Formation of the Solar System
advertisement

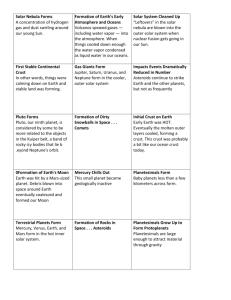
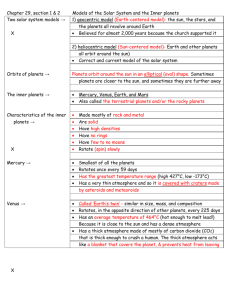
Formation of the Solar System Chapter 27 section 1 Objectives • Explain the ___________________ of the origin of the solar system. • Describe the formation of the __________ _________________________________ of Earth. Definitions • ______________________- the sun and all of the planets and other bodies that travel around it • __________________- any of the primary bodies that orbit the sun The Nebular Hypothesis • ____________- a rotating cloud of gas and dust • ____________________________- rotating cloud of gas and dust from which our sun and the planets of our solar system formed • The sun contains about _____________ of the material that was contained in the solar nebula How Did It Start? • During rotation, _____________________ __________________________________ __________________________________caused the center of the nebula to become very hot. • At ~ ______________________ hydrogen fusion began. Formation of the Planets • As the sun formed in the center the planets formed to the outside in 3 stages. • ____________________________- small bodies from which planets originated—joined together through collisions & gravity to form • _____________________- large bodies made of planetesimals— large body = ______________________________ • Protoplanets condensed to form planets and some moons. The Inner Planets • _______________________________________________ _____________________ • Contain lots of heavy elements— ________________________________ • Lost less dense gases—not enough _______________________ to hold them • All have solid surfaces and are _________ and ____________ than the outer planets The Outer Planets • _______________________________________________ _____________________ • Formed far from the sun and did not lose ___________________________ • Called _____________________ because they are composed mostly of gas. They have low density and are HUGE. Pluto • Farthest from the sun • Tiny—smaller than __________________ • Ice ball made of frozen __________________________________ • No longer a planet more on this in section 4 Formation of Solid Earth • When Earth first formed, it was extremely ___________________ because of: – ______________________ produced when planetesimals collided – Increased ____________________ of outer layers compressing inner layers – Abundance of _________________________ ______________________________ Early Solid Earth • Formed through _________________________ • Differentiation- process through which dense material sinks to the ______________________ and forces less dense material to the ______________________________________ – __________________- dense center of iron & nickel – ________________- thick layer of iron & magnesium rich rock – _______________- thin outermost layer of less dense silica rich rock Present Solid Earth • Surface cooled enough for ____________ ________________ to form • Surface continued to change because of – ____________________________________ – ____________________________________ – Interactions with the forming _____________ ______________________ Formation of Earth • • • • • • Solar nebula—spinning & becoming warm near the center ↓ Planetesimals form ↓ Gravity causes planetesimals to collect more nebular material ↓ Protoplanets form then condense to form planets and some moons ↓ Very hot Earth with 3 energy sources: (1) planetesimal collisions, (2) compression of inner layers, (3) radioactive materials ↓ Earth began to cool and experience differentiation: core- iron & nickel, mantle- iron & magnesium, crustsilica rich rock • ↓ Earth’s surface cooled enough for solid rock to form—changes continue due to interior heat, impacts, & atmospheric interactions Formation of Earth’s Atmosphere • Earth’s atmosphere formed because of _________________________________. • Least dense materials (_______________ ____________________) rose to the surface and formed our original atmosphere. Early Atmosphere • Original atmosphere was made of hydrogen & helium. • As the sun heated the gases, they began to expand and move rapidly. • Earth’s gravity wasn’t ________________ __________________________________ • Hydrogen and helium were probably blown away by the solar wind. Outgassing • ___________________- process whereby gases were expelled by Earth. • Main gases released were H2O vapor, CO2, N2, CH4, SO2, & NH3 Present Atmosphere • Organisms that were able to survive the early atmosphere developed—mainly bacteria and plants—used CO2 for ______ _________________________ which left us with an oxygenated atmosphere. • About __________________ years ago, the atmosphere reached its present composition Formation of Earth’s Oceans • Most of the water started out as comets—icy bodies--got too close to the ________ ________________________ early Earth. • Because of the heat, the water _____________ and became part of the ___________________. • As Earth cooled, the water _________________ and fell as _______________. • As it ran over the surface, _________________ dissolved in the water. The Oceans’ Effects on the Atmosphere • Oceans keep _______________________ down by dissolving and holding __________________.