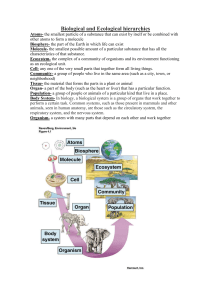
ANTH 307/ Ecological Anthropology
advertisement

ANTH 307/ Ecological Anthropology Final Exam Review Sheet Spring 2009/Minnesota State University Moorhead Dr. Roberts Yes ladies and gentlemn, the final is cumulative. The first part (~ 50 points) will cover material up to the mid-term. Look back at your notes on theory, foraging, horticulture, pastoralism, and intensive agriculture and you should be okay. The second part (~ 100 points) will be much more fun and cover material since the midterm lectures, Bates' chapters 7 and 8, assigned on-line readings, and the videos shown in class. The latter include: Life Running out of Control; The Riches of the Elephants - Zimbabwe; A Land of Immense Riches - Mozambique; The Shaman’s Apprentice. You'll find that I have links for most of these on the course web-site. In some cases the descriptions are more elaborate than others. The exam will consist of objective questions – multiple-choice, true-false, and matching – and a couple of essays with some leeway for choice. Industrial Agriculture Readings: Bates Chapter 7 and Industrial Agriculture in Evolutionary Perspective, by Peggy Barlett. What is the demographic transition and what's for food production? In what ways did the industrial revolution contribute to greater intensification of food production? What were the Green and Blue Revolutions? Were they without costs? What types of centralized administrative systems were developed in China and the former Soviet Union in the 20th century and why? Generally speaking, what happens to people when agriculture becomes mechanized and agricultural products and labor become devalued in relation to other commodities? Be familiar with the changes which took place in the case of Shinohata, Japan over the course of the 1950s to 1990s. Why is the case of Wasco, California illustrative of the development of agribusiness in the U.S? What kinds of differences did Sonya Salamon find between German and "Yankee" immigrant farmers in the Midwest? What did Creed's study of Zamfirovo reveal about collective agriculture in Bulgaria? Biotechnology and genetically modified foods Readings: Stone – Biotechnology and Suicide in India; Brenton – HIV/AIDS, Food Insecurity, and Genetically Modified Food Aid in Southern Africa; Tudge – The Greatest Folly of Our Age; Whitman – Genetically Modified Foods: Harmful or Helpful? What are genetically modified organisms? What are some of the potential benefits they are thought to have? What are some of the potential risks involved in their development and dissemination? How do GMOs affect people at the level of both producer and consumer? Why are corporations trying to patent crop genetic resources? How are some individuals – e.g., indigenous peoples, social activists and organic farmers— trying to fight this process? What can/should anthropologists do about this? Video: Life Running Out of Control. Conservation of Natural/Communal Resources Readings: Igoe – Measuring the Costs and Benefits of Conservation to Local Communities; Brockington and Igoe – Eviction for Conservation: A global Overview; Sodikoff – An Exceptional Strike: A Micro-History of "People versus Park" in Madagascar. Videos: The Riches of the Elephants - Zimbabwe; A Land of Immense Riches - Mozambique What are the basic approaches to conservation we talked about in class? Which type(s) is/are represented in the videos on CAMPFIRE in Zimbabwe and the Basaruto Archipelago Project in Mozambique? What kind of generalizations do Brockington and Igoe make with regard to evictions and conservation? Culture Change, development, and globalism Reading: Bates Chapter 8. Video: Thirst Over the course of human cultural evolution, what kinds of things have occurred during longterm culture change? Please try to understand the reasons for these related trends (i.e., do not just memorize and regurgitate them!) What are the differing assumptions of the modernization and dependency paradigms of development? What happened during and after the rapid entry of women into the industrial workforce in the cases of Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, and Cuba? What is cyberculture and what effect is it having upon cross-cultural diversity? What are the various ecological consequences of postindustrialism that Bates discusses? What are some of the critical contributions that have been made by development anthropologists? How does Della McMillan's involvement in the AAV planned settlement project illustrate what Bates calls "impact assessment?" What lessons does she draw from her experience? What does Bates say about those anthropologists who consider it unethical to interfere directly in peoples' lives by participating in development projects? Video: Thirst Indigenous Knowledge and Sustainable Development Readings: Shebitz – Weaving Traditional Ecological Knowledge into the Restoration of Basketry Plants; Demenge – Measuring Ecological Footprints in Subsistence Farmers in Ladakh. What is development and what is meant by the term sustainable development? Who are the stakeholders involved in the utilization of indigenous knowledge in development? What roles can/should anthropologists play in this process? What happens if we don't get involved? How does the concept of ecological footprint apply to ecological anthropology? Video: The Shaman's Apprentice.