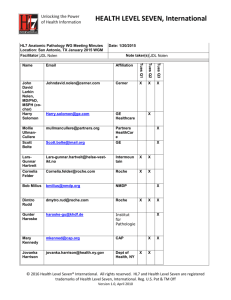
HL7 Version 3 Impact Assessmentt
advertisement

HL7 Version 3 An impact assessment Information for Personal Health V1.0 March 2001 2 of 50 Purpose of this document To assess the implications of HL7 version 3 on clinical messaging within the NHS. In particular implications for strategy, terminology, drug databases, and UK models. Distribution NHSIA Website Authors David Robinson, Paul Frosdick, Els Briscoe David Robinson, NHS IA, Aqueous 2 Rocky Lane Aston Cross Birmingham Further copies from B6 6RQ E-mail: david.robinson@nhsia.nhs.uk IA Reference Number 2001-IA-566 Date of issue 23rd March 2001 Revision History © Crown Copyright 2001 Published by the NHS Information Authority on behalf of the NHS Executive. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 3 of 50 HL7 Version 3 Impact Assessment 1. INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................. 4 2. HL7 VERSIONS ............................................................................................................................... 6 3. RELATED ORGANISATIONS AND STANDARDS ........................................................................ 9 4. HL7-UK .......................................................................................................................................... 11 5. USE OF HL7 AND THE UK HEALTHCARE MARKET ................................................................ 12 6. THE HL7 REFERENCE INFORMATION MODEL VERSION 3 .................................................... 13 7. THE MESSAGE DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK ....................................................................... 17 8. CLINICAL TERMINOLOGY .......................................................................................................... 20 9. SUMMARY .................................................................................................................................... 25 10. NEXT STEPS ................................................................................................................................. 26 APPENDIX A GLOSSARY ................................................................................................................ 28 APPENDIX B ACKNOWLEDGMENTS............................................................................................. 29 APPENDIX C IMPLICATIONS FOR THE UK THE HEALTH CARE MODEL ................................... 30 HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 4 of 50 1. Introduction Health Level 7 (HL7) (www.hl7.org) is a clinical interface standard, the 7 refers to the 7th (application Layer) of the International Standards Organisations (ISO) Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model for networks. This layer includes protocols for file transfer, and is the prime focus for HL7. HL7 was formed in 1987 in the USA to develop standards for electronic interchange of clinical financial and administrative information between different clinical and supporting systems. Within the application layer HL7 is concerned with definitions of data, timing of data exchange and error handling. The stated goals of the standard include: The standard should support exchanges in the widest variety of technical environments The greatest possible degree of standardisation possible should be achieved, although site-specific variations should be accommodated The standard should support evolutionary growth The standard should not favour interest of specific companies The standard should define formats for all healthcare environments Decisions are made by consensus balloting Co-operation with other related healthcare standards is a stated priority The HL7 working group has met approximately every 4 months since 1987. The group is structured into a number of Technical Committees (TCs) each concerned with particular aspects of the standard. There is overlap between many of these committees, and joint meetings are also held during working group meetings. Architecture Review Board Clinical Context Object Workgroup Clinical Decision Support Control Query Education & Implementation International Affiliates Medical Records/Information Modelling & Methodology Orders/Observations Patient Administration/Finance Patient Care Publishing Scheduling & Logistics Clinical Document Architecture Vocabulary HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 5 of 50 In addition to the technical committees there are a number of Special Interest Groups (SIGs), these include: Arden Syntax Blood Bank Community-Based Health Services Conformance Guideline Interchange Format Imaging Integration Laboratory, Point of Care and Automated Testing Security And Accountability Clinical Templates XML HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 6 of 50 2. HL7 Versions 2.1. Version 1 The Version 1.0 draft standard was presented in October 1987. The available timeframe did not permit the standard to address all the recognised issues. 2.2. Version 2 The prototype Version 2.0 was prepared following Version 1.0 and was first presented in 1988. There have been a number of subsequent revisions: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.3.1 2.4 (1988) (1990) (1994) (1997) (1998) (2000) Prototype First standard Widely adopted Most widely used current ANSI standard Current ANSI standard Current ANSI standard V2 includes message standards covering: patient admission, discharge, transfer and registration, scheduling, order entry, patient accounting (billing) systems and clinical observation data, such as laboratory results, that are sent as identifiable data elements (rather than display oriented text). 2.3. Version 3 Since 1996, HL7 has been working on a new generation of standards known as Version 3. The motivation for Version 3 arises from known implementation difficulties with Version 2. The multi-disciplinary efforts to achieve a workable and in-use Version 2 standard have resulted in: Complex integration process Misunderstanding of specifications Different and implicit information models Difficulty in verifying conformance Difficulty in measuring progress Widespread optionality Lack of explicit support for new technologies Object oriented technologies Extensible Mark-up Language (XML) Web technologies Lack of explicit support for security functions HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 7 of 50 Version 3 differs from Version 2 in that all standards developed will arise from an underlying Reference Information Model (RIM). Messages will be developed according to a defined set of development requirements, the Message Development Framework (MDF). The aim is to produce consistency in definition of different information objects and their representation in messages, thus allowing for easier implementation and the definition of clearer conformance requirements. Furthermore, the underlying modelling approach allows for the definition of standards for information representation other than just messages including documentary forms, decision-support mechanisms and electronic patient record structures. The process of HL7 can be defined in terms of deliverables within 4 phases. The process follows standard software development stages, and the methodology follows the Unified Modelling Language (UML): Analysis Use Case Model Information model Reference Information Model Domain Information Model Vocabulary Domain Specification Design Interaction Model Message Information Model (MIM) Hierarchical Message Description (HMD) Voting & Publishing HL7 Management Implementation guide Implementation Technology Specification (ITS) HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 8 of 50 Use case model Identifies: Healthcare requirements Actors and events Scope Information model Drawn from: RIM Models new concepts Harmonise with the RIM Produces: Class diagram State diagram Interaction model Drawn from: Use case model Defines: Trigger events Interactions Creates: Conformance claims Message design Drawn from: Interaction model Information model Develops: Message information model (MIM) Refined message information model (RMIM) Hierarchical message description (HMD) Figure 1: Summary of message development process HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 9 of 50 3. Related organisations and standards 3.1. CEN TC251 CEN is the Committée Européan de Normalisation, Technical Committee 251 (CEN TC 251) have produced a number of standards relating to messages e.g. ENV 13606 1-4 Electronic healthcare record communication ENV 1613 Messages for exchange of laboratory information There has been considerable input from players within CEN TC251 and there are ongoing processes to harmonise work within CEN and HL7. Implementation of CEN standards has been limited. 3.2. ISO TC215 The International Standards Organisation (ISO) Technical Committee 215 was established in 1998 to support “standardisation in the field of information for health…and to reduce duplication of effort and redundancies”. There are a number of ongoing work items with the TC, but no standards for clinical messaging. Under the Vienna Agreement ISO TC215 and CEN TC251 will not engage in parallel work activities. 3.3. CORBAmed CORBAmed is the Healthcare Domain Task force of the Object Management Group (OMG) which promotes the use of Object oriented Methodologies. CORBAmed therefore presents an alternative way of integrating a medical record through software components. Its focus is therefore on software components, but does identify a need for an integrated presentation of the medical record. 3.4. GEHR The Good Electronic Health Record (www.gehr.org) is an evolving health record architecture based on the Good European Health Record Project (www.chime.ucl.ac.uk/HealthI/GEHR ). Trials are currently taking place in Australia in transforming records to GEHR format, including pathology and radiology data. This work will maintain compatibility with HL7 and is inputting into HL7 itself. Although GEHR is not in itself a standard, the original GEHR influenced work within CEN. 3.5. HISA The Healthcare Information Systems Architecture originated from CEN (ENV 12967). It persists primarily as middleware services, including generic and specific healthcare HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 10 of 50 categories. These are published as information models and service interaction definitions. Information systems have been developed based on HISA in Europe and the Middle East. 3.6. SynEX The SynEX consortium, with support from the Telematics Applications Programme of the European Commission produced an open, generic solution for communicating and sharing records. SynEX enables authorised persons to share and present medical records from any system in any place, and assists them in understanding their clinical significance. SynEX is offered as a set of components and these deal with issues such as security and authorisation, terminology and protocols. Data exchange uses XML as preferred method but also covers data exchange using HL7. