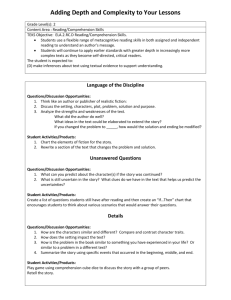
Download, Print, & Share
advertisement
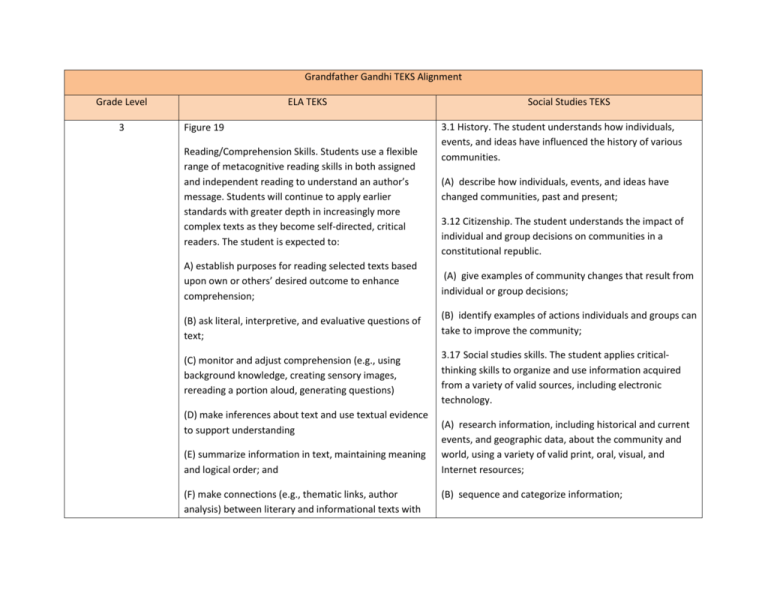
Grandfather Gandhi TEKS Alignment Grade Level 3 ELA TEKS Figure 19 Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author’s message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: Social Studies TEKS 3.1 History. The student understands how individuals, events, and ideas have influenced the history of various communities. (A) describe how individuals, events, and ideas have changed communities, past and present; 3.12 Citizenship. The student understands the impact of individual and group decisions on communities in a constitutional republic. A) establish purposes for reading selected texts based upon own or others’ desired outcome to enhance comprehension; (A) give examples of community changes that result from individual or group decisions; (B) ask literal, interpretive, and evaluative questions of text; (B) identify examples of actions individuals and groups can take to improve the community; (C) monitor and adjust comprehension (e.g., using background knowledge, creating sensory images, rereading a portion aloud, generating questions) 3.17 Social studies skills. The student applies criticalthinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including electronic technology. (D) make inferences about text and use textual evidence to support understanding (E) summarize information in text, maintaining meaning and logical order; and (F) make connections (e.g., thematic links, author analysis) between literary and informational texts with (A) research information, including historical and current events, and geographic data, about the community and world, using a variety of valid print, oral, visual, and Internet resources; (B) sequence and categorize information; 4 similar ideas and provide textual evidence. (C) interpret oral, visual, and print material by identifying the main idea, distinguishing between fact and opinion, identifying cause and effect, and comparing and contrasting Figure 19 5.5 History. The student understands important issues, events, and individuals in the United States during the 20th and 21st centuries. Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author’s message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: A) establish purposes for reading selected texts based upon own or others’ desired outcome to enhance comprehension; (B) ask literal, interpretive, and evaluative questions of text; (C) monitor and adjust comprehension (e.g., using background knowledge, creating sensory images, rereading a portion aloud, generating questions) (D) make inferences about text and use textual evidence to support understanding (A) analyze various issues and events of the 20th century such as industrialization, urbanization, increased use of oil and gas, the Great Depression, the world wars, the civil rights movement, and military actions 5.24 Social studies skills. The student applies criticalthinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including electronic technology. (A) differentiate between, locate, and use valid primary and secondary sources such as computer software; interviews; biographies; oral, print, and visual material; documents; and artifacts to acquire information about the United States; (B) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making 5 (E) summarize information in text, maintaining meaning and logical order; and generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions; (F) make connections (e.g., thematic links, author analysis) between literary and informational texts with similar ideas and provide textual evidence. (D) identify different points of view about an issue, topic, or current event; and Figure 19 Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author’s message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: A) establish purposes for reading selected texts based upon own or others’ desired outcome to enhance comprehension; (B) ask literal, interpretive, and evaluative questions of text; (C) monitor and adjust comprehension (e.g., using background knowledge, creating sensory images, rereading a portion aloud, generating questions) (D) make inferences about text and use textual evidence (E) identify the historical context of an event. to support understanding (E) summarize and paraphrase texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order within a text and across texts; and (F) make connections (e.g., thematic links, author analysis) between and across multiple texts of various genres and provide textual evidence. 6 Figure 19 Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author’s message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: (A) establish purposes for reading selected texts based upon own or others’ desired outcome to enhance comprehension; (B) ask literal, interpretive, evaluative, and universal questions of text; (C) monitor and adjust comprehension (e.g., using background knowledge; creating sensory images; rereading a portion aloud; generating questions); 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. (A) trace characteristics of various contemporary societies in regions that resulted from historical events or factors such as invasion, conquests, colonization, immigration, and trade; and (B) analyze the historical background of various contemporary societies to evaluate relationships between past conflicts and current conditions. 6.2 History. The student understands the influences of individuals and groups from various cultures on various historical and contemporary societies. (B) evaluate the social, political, economic, and cultural contributions of individuals and groups from various societies, past and present. 6.15 Culture. The student understands the similarities and (D) make inferences about text and use textual evidence to support understanding; (E) summarize, paraphrase, and synthesize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order within a text and across texts; and (F) make connections (e.g., thematic links, author analysis) between and across multiple texts of various genres, and provide textual evidence. differences within and among cultures in various world societies. (A) define culture and the common traits that unify a culture region; (F) identify and explain examples of conflict and cooperation between and among cultures. 6.19 Culture. The student understands the relationships among religion, philosophy, and culture. (A) explain the relationship among religious ideas, philosophical ideas, and cultures; and 6.21 Social studies skills. The student applies criticalthinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including electronic technology. (B) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions; (D) identify different points of view about an issue or current topic; (E) identify the elements of frame of reference that influenced participants in an event; and 8 8.20 Citizenship. The student understands the importance of voluntary individual participation in the democratic process. (C) analyze reasons for and the impact of selected examples of civil disobedience in U.S. history such as the Boston Tea Party and Henry David Thoreau's refusal to pay a tax. 8.29 Social studies skills. The student applies criticalthinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including electronic technology. (B) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions; (D) identify points of view from the historical context surrounding an event and the frame of reference which influenced the participants;