diagram of the solar system, each student labels the objects orbiting the sun and gives a description of each. SC HS 932 Given information about the moon, each student lists and identifies its phases and discusses its affects on the earth. SC HS 940 Given a diagram of the sun, each student labels and describes the parts and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of solar energy. SC HS 952 Given the name of a U.S. space exploration program, each student describes the historical climate of the program, the mission of the program, and the outcome of the program. SC HS 960 Given the pattern of earth movement, each student identifies the patterns of movements, what these movements cause, and what evidences there are for these motions. Science Biology High School SC HS 004 With respect to the understanding of truth from a Biblical basis, each student will specify six limitations of science. SC HS 005 When given a statement made by an evolutionist, each student proposes and defends the Christian view of Creation related to the statement using physical evidence as well as Scripture. SC HS 055 When given a biological key, each student accurately classifies the organism and/or identifies the reasons the organism cannot be classified without error or question. SC HS 056 When given the kingdom of any two organisms, each student compares and contrasts possible characteristics of the organisms. SC HS 057 When given the name of a particular organism, each student correctly classifies, describes, and lists possible effects of the organism on human population. SC HS 080 Given articles concerning present day ecological and biological issues, each student analyzes the article, formulates a position concerning the issue, and discusses the social and Christian perspectives of each issue. SC HS 105 Given a plant or plant part, each student correctly classifies and describes the characteristics of the plant and its parts. SC HS 106 Given a particular environmental condition, each student correctly predicts three possible effects of the condition on plant life. SC HS 214 When given cell slides or diagrams, each student correctly compares and contrasts cell types, cell parts, and the function of cell parts. SC HS 215 Given a specific life situation, each student correctly predicts the metabolic results of the situation. SC HS 301 Given the name or classification of an animal or group of animals, each student correctly lists seven characteristics describing the animal or group. SC HS 302 Given the name of two animal groups, each student compares and contrasts the anatomy and physiology of the two animal groups. SC HS 412 Using prior knowledge of human anatomy and physiology each student describes similarities and differences between human and animal anatomy and physiology in terms of systems and system function. SC HS 430 When given a specific parental genetic situation, each student correctly predicts the possible outcomes produced by the situation and discusses critically any social, ethical, or Christian issues surrounding the problem. SC HS 570 Given a list of 25 chemical terms, each student correctly defines and applies each term in scientific discussion. Science Chemistry High School SC HS 083 Given an explanation of the basic facts involved in a scientific article, each student analyzes the information from the article to make inferences, draw conclusions, make predictions, and evaluate the validity of the information. SC HS 084 Using sample questions to conduct an interview of a professional in the chemistry field concerning career opportunities, each student describes that career according to educational preparation, job descriptions, salary, and projected future availability. SC HS 512 From memory, each student delineates the history of the atomic theory and describes the atom by listing at least three properties of each of the three basic parts. SC HS 513 When given the atomic number of an element, each student writes its electron configuration. SC HS 522 When given the electron configuration of an element, each student describes three of more properties of the element. SC HS 532 When given the name or formula of a compound, the student states its corresponding formula or name. SC HS 533 When given a compound, the student classifies it as an acid or a base, clozes equations of reactions involving that compound, and applies formulas to correctly solve pH and titration problems. SC HS 541 When given ten stimuli undergoing changes, the student identifies the properties and changes in the matter and uses the classification pyramid to label the type of matter for a minimum of nine changes. SC HS 551 When given ten equations, the student identifies the redox reactions and balances the equations using the half-reaction method for at least eight of the equations. SC HS 552 When given a simple nuclear reaction equation, each student correctly identifies the type of reaction and balances the equation. SC HS 561 When given the periodic table, each student identifies five properties of a given element according to its placement on the table. SC HS 571 When given a basic chemical term or measurement, each student correctly defines it and applies it to a particular situation. SC HS 580 When given five problems, each student correctly solves at least four using the factor-label method. SC HS 581 Given the description of a mole and its function in problem solving, the student correctly solves molarity, percentage composition, and empirical formula problems. SC HS 582 When given a balanced equation, the student correctly solves three types of stoichiometry problems applying mass-mass, volume-mass, and volumevolume formulas. SC HS 583 Given the gas laws, the student correctly solves problems and makes predictions using the laws. Science Physics High School SC HS 085 Using sample questions to conduct an interview of a professional in the physics field concerning career opportunities, each student describes that career according to educational preparation, job description, salary, and projected future availability. SC HS 626 When given a stimulus circuit, each student determines voltage, current, and resistance in a simple series or parallel circuit. SC HS 647 When given a water wave, each student analyzes its properties and concludes parallel properties for light and sound waves. SC HS 653 From memory, each student correctly applies the formulas of thermodynamics to heat transfer and quantifies values such as specific heat and final temperature. SC HS 665 When given a moving object, each student correctly quantifies the momentum, work, energy, power, and efficiency of the movement. SC HS 682 When given the formula, each student applies the formula to solve at least four velocity and acceleration problems. SC HS 683 Given ten movement-stimulus problems, each student classifies the stimulus according to Newton's three laws of motion and solves the corresponding problems. SC HS 684 When given two vectors or a resultant, each student incorporates the proper procedures to determine the corresponding resultant vectors. SC HS 685 When presented with ten motion problems with projectiles or related moving objects, each student solves a minimum of eight problems to determine velocity, distance, or time. SC HS 686 Given Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation and Kepler's three laws of planetary motion, each student applies each to situations on the earth and in space. SC HS 690 When given a nuclear equation, each student analyzes the equation and concludes the potential of the reaction. SC HS 701 When given a lens or mirror, each student applies the appropriate formulas to determine the optical properties of focal length and magnification. SC HS 710 When given the necessary materials, each student correctly applies the SI system to determine mass, length, and time measurements. SC HS 711 When given a table of data, the student graphs the date, evaluates the graph, and interprets the data. Science Advanced Biology High School SC HS 081 Given evidences of embryology, each student defends the Christian approach to the issue of abortion. SC HS 082 When given a current event or situation relating to biological or ecological issues, each student critically discusses the social perspectives and defends the Christian perspective on the issue. SC HS 216 When given a slide of a particular biological tissue, each student identifies the tissue type and characteristic of the sample. SC HS 414 Given the name of a human biological system, each student names and describes the structures and functions of the system. SC HS 415 When given a diagram of the parts of a human biological system, each student identifies each part of the system. SC HS 416 When given a description of an injury, each student accurately predicts the outcome of the injury, the effect to the biological systems involved, and the healing process that will logically occur. SC HS 417 When given a particular life or nutritional situation, each student accurately predicts the outcome and effects on the corresponding systems of the human body. SC HS 418 Given a list of muscle types, each student compares and contrasts the structure and function of the various muscles. SC HS 419 Given the normal hormonal ranges, each student accurately predicts the effects of an increase or decrease in hormone levels of the body. SC HS 420 Each student accurately describes the role of the lymphatic system in immunity.