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 11 of 50 4. HL7-UK HL7-UK (www.hl7.org.uk ) is an official affiliate of HL7, membership includes representatives of: Primary and secondary system suppliers Universities Consultancies NHSIA ACIG Health Authorities NHS Trusts Pharmaceutical knowledge base providers The Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain The mission statement of HL7-UK is: “To support the development, promotion and implementation of HL7 standards in ways which meet the needs of healthcare organisations, health professionals and healthcare software suppliers in the United Kingdom. “ The policy of HL-UK is to: Work within HL7 to ensure its fitness for purpose in the UK Identify those HL7 standards that are directly applicable to UK healthcare and those that require adaptations or national implementation guidelines to meet UK requirements Propose solutions that meet the need for consistent national implementation, while avoiding the need for massive changes to systems and unnecessary divergence from HL7 standards Ensure the RIM can capture record architecture principles Facilitate agreement between the boundaries of responsibility between modellers and terminology maintenance organisations Historically there are have been 2 sub-groups within HL7-UK: HL7-UK Version 2 subgroup Concerned with supporting consistent implementation of HL7 Version 2 for use within NHS trusts. HL7-UK Version 3 subgroup Concerned with ensuring that HL7 Version 3 development meets the needs for widespread, effective communications within and between UK healthcare institutions. For the last eight months there has only been one group, the Technical Sub-group. This group is divided ‘virtually’ into a number of interest groups that communicate via a list server. One of the most active of these is drafting the Version 2 implementation guide. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 12 of 50 5. Use of HL7 and the UK Healthcare Market Version 2 of the HL7 standard now has a widely installed base across many countries outside the USA, including Canada, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, Germany, the UK, the Netherlands, Finland, South Africa, Argentina and India. All these named countries have national affiliate organisations to the parent body of HL7. 5.1. Primary Care The UK primary care Clinical Information System (CIS) market is relatively well developed and controlled, with approximately 85% of users being supplied by three main system suppliers. Products have usually been developed within the UK, although the owners of such systems may be from outside the UK. There has been input from primary care clinicians into the development of these systems. Some suppliers have been active within CEN TC251, and have contributed to standards arising from that body. Some are active within HL7-UK, however it is felt to be unlikely that the majority of suppliers will re-tool to HL7 without a strong business case, which currently does not exist. 5.2. Secondary Care The UK Industry for clinical information systems within Secondary Care has a much higher proportion of international companies, with many of these systems being US-based. There are a number of smaller enterprises who are potentially disadvantaged by the lack of a universal standard. The business requirements within this segment place emphasis on intra-organisational use, and a requirement for automated production of data to support central returns and internal governance. Clinicians who use systems have slightly differing requirements, e.g. real-time use and decision support, however the two requirements cannot be divorced. International companies, especially those that are US-based, are likely to be compliant with some version of HL7, most probably version 2.3. HL7 Version 2 is used in at least two of the major suppliers in the UK. They are unlikely therefore to subscribe to alternative standards such as those arising from CEN TC251 unless they are mandated, the business case from the UK market for these companies is unlikely to be sufficient to support this. 5.3. NHS Information Authority The NHS Numbers for Babies project (www.nhsia.nhs.uk/nn4b) is using HL7 Version 2.3, in messages between Maternity Units and the Central Issue System and Child Health. This was specified in June 2000. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 13 of 50 6. The HL7 Reference Information Model version 3 This report provides an assessment of the usefulness of the HL7 Reference Information Model (RIM) for current developments in the NHS more specifically the recommendations of Information for Health. The NHS Information Authority’s Health care Model (HcM) has been used as a check list to assess the HL7 RIM not because it is believed to be a better or more complete model but because it does incorporate knowledge of years of clinical application development in the NHS. A detailed comparison between the two models has been included in Appendix C. The main focus of the work has been to find answers to the following questions: Is the HL7 RIM a stable information model? Is the HL7 RIM able to support both message development and interface design? How well does HL7 support the clinical scope? 6.1. Status and stability of the HL7 RIM version 3 The current version of the model contains a considerable amount of open issues. These include issues about the definition of classes and their attributes and the recognition that some classes and attributes will need to be removed and their functionality incorporated into other classes. It is not made clear what the relation of the USAM model version 2.6 is to this version of the RIM. The RIM refers for information about important attributes to the USAM model (no version number included) but does not take on board all of the classes in the USAM model1. The RIM Version 3 is expected to undergo extensive revision as and when messages are developed to support clinical requirements. An indication of the developmental nature of the RIM is that it has already passed version 100, this instability is a natural feature of the development phase and offers an opportunity for the NHS to participate in development. 6.2. RIM, message development and interface design The RIM is an essential part of the HL7 Version 3 development methodology, as it provides an explicit representation of the semantic and lexical connections that exist between the information carried in the fields of HL7 messages. The RIM is there to support the development of messages. To date, no messages have been developed for Version 3 and as such the model has not yet been tested, it is expected that this will start to happen in the near future. HL7 Version 3 interfaces between systems via messages, however there are viable alternatives to support electronic communication between systems such as standard interfaces developed by OMG and SynEX. The NHS faces the task of implementing the EHR and indications from the Electronic Record Development and Implementation Programme (ERDIP) projects are that the functionality required will not be able to be supported solely by messages. Common interfaces will need to be developed. 1 For instance the class Condition Node. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 14 of 50 6.3. The RIM and clinical scope. 6.3.1. Security / confidentiality This most important component of any clinical information system and a crucial factor in the realisation of an EHR has not received a great deal of attention in the model. Confidentiality is expressed as a coded 2 attribute of a limited number of classes such as Act and Clinical Document. Therefore, because the RIM does not deal with security for the total of the clinical record, the security requirements for EHR would not be met in this version of the RIM. It is worth noting that there are structures available for this and one ought to be included within the RIM. There is recent evidence that HL7 shares this view. 6.3.2. Clinical reasoning ( the Activity class) There are limitations in ability of the RIM to express the clinical reasoning process. In clinical reasoning it is necessary to focus attention on a specific property of a patient (symptom, measurement, result), then assign an intention to it, before identifying specific activities to change/understand it. The RIM cannot do this because the Act class incorporates the results of the Act within its specification. This has a number of implications. These include the fact that it restricts the ability to look at patient characteristics separately from the activity observing them. It requires knowledge of the results of an activity before it is undertaken. It does not allow for instance a single observing activity to observe multiple properties. It also makes it difficult to relate clinical findings to one another since it is always the activity that is being related. The RIM does not include certain activity states which are particularly important when dealing with referrals in the context of the NHS. The mood_cd attribute and state attribute of Act do not cover several activity states distinguished in the HcM. These omissions include performer accepted activity, performer selected activity, performer rejected activity and performance rejected activity. The RIM currently can only represent repeat prescribing and self-treatment with difficulty. The specification of repetitive activities is incomplete with the sole attribute maximum_repetition_nbr in the Act class. The complex relationship between activities has been generalised in the many-to-many Act_relationship class. The definition of the relationships is poor and overly complicated as it is trying to also cater for the complex relationship between individual patient observations (results).3 6.3.3. Consent Clinical consent is a complex matter, often qualified and conditional. Because in the RIM, consent is viewed as an Act but with no additional attributes or associations for this activity nor for the resulting consent, it is limited in its ability to handle this issue. It is not possible to talk about the consent without referring to the activity of giving consent This makes it difficult 2 3 HL7 has a specific set of confidentiality codes. Please refer to appendices for further detail. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 15 of 50 to store information particular to that consent such as which activities were consented to, if consent was withdrawn or conditional to certain health care practitioners. 6.3.4. NHS number and other identifiers All health systems have to deal with multiple patient identifiers. In this country there are the NHS number, PAS numbers, GP practice numbers, lab numbers etc.. Similarly in the US, all health providers have their own patient identifier (although their Government is planning to create a unique national health number). In order to deal with multiple identifiers, it is necessary to know which identifier is associated with which institution or practitioner and whether it is currently valid. The RIM does not currently handle this. The class Entity_name is an attempt to create identifiers, however it does not refer to any context. There is no reference to the state of the Entity_name which may no longer be valid and there is no association with the Agent that may prefer to use this name. Therefore it is difficult to distinguish between the many entity names an entity may have. The unique identification of the patient required for EHR would not be possible if this class is used. Alternatively the Id attribute of Entity could be used but the RIM states it is not to store information about the kind or type of entity this is, so no reference to NHS patients can be made to distinguish this identifier. 6.3.5. Places and locations Place is a subtype of Entity and hence inherits its attributes. However it is only used as the location for an encounter. It is not currently possible to link a patient (person) with several locations/places as they move through a process of care (information needed for booking of ambulances, porters, etc). Additionally it is not possible to link a person with several addresses or contact numbers or to document the relationship places have with one another. 