Havard Reference System
advertisement

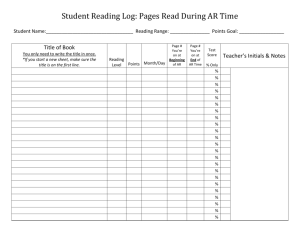
Centre for Instructional and Technology Support Referencing – The Harvard System Referencing Within the Text (a) To refer to a single author (surname, date) E.g. (Chan, 2007) After a summary of the author’s work or a reference to his work you must insert the author’s surname follows by the date of publication. Example: The world weather has changed significantly and it has caused havoc in many countries including Malaysia which all this while has been spared by natural disaster (Chan, 2007). If you include the author’s name as part of your sentence, then you must put the date of publication in brackets. Example: Chan (2007) believed that the world weather has changed significantly and it has caused havoc in many countries including Malaysia. (b) Other variations include Dual authors • (surname and surname, date) • E.g. (Chan and Peter, 2007) 2/12/2016 Page 1 of 5 More than two authors • (surname et al., date) • E.g. (Chan et al., 2007) Work by different authors generally • (surname, date; surname, date) in alphabetical order • E.g. (Lee, 2005; Sue, 2006; William, 1999) Different publications by the same author • (surname, date, date) in ascending order • E.g. (Lewis, 1991, 1998). (c) Secondary Reference: An author referred to by another author where the original has not been read. (surname, date; cited by surname, date) E.g. (Smith, 1999; cited by Lim, 2003) In this situation you are reading an article written by Lim and there is a quote in the article from another source by Smith. You want to include the quote by Smith in your assignment, but you have not read Smith’s original source. Example: Many studies conducted in Asia support the assertion that online forum discussions play a crucial role in support of a face-to-face teaching in particular where collaboration is essential in the construction of knowledge (Smith, 1999; cited by Lim, 2003). Your bibliography at the end of the assignment should contain the text from Lim. You cannot include the text from Smith because you have not read it. (d) A newspaper article with no obvious author (publication name, date) E.g. (The Sun, 2007) You have read an article in the newspaper and you would like to quote that article in your assignment. The way to do it is similar to the single author reference mentioned in part (a). Example: It was reported in The Sun (2007) that the five accused in a high profile murder trial were freed, with the judge putting the blame squarely on sloppy police investigation and poor prosecution. 2/12/2016 Page 2 of 5 (e) An article from online journal (surname, date) E.g. (Goodwood, 2002) Surfing the Internet can give you a rich source of information but you have to be careful as to which one is relevant and valid for your assignment. Always use articles obtained from respectable online journals, big corporation reports, government reports, and many others. Do be wary of papers from individual unless it is a well known personality like Mr. Bill Gates. You should quote the article in similar manner as in part (a). (f) A direct quotation (surname or corporate name, date: page) where ‘page’ is the page in the original publication on which the quotation appears. ■ E.g. ‘ … Malaysian students are rather weak in their cognitive skills’ (Bell, 1998: 32) In a direct quotation you copy another author’s material word-for-word. You should indicate in your assignment that it is a direct quotation by placing the material in inverted commas. Traditionally, we use double inverted commas ( “ ) but it is now acceptable to use single inverted commas ( ‘ ). Please note that when you use a direct quotation, you must reproduce the author’s words exactly as it was written including all spelling, punctuation, capitalization and errors. Example: ‘… referencing is important for reasons other than avoiding plagiarism. When you reference correctly you are demonstrating that you have read widely on a topic.’ (Michael, 2007: 25) The Bibliography At the end of your assignment you should indicate all the sources you have referred to in the text. The list of all the sources is known as bibliography. Please note that you must arrange the list in alphabetical order by author’s surname and do not separate out the articles from books, journal and other sources. (a) Journal articles 2/12/2016 Page 3 of 5 Surname, initials. and surname, initials. (date) ‘Title of article’, Journal name, volume number:part number, pages. Example: Storey, J., Cassy, K. and Wilkinson, M. (2001) ‘Changing Economics Tide’, Economics Review, 23:1, 23 – 43. (b) Book other than first edition Surname, initials. and surname, initials. (date) Title (? edn), place of publication, publisher. Example: Morris, B. (1997) Quantitative Methods in Business (3rd edn), New York, Mintel International Group Ltd. (c) Chapter in a book Surname, initials. and surname, initials. (date) Title, place of publication, publisher, Chapter ?. Example: Robson, D.C. (1994) World Research, Oxford, Blackwell, Chapter 5. (d) Newspaper article Surname, initials. and surname, initials. (date) ‘Title of article’, newspaper name, day, month, pages. Example: Lee, G.H. (2006) ‘Selangor State Government to Answer’, The Sun, 10 August, p. 2. 2/12/2016 Page 4 of 5 (e) Conference papers Surname, initials. and surname, initials. (date) ‘Title of paper’, paper presented at the conference name, days, month, location of conference. Example: Chan, C.T. and Michael, L. (2005) ‘E-Learning in a Private College’, paper presented at the INTI International Congress, 28-29, August, Nilai Malaysia. (f) Journal published on the Internet Surname, initials. and surname, initials. (date) ‘Title of article’, journal name, volume number:part number, (online)(cited day month year). Available from URL:http://www. remainder of full Internet address Example: Jenkins, M (2003) ‘The Role of CITS in Supporting Academic Staff’, Journal of Teaching and Learning, 2:3, (online) (cited 13 April 2006). Available from URL:http://www.chlt.ac.uk./cwls/pubs/issue2.3/page5.htm 2/12/2016 Page 5 of 5