6.3.6. Roles, participation and responsibilities The RIM makes it complicated to represent that patients are treating themselves. A patient would need to take on a Role of Healthcare practitioner, which seems to be an abuse of the concept. The attributes for the class Health care practitioner refer to qualifications. The relationship between roles has been generalised in the Role_relationship class. This forces one to create a role for an Entity in order to express a relationship between two entities for instance the relationship between the patient (living subject) and his/her sample. No direct relationship between entities can be expressed. This is particularly significant in the transplant arena. Role relationship can not be further qualified through its attributes. The specification of the Role class does not include an indication if the role was authorised and by whom. No chain of devolved responsibility exists. No distinction has been made between those roles which have been authorised and those that are not subject to authorisation. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 16 of 50 6.3.7. Health Chart A Health chart (patient health record) is composed of health chart deficiencies. There is no definition what a deficiency is and this lack of clarity makes it impossible to assess what this class means and how it would be implemented. 6.3.8. Encounter_drg There is no association in the model between the class Encounter_drg and Patient_encounter to which the first relates. The concept of DRG closely assembles the HRG coding that takes place in the NHS but further investigation of the attributes of this class may be needed to ensure adequate use in the NHS. 6.3.9. Knowledge The RIM classes document the knowledge level within the same classes as would be used to record individual patient information. This severely restricts its use. How would one represent genus/species relationships between concepts and categories? Where do protocols and guidelines fit within this model? As the RIM currently exists, it appears that the use of attributes and code sets within classes to represent knowledge will make it difficult to take on board SNOMED CT. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 17 of 50 7. The Message development framework 7.1. Overview of the HL7 MDF The HL7 Version 3 MDF is a methodology describing the generic tasks which must be undertaken in order to produce a set of technical products, to wit EDI message specifications. The philosophy is that by following the steps rigorously, high quality products will emerge. The MDF has evidently been conceived in a system4 development context in that the method has distinct similarities in approach to other system development methodologies (SSADM, Information Engineering etc), and much of the methodology is familiar from elsewhere. UML modelling constructs are used almost exclusively: relying on storyboards and Use Cases to capture the processes which are being performed, Interaction and Sequence diagrams to show the detailed processing, Class and State diagrams to indicate the information classes and their behaviour. The use of Use Cases both within the method and as a means of describing it (a metamodel) highlights one of the weaknesses of the technique in that the connections between Actors and Use Cases cannot have their content described (e.g. in terms of Classes). There is also no conception of sequence in the notation. The HL7 RIM is used as a standard Information Model for the process, and a description is given of how the Rational Rose CASE tool is extended and used to support the method. The method falls into four major stages: Stage Identify the Message Requirements Identify the Message Contents Specify the Messaging Behaviour Build the Message Specification(s) Principal Product Use Case Model Information Model Interaction Model Message Design Model A detailed worked example of using the methodology for generating a message set dealing with patient encounters is provided but it is not made clear whether this is hypothetical or is a real example. The document is a substantial piece of work and clearly much effort has gone into its development and production. 7.2. Scope of the MDF The MDF describes a set of processes necessary to develop the specification for a set of one or more messages from the point at which the messages have been considered necessary to the point at which the specification is complete. It does not describe processes for: Identifying the business requirement, and attaching relative priorities Ensuring that the products generated are of appropriate quality5 Prototyping, testing and implementation of the messages 4 The word system is used in its widest sense throughout this document to mean any electronic mechanisms to support business processes. 5 There is a reference to the Architecture Review Board but this seems to be post-hoc and to have few if any teeth. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 18 of 50 Supporting roll out 7.3. Some features of the Methodology 7.3.1. Approach The process described in the manual does not recognise the benefits which can be gained by adopting a rapid development approach, i.e. by multiple iterations of some processes, and by using the early results of testing, prototyping and simulation to feed back into the specification process. The result is that once the message requirements were defined that these would remain constant for the whole of the process. There is no mention of prototyping and how that may affect the requirements specification. 7.3.2. Modelling the Business The MDF displays (along with many other methodologies) a weakness. It does not address the question of “What should we be building” based on an understanding of the business which the system is intended to support. One lesson, which has been learnt the hard way by many a system developer, is that the most difficult task is understanding the working of the environment into which any system is to be installed, and how the system is intended to support that environment. All too often, assumptions are made about that environment and although the process of designing and building the system may be of the highest quality, if it does not support the business it is wasted effort. An effective way of understanding the business is to model the processes which are undertaken with no preconceptions as to which of these may be supported (or indeed partially or completely performed) by IT systems. This understanding can then be used to identify which business processes need to be supported by technology, and the nature of this support. This provides a sound basis for taking forward the processes described in the MDF such as storyboarding and Use Cases. It also helps to ensure that, especially if a consistent business model is adopted, messages developed by different technical committees are consistent in their approach and use of data. The MDF could therefore be substantially improved by the adoption of such a business model describing the processes of delivering healthcare, and its incorporation into the earlier stages of the method. 7.3.3. Scaleability A United States oriented approach is evident in some areas, for example the statement on p5-18 of the MDF “....one can not expect that Location objects be tracked individually by information systems, and one can not expect that information systems could know about all persons associated with the same physical location”. In the UK this is precisely what many systems do by means of the Post Office Address File (PAF). The RIM view in this case weakens the model by making an address merely an attribute of Stakeholder (the supertype of Person). This also has the drawback that only a single address can be so associated, precluding both multiple concurrent addresses of different types (home, work, weekend cottage) and the retention of a history with the timepoints at which each became effective. Similar points may be made regarding other characteristics e.g. educational status, marital status. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 19 of 50 7.3.4. Subject Classes One concept, which is central to the methodology and the identification of messages, is that of the “subject class”. This is defined as “...a class the committee designates as the central focus of a collection of messages.” The document goes on to say “Identifying class states and state transitions specifies behavioral characteristics of a class. Class states and state transitions are defined for subject classes.” In other words, only where a class’s state behaviour can be defined would it form the basis for a group of messages. However, it is quite possible that the change of one of the attributes described for Person may be a candidate for such a message - let us take the previous example of a person’s home address. Change of such demographic details would quite feasibly be the topic for a message. It seems unlikely that the mere change of the value of an attribute would be considered as a state change as the state machine would be of little interest: Person change address In Progress Figure 2: Change of demographic details state chart 7.3.5. Metamodels A series of metamodels describing the MDF in UML Class notation is provided, giving a very useful view of the concepts being dealt with. There are however a few limitations in this (e.g. the association between Subject_class and State is described as 1 to 0..* rather than 1..* (or indeed 2..* to avoid triviality. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 20 of 50 8. Clinical Terminology 8.1. SNOMED Clinical Terms SNOMED CT (www.nhsia.uk/clin_term/snomedct), is a new clinical terminology currently in development through a collaborative project run jointly by the NHS Information Authority (on behalf of the National Health Service throughout the United Kingdom and the College of American Pathologists (CAP) in the United States of America. The project’s key deliverable is to create a new terminology which, as a minimum standard contains a breadth of content equivalent to the sum of its two constituent components; Clinical Terms Version 3 (The Read Codes) produced by the NHS, and SNOMED RT produced by CAP. Currently almost 2 years into a three-year programme, the new terminology is scheduled for release on 10th December 2001. This scheduled delivery date was reinforced at the Editorial Board of 09/10 February 2001, where it was reported that the product is still considered on schedule at the time of reporting. Information for Health discussed the need for SNOMED CT to be mandated for use within the NHS, a situation that has been confirmed by statements with the strategies refresh Building the Information Core published in January 2001. Section 1.7 introduces specific time-scales for the terminology’s adoption across the service stating: “By March 2003 - clinical information systems start to use SNOMED Clinical Terms” a statement which is reinforced in Section 4.8 which says: “Users/suppliers are advised not to develop new Read Code based systems from April 2003” Section 4.7 outlines the strategic importance of SNOMED CT to NHS information policy by saying: “The use of a modern set of clinical terms underpins many aspects of the development of health information systems . . . the development of SNOMED CT is being vigorously supported”, and is followed in Section 4.8 by the statement: “After 1 April 2003 any computerised information system . . . should use the NHS preferred clinical terminology, SNOMED CT”. The proposed use of SNOMED CT in the UK means it is essential that the impact of HL7 on the development of the terminology is considered: HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 21 of 50 The impact of HL7 Version 3 on terminology use within the UK is related to the use of terminologies and value sets within HL7. These can be considered in three areas: Structural data - HL7 includes sets of codes representing structural constraints within a message. These include ‘mood codes’ which provide additional information about the meaning of a message, e.g. whether it refers to a test, its status or the results of the test. There is potential for overlap with representation of Context of Care (www.nhsia.uk/context) within SNOMED Clinical terms. it is important to ensure that these facets of information within SNOMED Clinical terms can be represented within HL7. Small data sets – HL7 maintains a small set of coded data sets covering domains such as site, ethnicity and healthcare professionals. These domains are also covered by large scale vocabularies including SNOMED Clinical Terms These sets are maintained by HL7, but are intended to be inclusive, it is important therefore that all SNOMED Clinical Terms codes terms covering the UK realm are included. Large-scale terminologies – HL7 has a process for registration of terminologies, covering areas such as disorders, findings, procedures and drugs (considered in a separate section). Currently Clinical Terms Version 3 is in the process of being registered. SNOMED RT is already registered, and it is anticipated that SNOMED Clinical Terms will be registered after its release in December 2001. HL7 has a datatype (CD – Codephrase) which allows codes to be combined, This is consistent with the proposed post-co-ordinated approach of SNOMED Clinical terms. However, some aspects of information (e.g. negation, family history) likely to be represented by this mechanism in SNOMED Clinical Terms are thought by HL7 to be sufficiently safety-critical as to require explicit representation elsewhere within the message structure. These come under the area of context of care, it is essential therefore that SNOMED Clinical Terms contextual attributes and values are aligned with HL7. 8.2. Other vocabularies 8.2.1. LOINC LOINC (Logical Observation Identifier Names and Codes) (www.regenstrief.org/loinc/) is a terminology compiled and maintained by the Regenstrief Institute in Indianapolis. Initially it aimed to ‘provide a set of universal names and ID codes for identifying laboratory test results - to facilitate the exchange and pooling of clinical laboratory results, for clinical care, outcomes management, and research’. Input has been predominantly from the USA, but also from WHO, Sweden & Belgium. Recently it has expanded into Clinical LOINC including: Vital signs CNS pressure monitoring Intake and output ECG measurements Obstetric ultrasound measurements It is updated quarterly, is free of charge, and is downloadable from the Internet. The LOINC codes themselves are copyright. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 22 of 50 LOINC is in widespread use within the USA, and has had a considerable input into HL7. Its use in the UK appears to be limited to a single laboratory. LOINC names go into more detail than is present within either CTV3 or SNOMED CT, however there is a possibility of post-coordinated concept representations mapping onto LOINC concepts. SNOMED RT and Lab LOINC have an agreement not to overlap, and this issue, while not an HL7 Version 3 issue does need to be resolved for UK users. 8.2.2. DICOM Digital Imaging Conformance (DICOM) (www.hl7.org/standards/dicom) evolved from standards produced by a joint committee formed in 1983 by the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA). DICOM aims to: Support communication of digital image information independent of device Facilitate archiving systems Be applicable to a networked environment There are significant differences between HL7 and DICOM, indeed each was designed for different applications. However there are areas of overlap such as diagnostic reports, and efforts are underway within HL7 to promote interoperability between different image management systems, and to ensure that the RIM has appropriate classes to support this. DICOM is in use within the UK and the structure approximates to HL7 Version 2.x. Virtually all digital image communications in the UK are DICOM compliant, and all new systems within the last 5 years have been. Some manufacturers may have their own interpretation of DICOM, (there are no use case profiles to which it is possible to comply) and as a result inter- vendor connectivity is very difficult, but is possible if considerable care is taken. DICOM are currently working with HL7 in the context of the Image Integration Special Interest Group to their structured reporting methodology to introduce images into HL7 structured documents (CDA). HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 23 of 50 8.3. Drug Terminology The situation with respect to the representation of drugs messaging in Version 3 is the subject of considerable ongoing debate within HL7 at present and can be described as ‘fluid’ at the time of writing. One reason for the current debate is the need to ensure the Reference Information Model is capable of representing the varying ways in which drugs can be expressed in messages. These can be seen to lie on a spectrum from the atomic representation of generic concepts, through to the specific representation of manufacturers’ products in particular pack sizes (Figure 3). Atomic Representation Specific Representation e.g. e.g. Atenolol; + 100mg; + Oral; Atenix 100mg Tablets (Ashbourne Pharmaceuticals) x28 Figure 3: Spectrum of Potential Drug Representation Drug messaging will be managed through two elements working in combination; the message structures (R-MIMS) which build the relationships between the components of the RIM, and the registered vocabularies that provide the drug concepts to populate the message. It is anticipated the contents of these vocabularies will be held in a ‘Medication Master File’. However, as part of the ongoing debate there is currently some diverging opinion over which elements of the message are required to be represented in the RIM and which in the vocabulary. One element of the Medication Master File which has been agreed in principle, although the specific detail required to populate it is still being collated, relates to the representation of standard dosage forms and routes of administration which will be recognised within the HL7 standard. Within the UK and Europe it will be necessary that HL7 recognises the ‘Standard Terms, Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Routes of Administration and Containers’ which is managed on behalf of the Council of Europe by the European Department for the Quality of Medicines and The European Pharmacopoeia. The impact of HL7 Version 3 on drug terminology within the NHS can be considered in six areas: A continuation of the ongoing positive input to the current development of drug messaging standards through representatives of HL7-UK is required in order to ensure HL7 Version 3 can support those use cases required specifically in the United Kingdom. The structure of drug representation within SNOMED CT, as the NHS preferred clinical terminology, will need to consider the messaging requirements of HL7 in order that any necessary decomposition of drug concepts required to support messaging standards is achievable from within the data provided by the terminology. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 24 of 50 Any definition of drug concepts with respect to their dose form and route of administration within SNOMED CT should ideally be consistent with the HL7 adopted standard forms and routes. It is a strategic necessity that SNOMED CT at its international core level, any UK specific extension and the final format of the UK Standard Clinical Products Reference Source must be fully integrated. This would be best achieved by the use of SNOMED CT identifiers throughout, with the Reference Source concepts being hierarchically linked to their terminological parents. The hierarchy of SNOMED CT will need to consistently represent the types of concept specified in HL7 as necessary components of some/all drug related messages. Organisations involved in the procurement of systems intended to support drug and appliance representations will need to consider the strategic requirement to support messaging within the expected system lifetime when writing procurement specifications. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 25 of 50 9. Summary HL7 has a momentum and uptake by suppliers world-wide, but particularly in the US, that already makes it the world leading standard for clinical messages, at the very least in secondary care. Other standards have not provided a “solution” of the scale of HL7. Version 2 has a number of problems relating to the way it has evolved. Many, though not all of these relate to the wide degree of optionality or interpretation permitted, an approach that allowed the standard to be taken up, but which has generated problems in later years. The HL7-UK Implementation guide should have a beneficial impact in this problem in the UK. Version 3 addresses these issues, and is likely to be a more generic approach but the underlying RIM is not yet stable. The impact of ongoing development of messages on the RIM has implications for the stability of the model. The instability of the RIM, whilst a concern, also offers an opportunity for the NHS to ensure its needs can be represented. HL7 Version 3 signifies a big step change from Version 2 and there are no indications at present when the RIM version 3 will be adopted and how successful its uptake will be. Opinion amongst those consulted varies as to the timeframe for implementation, some system suppliers are ready to implement in a limited environment while others believe it will be 3 years or more. There are a number of existing Version 2 users and vendors, predominantly in the secondary care sector. It is unlikely to be productive to attempt to re-engineer all existing messages as a first step, however new developments should be looking to Version 3. Taking into account the NHS plans for widespread adoption of health information systems, the NHS could become a major user of HL7, probably ranking alongside the US Department of Defence and the US Healthcare Finance Administration (HCFA), the funders of Medicare and Medicaid. This could be used as a negotiating lever with HL7 to ask them to address any weaknesses and gaps identified in this report. Any action taken by the NHS should also address the e-Government Interoperability Framework version 2 (www.e-envoy.gov.uk/egovernment/egif2/intro.htm) which provides the policies and standards for achieving interoperability across the public sector. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 26 of 50 10. Next Steps 10.1. Actions for the NHS Given the likelihood of HL7 becoming a de-facto worldwide standard, The NHS needs to decide at a strategic level whether to adopt HL7 as a standard and if so identify appropriate timescales. Most of he skills residing within the UK are currently outside the NHS, the NHS should actively participate in ongoing development of Version 3 and look at how it can acquire and develop the necessary skill mix. The NHS has considerable experience, and has undertaken work in many areas covered by HL7 Version 3. It is apparent that there are elements of the HcM within the RIM, and concerns as to how these elements have been handled. It is important for this knowledge to be fed into the HL7 process. Implementation, including testing of Version 3 will require commitment of considerable resources, along with effective stakeholder communication. This is consistent with lessons learnt in previous NHSIA projects, and neglecting these aspects would be a significant risk. The resource implications should therefore be assessed. One way of addressing the scale of these resources set against the skills available to the NHS and at the same time aligning with the modernisation and quality of care agenda would be to break down larger work packages and to accelerate those associated with key health conditions. For example with one or more of the major areas identified in the NHS Plan – consideration should be given to how this might be achieved. The HcM has had considerable investment, and is considered to have intellectual rigour and integrity. However it does not appear to have had the impact on the marketplace of HL7, and thus healthcare that one might have hoped. The NHS needs to learn from this, both in this context, but also in other work areas within the NHSIA. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 27 of 50 10.2. Risks of inaction by the NHS Most observers agree that HL7 V3 is strategically correct (it is the only model that is subject to a process of continual review and update). Failure to engage in the process could leave the NHS disadvantaged in a number of ways: Delay of adoption of any standard as part of a comprehensive clinical messaging infrastructure to support the EHR approach A need to implement international standards which do not fully support the needs of the NHS A shortage of appropriate knowledge and skills within the NHS Considerable effort centred on producing and rolling out alternative messages of limited value outside the NHS. Inability to align NHSIA projects such as SNOMED Clinical Terms with international standards HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 28 of 50 Appendix A Glossary ACIG Academy of Royal Colleges Information Group ANSI American National Standards Institute ACR American College of Radiologists CAP College of American Pathologists CCOW Clinical Context Object Workgroup CEN Committée Européan de Normalisation CIS Clinical Information System CORBA Common Object Broker Architecture CTV3 Clinical Terms Version 3 EHR Electronic Health Record EN Europäische Norm (European standard) ENV Europäische Vornorm (European pre-standard) EPR Electronic Patient Record DICOM Digital Imaging Conformance DIM Domain Information Model ERDIP Electronic Record Development and Implementation Programme HcM UK Health Care Model ISO International Standards Organisation LOINC Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes LHSR Left hand side of the RIM MDF Message Development Framework MIM Message Information Model NEMA National Electrical Manufacturers Association OMG Object Management Group OSI Open Systems Interconnection RIM Reference Information Model RMIM Refined Message Information Model SIG Special Interest Group SNOMED RT SNOMED Reference Terminology SNOMED CT SNOMED Clinical Terms TC Technical Committee UML Unified Modeling Language XML Extensible Markup Language HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 29 of 50 Appendix B Acknowledgments This document has been reviewed, both internally within the NHSIA and externally. Thanks are extended to the following people who have reviewed or contributed information. NHSIA Nigel Bell Graham Folmer Dr Colin Price Dr David Jones Peter Nicklin Ian Soady Andy Brown John Willis Chief Executive Director, Programme and Service Delivery Head of Delivery, Information for Personal Health Head of Capability, Information Management Senior Consultant Senior Consultant Project Manager, NHS Number for Babies Senior Business Analyst, NHS Number for Babies External Dr Leo Fogarty Professor Alan Rector Dr David Markwell Dr Peter Johnson Ian Shepherd Charlie Bishop Melvin Reynolds Ann Harding Martin Whittaker Dr Mike Robinson Dr Dipak Kalra ACIG, HL7-UK University of Manchester, HL7-UK Clinical Information Consultancy, HL7-UK Newcastle University, HL7-UK Royal Pharmaceutical Society McKesson HBOC, HL7-UK AMSC iSOFT, HL7-UK Touchstone Consultancy, STEP, HL7-UK In Practice Solutions, HL7-UK Centre for Health Informatics and Multi-professional Education HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 30 of 50 Appendix C one. A comparison between the RIM version 0-100 and HcM version RIM version 0-100 is a non-draft release that will be used to develop the initial set of HL7 Version 3 messages. The model is divided in subject areas which each hold a collection of classes.6 Some subject areas hold only a few classes and some of those classes are due to disappear from the model in the near future. Although this further classification is not important in itself, it allows for a quick overview and comparison to HcM. Relevant Subject areas: Clinical documents, Healthcare service provider, Healthcare Stakeholders, LHSR, Patient encounter, Patient service event, Patient service material, Person, Scheduling. All other subject areas are or included in the relevant ones or related to financial and insurance US specifics. Comparison between HL7 classes and HcM classes7 Access This class is a subtype of the class Role. The Access class has quite a few open issues connected with it. Its description indicates that the class would map to the Subject class in HcM, related to the Subject patient via an Inter subject relationship. Attributes Body_site_cd : subject characteristic type . HL7 provides a limited, coded set of anatomical target sites for an Access, which HcM would list here as instances of the class Subject Characteristic Type. Recorded for a specific access: Category Subject Characteristic of type body site. Entry_site_cd : subject characteristic type. The HL7 coding set is identical to the above. Recorded for a specific access: Category subject characteristic of type entry site. Gauge_qty : subject characteristic type. Recorded for a specific access: measured subject characteristic of type gauge. Units are defined in the Unified Code for Units of measure, Unit of Measure in HcM. Act Terms such as Action, Activity, Service or Service Action are used as synonyms. Act is defined as an intentional action in the business domain of HL7. As such it corresponds to Activity in HcM. Composition Originates_ in_context_of 1,1 Act_context : corresponds to Activity in Context in HcM. Note however that the cardinality on this composition of HL7 suggests that an Act is always an activity in context which is not correct. The Act_context class adds very little information to the activity and is an open issue. 6 7 In the text the terms ‘subject areas’ and ‘classes’ appear to be used interchangeably. References to HcM are in italic. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 31 of 50 Associations Is_source_for 0..n Act_relationship : see under class Act_relationship Is_target_for 0..n Act_relationship :see under class Act_relationship Has 0..n Participation : see under class Participation Attributes Activity_time: completion timepoint association to State Change Activity. Availability_dttm: would be recorded as an Activity Qualifier Confidentiality_cd: code that limits disclosure of information about the service. In HcM covered by the association of Access Group for Object to Object which will include Activity. This association will also allow the specification of a level of confidentiality for the total of the patient record which is not covered by this HL7 proposal. 8 Critical_time: This attribute has a different interpretation for activities in different moods and for some of the subtypes of Act. This attribute is needed in HL7 because there is no separation between the action and its results. In HcM actions can be separated from the subject characteristics that they observe. Subject characteristics carry their own time points. Additional time points that relate to the activity will be recorded as Activity Qualifiers. Id: identifier attribute of Object in HcM. Interruptible_ind : record as Activity Qualifier. Max_repeat_nmr: In HcM if an activity is to be repeated it is recorded as a Repetitive Activity. This attribute would be an Activity qualifier of a repetitive activity. Mood_cd: corresponds to some of the Activity states in HcM. It is not totally clear from the document which moods are used, whether they are the same as in the USAM model or if changes have been made since the last version of that model and some additional moods have been added here such as trigger mood. Event mood: Completed Activity Definition mood: Activity Type Order mood: this could refer to Activity to be done, Performer selected activity, Scheduled activity Goal mood: Target property Trigger mood: no mapping. Orderable_ind: Activity Qualifier Priority_cd: Urgency association to Activity. Txt: Activity Qualifier Type_cd: Activity Type that may or may not be coded. Status_cd: is intended to cover activity states. Aborted: Abandoned Activity Active: could map to several activity states in HcM for instance Started Activity Cancelled: Not required Activity Completed: Completed activity Held: could refer to Activity under consideration, Performer suspended, Performance suspended New: has no meaning as a state of an activity. Superseded: Activity Substitution Suspended: could be Performance suspended activity or Performer suspended activity The RIM document does not provide a full description of the moods and states of an Act but it refers to the USAM model. What follows is from USAM version 2.6 States of action are a strictly defined code set, no exceptions allowed. 8 HL7 propose a code set from which the user will need to choose. This may not align with confidentiality policies used by institutions in the UK HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 32 of 50 The state transition model is uniform through all moods. Definition mood The states for this mood suggests some tips for the maintenance of the knowledge level in HcM. Relates basically to the state of the Activity Type instance in the knowledge level. New: service definition is in committee status, ie it is authored and may change before it can be instantiated. No mapping to HcM Cancelled: service definition has been abandoned before activation. No mapping. Held: rarely used. No mapping. Active; can be instantiated. Activity type instance Aborted: definition was wrong and is withdrawn. No mapping. Suspended: may be resumed later. No mapping. Completed: definition is retired, no longer used. No mapping. Superseded: service definition superseded by a new definition. New Activity Type. Intent mood New: service is being considered, Activity under consideration Cancelled: service was considered but now abandoned, Not required Activity Held: rarely used. No mapping. Active: service intent is committed to (on TODO list), Activity to be done Aborted: service intent is abandoned, Abandoned Activity Suspended: active intent suspended, Performance suspended Activity or Performer Suspended Activity Completed: intent is completed if the intended action has been performed (ripple effect of completion of the service event) Completed Activity Superseded: intent is completed but the record of intent was corrected. No mapping. Order mood New: order is being authored or is waiting to be issued. The filler does not yet know about it. Activity under consideration Cancelled: abandoned by placer before issued. Not required Activity Held: order is held before issued. No mapping Active: order has been issued, Activity to be done Aborted: Abandoned Activity Suspended: Performance suspended Activity Completed: as intent, only completed when event is completed, Completed Activity Superseded: order is amended after it was completed. No mapping. Event mood New: service is in preparation, waiting to be activated, Activity under consideration Cancelled: abandoned before activated Not required Activity Held: event on hold Activity under consideration Active: service event currently in progress Started Activity Aborted: Abandoned Activity Suspended: Performance suspended Activity Completed: Completed Activity Superseded: completed but superseded. In HcM the completed state is the final state of an activity. Predicate mood Active: main state, predicates only evaluated when active. No mapping. Aborted: active service is exceptionally terminated. No mapping. Suspended: a suspended predicate will not be evaluated. No mapping. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 33 of 50 Goal (i.e. predicate used as a goal) New: goal is being considered. Intention under consideration Cancelled: goal was abandoned before it was set, Abandoned intention Active: actively pursued goal, Established Focus Aborted: dismissed as being unachievable, Rejected Focus Completed: goal has been achieved Fulfilled intention Note here that the goal mood refers to a Subject Property which will be the goal. Activity states in HcM not covered by this proposal: scheduled activity, performer accepted activity, performer selected activity, performer rejected activity, performance rejected activity. Act_context This class is a subtype of Act. This class has open issues such as the implication of the implied inheritance from Act. This class is equivalent to Activity in context. Composition Originates_in_context_of Context Activity 1,1 Act = context association between Activity In Context and Attributes Level_cd: Is an open issue. Would be activity qualifier in HcM. Act_relationship This is a recursive associative class with a source association to Act and a target association to Act. Relationships between acts are explicitly expressed in HcM and some of the relationships in this class are covered by relationships between subject characteristics in HcM. Associations Has_source 1,1 Act : no mapping Has_target 1,1 Act: no mapping Attributes Checkpoint_cd: codes that indicate when associated pre-conditions are to be tested. No mapping to HcM. Conjunction_cd: no mapping Inversion_ind: reverses meaning of the relationship type. Needed because of fixed attribution of attribute to source of relationship. Not needed in HcM. Join_cd: codes that indicate how concurrent activities are synchronised. No mapping. Negation_ind: no mapping Pause_qty: no mapping. Priority_nbr: no mapping Sequence_nbr: no mapping Split_cd: no mapping Type_cd: indicates the meaning of the relationship. This is the most important attribute besides mood_cd, it is a structural attribute in that each of its values implies specific constraints to what kinds of acts can be related and in which way. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 34 of 50 The document refers to the USAM. (No version indicated) Act relationship types Has component: parent/component association between Activities Has specialisation : categorical knowledge about services – relation between Activity Types in HcM, genus-species link with Category Has pre-condition: this link restricts the target activity to be in pre-condition criterion mood : Activity Qualifier Has trigger: the target activity must be in pre-condition trigger mood. A delay between the actions can be specified . Activity Qualifier and further qualifier of that qualifier. Has reason: the reason will be another activity. In HcM, Reason is a class (not an Activity) associated with Activities in certain states: abandoned, rejected, not required. For activities in other states you could use Activity Qualifier. Suggests: inversion of above. Has contra indication: target service in criterion mood. Activity Qualifier which could be further qualified with the strength of the contra indication. Has outcome: target must be an observation, source is condition node or action (Note that condition node is not present in the RIM !): Property qualifiers, Outcome of Property or Outcome of Activity Has goal: target must be observation in goal mood. Target Property Has final objective: target must be observation in criterion mood (desired outcome). Target Property Has continuing objective: target must be observation in criterion mood (desired state to be maintained) Target Property Has risk: noteworthy undesired outcome Activity qualifier Has pertinent information : very unspecific relationship from one item of clinical information to another Has support: source must be observation: Subject Property Qualifier or a more specific association such as Subject Property has as basis Basis for Hypothesis Has explanation: reverse of above Is cause for: Causal relation Is manifestation of: reverse of above Causal relation Is derived from: both target and source are observations: source association between Subject Properties Has reference values: target in criterion mood. Use the genus-species in the knowledge level to associate a Subject Property Type with reference values. Assigns name: source is a condition node. Condition node is not a class in RIM. Is revision of: would be an Activity Qualifier Amends: used in the sense of amending reported results. No mapping. Updates (condition): used here for updates to condition nodes which are not present in the RIM Instantiates: maps to link between Activity and Activity Type Fulfills (order): state link between Completed activity and an Activity To be done or Scheduled Activity or Started Activity. Dispensing for (order): links between activities of type drug therapy and type drug administration Substitutes (brand product): link between the two activities through their state Matches (trigger): links actual service with service in criterion mood. Link between activities in different state Evaluates: the observation evaluates the goal link between Target Property and Actual Property Has option: source is in mood definition, intent or order. Activity Qualifier HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 35 of 50 Billing_information_item Subtype of Unmapped_financial_classes This class is not relevant for the NHS at this point in time. Champus coverage Subtype of Healthcare_benefit_product_policy, itself subtype of Financial_act. This class is not relevant for the NHS at this point in time. Clinical document This class is due to be deleted from the RIM and is to be incorporated within the Act class and/or a high level meta-model. 9 Associations Contains 1,1 clinical_document_body: clinical_document_body would be a subject characteristic of Subject Clinical Document. Attributes Confidentiality_cd: as Act. Access Group For Object in HcM Language_cd: Subject Characteristic Local_id: Identifier in Domain in HcM Originator: ‘performer’ association with Agent Clinical document header This class is a subtype of Entity and is due to be deleted from the RIM. Its functionality will be integrated with the Act class. View as Subject. 10 Attributes Availability_status_cd: this attribute is an open issue as no examples of codes for this attribute exist. This attribute would be a Category Subject Characteristic of type availability in HcM. Change_reason_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type change reason Completion_status_cd: (Open issue), Category Subject Characteristic of type completion status. Confidentiality_status_cd: Access Group for Object association with Object Content_presentation_cd: (Open issue), Category Subject Characteristic of type content presentation Document_change_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type document change Document_creation_dttm: Timepoint valued Subject Characteristic of type document creation 9 The idea of information containers separate from information is suggested. From that perspective the clinical document could be seen as a Subject in HcM with specific characteristics. 10 If integration with Act goes ahead then the document will be viewed as a container for information about the service/activity. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 36 of 50 File_nm : Text valued Subject Characteristic of type file name Last_edit_dttm: Timepoint valued Subject Characteristic of type of type last edit Reporting_priority_cd: (Open issue) Category valued Subject Characteristic of type reporting priority Results_ report_dttm: start timepoint association with subject characteristics which are the results. Storage-status_cd: Category valued Subject Characteristic of type storage status Transcription_dttm: Timepoint valued Subject Characteristic of type transcription Version_dttm: Timepoint valued Subject Characteristic of type version Version_nbr: (Open issue), replace with unique identifier for a document. Subject Identifier. Consent This class is a subtype of Act with no specific attributes or additional associations. This maps to the class Subject responsibility Act in HcM. Subject Responsibility Act is also a subtype of Activity but has mandatory link to a Subject Responsibility which is the result of the act. Container This class is a subtype of Manufactured_material, which itself is a subtype of Material which itself is a subtype of Entity. From that perspective Container would be viewed as a Subject and its attributes as Subject Characteristics. The attributes described for the class Container come from NCCLS it is unclear they represent. Device This class is another subtype of Manufactured_material. Again the Device can be considered to be a Subject in HcM. Attributes Alert_level_cd: Category Subject Characteristic Last_calibration_dttm: Timepoint valued Subject Characteristic Local_remote_control_state_cd: Category Subject Characteristic Manufacured_model_nm: Text valued Subject Characteristic Software_nm: Text valued Subject Characteristic Diagnostic_related_group_definition This class is a subtype of Financial_act and is associated with Encounter_drg. The NHS uses HRGs, closely related to DRGs. Diet This class is a subtype of Supply, itself a subtype of Act. Compares to HcM with an Activity of Activity Type Diet. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 37 of 50 Attributes Carbohydrate_qty: Measured Activity Qualifier Energy_qty: Measured Activity Qualifier One would expect that additional qualifiers or attributes would be needed for an Activity of type Diet such as for instance saturated/ unsaturated fat content of a diet, vitamins, minerals, etc. Document_service This class is defined a subtype of Act and would be an Activity of Activity Type document service. Most of the attributes specified for this class seem to relate to the document produced and not to the activity of document service (storage is a clear example of this). In HcM the document would be viewed as a Subject and the attributes defined here would be Subject Characteristics of the document as a Subject. Attributes Completion_cd: attribute may be deleted due to overlap with Act, Activity Qualifier of type completion. Copy_dttm: Activity qualifier of type copy (release_date) Origination _dttm: Activity qualifier of type origination Set_id: Activity qualifier of type set. Storage_cd: Activity qualifier of type storage Version_nbr: Activity qualifier of type version Employee_employer This class is a subtype of Role_relationship which is associated to Role. Would call this in HcM an Authorised Agent (employee) who is associated with another Agent (employer) which is given the Authorised agent authority. Attributes Addr: Authorised Agent at some specified (association) Location Hazard_exposure_txt: no mapping Job_cd: Authorised Agent Activity of type Activity Type Job_class_cd: no mapping 11 Job_title_nm: no mapping Protective_equipment_txt: no mapping Salary_qty: no mapping Salary_type: no mapping Status_cd: Agent State for Authorised Agent Telecom: no mapping12 11 The description of the job holds a job code, a job class (full time, part time), a job title. These attributes e would be further qualifiers of the Authorised Agent Activity but this is not possible in the current HcM . 12 The attributes for which no mapping is indicated point to changes required in HcM HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 38 of 50 Encounter_drg This class seems very specific to the US but as mentioned before DRGs are in use in the NHS. There is however no link between this class and the Patient_encounter class to which it must relate. Encounter_facility_association This class refers to the association between a Patient encounter and a Healthcare Facility and is an open issue. The class maps to two different constructs in HcM. Activities in certain states (started, scheduled, to be done, performer accepted and completed) will be associated with a Location. The HcM also has a class Subject Location which represents the association between a Subject and a Location which will have a timeperiod associated with it and can be further qualified. Associations Is_sited_at 1,1 Healthcare Facility: location_for Subject Location 13 Is_used_by 1,1 Patient_encounter: refers to the Activities for Subject and where they take place, which is the association of the Activity in certain states to a Location. Attributes Effective_tmr: Timepoint association with Subject Location Status_cd: (Open issue) the meaning of this attribute is not clear. Transfer_reason_cd: Category Subject Property Qualifier (of the Subject Location) Entity The closest mapping to HcM would be to Subject. Associations Has 0..n Entity_name : Subject has 0..n Subject Name Sends 0..n Message : not represented as an association for Subject but would be an association for Agent Shall_receive 0..n Message : not association for subject but would be an association for Agent Plays_a_role 0..n Role : Subject has role 0..n Agent Attributes Desc: Text valued Subject Characteristic of Subject Determiner_cd: (Open issue) unclear description of attribute Id: Identifier association with Object Importance_status_txt: (Open issue) Text valued Subject Characteristic Qty: Measured Subject Characteristic 14 Status_cd: (Open issue) state as in state transition. Subject has no state in HcM and a state attribute would not be relevant to all instantiations of Subject. This construct makes it difficult to record a patient encounter at the patient’s home since that would need to be a health care facility. 14 This could be added to HcM as an attribute of Subject. 13 HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 39 of 50 Telecom : Subject Contact association with Subject Type_cd: (Open issue) main classifying attribute. No subject type is used in HcM, as it is not envisaged that extra classes or associations will be needed. Entity name Would be mapped to HcM as Subject Name. Associations Is_for 1..1 Entity: subject 1..1 Subject Attributes Effective_tmr: start/end association of Timepoint with Subject characteristic Nm: name attribute of Subject Name Purpose_cd: Preferred name for Subject related to Agent Financial Act This class is a subtype of Act and is at present not applicable to the NHS. All defined attributes for this class would be covered through Activity class in HcM. Financial transaction This class is a subtype of Financial Act and is related to a patient billing account and as such not applicable to the NHS. Guarantor_contract This class is a subtype of Unmapped_financial_classes and seems specific to the US situation. Health_chart This class is a subtype of Entity and is referring to an individual patient record. In the HcM no subtypes of Subject are defined, so Subject should cover the Health Chart class. Associations Has_an_assessment_of 0..n health_chart_deficiency : it is not clear what a deficiency is and if that in effect is a characteristic of the patient rather than of the health chart. The HcM has a class Object Representation which can be used to represent information about any Object in a Subject. The Health chart as Subject will hold information about another Subject, the patient. It is unclear how the health chart is related to the patient since no associations are possible between entities only between roles. There is no relationship between this class and clinical document. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 40 of 50 Health chart deficiency This class can only be mapped as Subject characteristic of type Health chart deficiency. The subject here is the patient. Associations Is_assessed_against 1..1 Health_chart: see above comments. Attributes Assessment_dttm: Timepoint association with Subject Property Desc: Text valued Subject Property Qualifier Level_cd: Category Subject Property Qualifier Type_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type health chart deficiency Healthcare_benefit_coverage_item This class is a subtype of Financial_act and specific to US circumstances. Healthcare_benefit_product_ policy This class is a subtype of Financial_act and specific to US circumstances. Healthcare_facility This class is a subtype of Place, itself a subtype of Entity (Open issue) admit insufficient definition which makes it difficult to determine what is meant. As a subtype of Entity it would map to Subject, when it is used in the context of patient encounters it maps as Location. Associations (relevant for Location) Is_site_for states) 0..n encounter_facility_association : location for 0..n Activity (in some Attributes (relevant for Subject) Licensed_bed_nmr: Subject Characteristic of Healthcare_facility as Subject. Mobile_ind: Subject Characteristic of Healthcare_facility as Subject. Healthcare_provider This class is a Subtype of Role and would be described as an Agent in HcM. Attributes Speciality_cd: (Open issue) because it is felt this attribute should be moved to Individual_healthcare_practitioner: Would be a Subject Characteristic of the Subject linked to the Agent. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 41 of 50 Individual_healthcare_practitioner This class is a Subtype of Healthcare_provider and will map as the above to Agent in HcM. The attributes specified for this class are specific to US certificates. They would be Subject Characteristics of the Subject which has role of the Agent. Inpatient_encounter This class is a subtype of Patient_encounter. It would be viewed as an Activity of type Patient encounter. Attributes Length_of_stay_qty : Activity Qualifier for the Activity Insurance certification This class is a subtype of Unmapped_financial_classes and specific to US circumstances. Language ability This class would be considered in HcM as a Subject Property Qualifier of type language ability which qualifies Person Language as a Subject Characteristic for the Subject patient. Associations Specifies_ability_in 1,1 Person_language: qualifies 1,1 Subject Characteristic Attributes Mode_cd: Category Subject Property Qualifier of Subject Characteristic of type person_language (this is an additional qualifier of Person_language) Proficiency_level_cd: Category Subject Property Qualifier of Mode_cd. Qualifiers can themselves be further qualified which is the case here. Living_subject This class is a subtype of Entity and maps to Subject in HcM. Attributes Administrative_gender_cd: Subject Characteristic Birth_dttm: Subject Characteristic Deceased_dttm: Subject Characteristic Deceased_ind: Subject Characteristic Multiple_birth_ind: Subject Characteristic Organ_donor_ind: Subject Characteristic HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 42 of 50 Manufactured material This class is a subtype of Material, itself a subtype of Entity. This would again refer to the view of resources/material as a Subject Attributes Expiration_dttm: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic Lot_nbr: Subject Characteristic Material This class is a subtype of Entity and maps to Subject in HcM. Attributes Danger_cd: Subject Characteristic of type Danger/hazard Effective_tmr: Subject Characteristic of type effective_time Form_cd: Subject Characteristic of type form Handling_cd: Subject Characteristic of type handling Medication This class is a subtype of Act and would map to Activity. Medication is not seen as a separate activity in HcM and the material used is described as Qualifiers of the activity or included in the Activity Type description of the medication activity. Attributes Body_site_cd: Activity Qualifier of type body_site Dose_check_qty: Activity Qualifier of type dose check Dose_qty: Activity Qualifier of type dose Form_cd: Activity Qualifier of type form Method_cd: Activity Qualifier of type method Rate_qty: Activity Qualifier of type rate 15 Route_cd: Activity Qualifier of type route Strength_qty: Activity Qualifier of type strength. 16 Substitution_cd: Activity Substitution Military Person This class has open issues on most attributes and needs a description. This class will be mapped to Subject in HcM. 15 Dose_qty and rate_qty must be both used to express 100mL/h where 100mL = dose_qty and 1h = rate_qty. 16 HL7 is discouraging use of this attribute, dose specification is usually sufficient and if specific preparation is dispensed then the Material class is used. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 43 of 50 Attributes Military_branch_of_service_cd: Subject Characteristic of type military branch of service Military_rank_nm: Subject Characteristic of type military rank Military_status_cd: Subject Characteristic of type military status Non_Person_living_subject This class is a subtype of Living_subject and will map again to Subject in HcM Attributes Breed_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type breed Euthanasia_ind: Category Subject Characteristic of type euthanasia Gender_status_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type gender status Production_class_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type production class Strain_txt: Text valued Subject Characteristic of type strain Taxonomic_classification_cd: Category Subject Characteristic of type taxonomic classification HL7 has fixed set of attributes for this class. This may not cover all characteristics that are important to record about a Non_Person_living_subject. Notary public This class is a subtype of Role and will map to an Authorised Agent in HcM. Attributes Notary_county_cd: specific to US. Would be a Location attached to the Authorised Agent Notary_state_cd: specific to US. Would be a Location attached to the Authorised Agent Observation This class is a subtype of Act. Activity in HcM covers the activity of observation. Attributes Body_site_cd: Activity Qualifier of type body_site Derivation_expr: this refers to the result of the observation which is separately handled in HcM. This attribute could be expressed as a Subject Property Qualifier of the subject characteristic observed. Interpretation_cd: again this attribute refers to the result/outcome of the observation which are Subject Characteristics in HcM. If a coded classification existed to roughly interpret subject characteristics then this would be a Subject Property Qualifier of the subject characteristic observed during the observation Method_cd: Activity Qualifier of type method Value: Subject Properties observed by the activity HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 44 of 50 Organisation This class is subtype of Entity and will be Subject in HcM. Attributes Addr: Subject Location linked to Location Org_nm: Subject Name Standard_industry_class_cd: Subject Characteristic of type standard industry class Outbreak This class is a subtype of Public_health_case itself a subtype of Observation. This conflicts with the definition of Act (its supertype) as an intentional action. An outbreak is not intentional. HcM has a class Event which is the supertype of Activity and Incident. Attributes Tmr: start and end associations from Timepoint to Incident. Participation There is no equivalent class in HcM. The construct refers to Authorised Agent classes in HcM and the functionality implied by its associations to Activity. Associations For 1..1 Act: Agents associated with Activities Has_as_participant 0..1 Role: Authorised agents associated with Activities Attributes Awareness_cd: only for person targets. Would be a Subject Characteristic of the Subject (patient) Encounter_accommodation_cd: (Open issue) Maps to Subject location. Function_cd: 17 Activities must be decomposed so the activity type indicates the function performed by the role. Note_txt: comment attribute on Object Signature_cd: 18 could be viewed as a Qualifier of the Activity Signature_txt: could be viewed as a Qualifier of the Activity Status_cd: covered by states of activity related to agents such as performer selected/rejected/suspended Tmr: time points on the decomposed activities Type_cd: activities must be decomposed to the level that individual agents are related to it 17 The text refers to Actors, which are a class in USAM but not in this RIM. There is no facility in HcM to indicate the particular role an agent had in an activity other than those outlined in existing associations with activity. 18 This also points towards Subject Responsibility. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 45 of 50 Patient billing account This class is a subtype of financial act and not relevant to the NHS at this point in time. Patient_encounter This class is a subtype of Act and would be an Activity in HcM Associations Uses o..n Encounter_facility_association : refers to location link to Activity Is_authorised_by 0..1 Preauthorisation: related to finance. No equivalent in NHS Utilises 0..n Transportation : (Open issue) the activity of transportation would form part of the overall Activity of type patient encounter Attributes Acuity_level_cd: (Open issue) Activity qualifier of type acuity Birth_encounter_ind: indicates if person is new-born baby. This could be mapped to Activity Qualifier Classification_cd: Activity type of the Activity Discharge_desposition_cd: Subject Characteristic observed by the Activity of type discharge Effective_tmr: start/end timepoint associations with Activity Encounter_classification_cd: Activity type of the activity or a further Activity Qualifier Practice_setting_cd: Location for the Activity Pre_admit_test_ind: Activity Qualifier Source_cd: Activity Qualifier Special_courtesies_cd: Activity Qualifier Status_reason_cd: (Open issue) Activity Qualifier of the State change Activity Valuables_desc: Subject Characteristic Valuables_location_desc: Qualifier of the Subject Characteristic of type valuables Patient _Provider This class is a subtype of Role_relationship and would refer to Subject Responsibility in HcM Attributes Confidentiality_constraint_cd: this attribute relates to the person (Subject) so would be a Subject Characteristic. Preferred_pharmacy_id: (Open issue) could call this a Subject Responsibility of type preferred pharmacy Status_cd: state attribute of Subject Responsibility Very_important_person_cd: Subject Characteristic Person This class is a subtype of Living_subject and has some open issues. Would map to Subject in HcM HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 46 of 50 Associations Communicates_in language 0..n Person Language : Subject Characteristic of type Person Attributes Addr: Subject Location Ambulatory_status_cd: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type ambulatory status Birth_order_nbr: Subject Characteristic of type birth order Credit_rating_cd: Subject Characteristic of type credit rating Disability_cd: Subject Characteristic of type disability Education_level: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type education level Ethnic_group_cd: Subject Characteristic of type ethnic group Living_arrangement_cd: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type living arrangement Marital_status_cd: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type marital status Race_cd: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type race Religious_affiliation: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type religious affiliation Special_accommodation_cd: (Open issue) Subject Characteristic of type special accommodation Student_cd: Subject Characteristic of type student Person language (Open issue) Would be a Subject Characteristic of type person language in HcM Associations Is specified_by 0..n Is_communicated_by 1..1 Language_ability : qualified by 0..n Subject Property Qualifier Person: subject 1..1 Subject Attributes Cd: Identifier associated with Object Preference_cd: Subject Property Qualifier of type preference Place This class is a subtype of Entity and as such relates to Subject. Attributes Addr: Location Directions_txt: Subject Characteristic of type directions Gps_txt: (Open issue) specific US Position_txt: Subject Characteristic of type position Practitioner_Certifier This class is a subtype of Role_ relationship and maps to Authorised Agent in HcM HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 47 of 50 Attributes Board_certification_type_cd: could be seen as the Activity types related to the Authorised Agent Certification_dttm: Timepoint start association with Authorised Agent Recertification_dttm: Timepoint end association with Authorised Agent Residency_field_cd: (Open issue) Location for the Authorised Agent Practitioner provider This class is a subtype of Role_relationship and as such another Authorised Agent Attributes Position_cd: no definition for this attribute Primary_care_ind: would be included in the description / associations of the Authorised Agent Preauthorisation This class is a subtype of Unmapped_financial_classes and is related to financial authorisation before patient services are delivered. Therefore it is not applicable to the NHS. Procedure This class is a subtype of Act and would be covered under Activity in HcM Attributes Body_site_cd: Activity Qualifier of type procedure body_site Entry_site_cd: Activity Qualifier of type procedure entry_site Method_cd: Activity Qualifier of type procedure method Public health case This class is a subtype of Observation but could best be seen as an Incident of type Public health case. Attributes Detection_method_cd: (Open issue). An Incident in itself in HcM cannot be qualified, would need to be a Qualifier of Involvement in incident which relates to one Subject.19 Disease_imported_cd: Qualifier of Involvement in Incident for one Subject Transmission_mode_cd: (Open issue) Qualifier of Involvement in Incident Referral This class is a subtype of Act and relates to Activity in HcM 19 This Subject may be a defined population HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 48 of 50 Attributes Authorised_visits_qty: (Open issue) Activity Qualifier Desc: (Open issue) Activity Qualifier Reason_text: (Open issue) Activity Qualifier Resource slot Would correspond to Temporal Resource Act in HcM. Associations Is_managed_by 1,1 Schedule: decomposition of Activities Attributes Status_cd: Activity State Time_slot: Timepoint associations with Activity Role This class maps to Authorised Agent in HcM Associations Is_played_by 1..1 Participates_in Is_source_of Is_target_for 0..n Entity: Agent 1..1 subject association with Subject 0..n Participation: Agent 0..n associations with Activity 0..n Role_relationship: no mapping Role_relationship: no mapping Attributes Addr: Location association with the Authorised Agent Effective_tmr: timepoint association with the Authorised Agent Telecom: can only be recorded on the subject as subject contact. Type_cd: HcM has no types for authorised agent, the details lie in associations to Subject Characteristic Type and Authorised Agent Activity Role_relationship Relates again to Authorised agent but also to Inter Subject Relationship. In HcM Authorised Agents can only be linked together by creating another Authorised Agent . Associations Has_as_source Has_as_target 1..1 Has_parts 0..n Is_part_of 0..1 1..1 Role: no mapping Role: no mapping Role_relationship :no mapping Role_relationship: no mapping HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 49 of 50 Attributes Certificate_txt: no mapping Effective_tmr: Timepoint association to Authorised Agent Id: cannot quite see the relevance of this attribute which is referring to material. Identifier association with Object takes care of any additional identifiers. Position_nbr: limited to associations between entities where position is important. In that case this would refer to Inter subject relationship between Subjects which can be qualified with Subject Property Qualifier of type position Qty: how much of the target material is held in source material of a relationship, Subject Property Qualifier. Responsibility_cd: Access Group for Object Status_cd: (Open issue) depends on states possible. Type_cd: codes include codes for Inter subject relationships, Agents, and Authorised Agents. Schedule This class is a subtype of Role_relationship and would map to Temporal Resource Act in HcM. Associations Manages 0..n Resource_slot: parent/component association between Activities Attributes Slot_size_increment_qty: quantity attribute of Activity Status_cd: Activity State Specimen This class is a subtype of Role and would be viewed as a Subject in HcM. Attributes Body_site_cd: Subject Characteristic of type body_site Supply This class is a subtype of Act and maps to Activity in HcM Attributes Quantity: quantity attribute of Activity HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001 50 of 50 Transportation This class is a subtype of Act and maps to Activity in HcM Associations Is_utilised_during parent/ component 1..1 Patient_encounter: activities are linked with each other as Unmapped financial classes (Open issue) Not relevant to NHS Working list This class is a subtype of Act and an (Open issue). It would map to Activity in HcM. Attributes Ownership_level_cd: Access Group for Object In addition to the above classes there are also a set of Infrastructure classes and Data Type classes. Infrastructure classes These classes seem to be specific to the sending of messages/queries and the retrieval of structured information from tables. Important is where these classes link to the above classes. Message (Infrastructure) is associated with Entity (sender/recipient): message would be related to an Agent Message interaction is subtype of Act_context : no mapping Clinical_document_body is contained in Clinical_document and contains 1..n Structure. : these classes are under revision. HL7 Impact Assessment v1.0 March 2001