Forecasting Practice Problems
advertisement

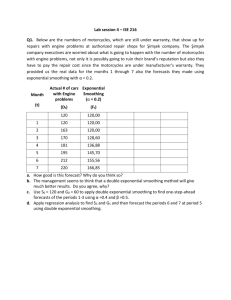
Forecasting Practice Problems 1. Given the following actual sales, t A(t) 1 8 2 4 3 9 4 11 5 10 a. Use Simple Moving Average method (with n = 3) to forecast sales in periods 6, 7, and 8. b. Use Weighted Moving Average method (with weights of 0.6, 0.3, 0.1) to forecast sales in periods 6, 7, and 8. c. Use Exponential Smoothing method (with = 0.4) to forecast sales in periods 6, 7, and 8. (Hint: Use the first 2 data sets to initialize the Exponential Smoothing forecasting model, then update the forecasts in periods 3, 4, and 5.) 2. Given the data below, what is the Simple Linear Regression model that can be used to predict sales? t A(t) 1 150 2 157 3 162 4 166 5 177 3. Given the following actual sales, t A(t) 1 2 2 6 3 5 4 8 5 10 6 13 7 15 8 14 a. Use the first 4 sets of data and Simple Linear Regression to initialize the Holt’s Trend Model. b. Use Holt’s Trend Model (with = 0.2, = 0.4) to update the forecasts in periods 5, 6, 7, and 8. c. Use Holt’s Trend Model (with = 0.2, = 0.4) to make forecasts for periods 9, 10, 11, and 12. 4. Given the following actual sales, 2003 2004 Spring Summer Fall Winter Spring Summer A(t) 33 12 18 27 36 13 Fall 15 Winter 29 2005 Spring 34 Summer 10 Fall 16 Winter 30 a. Use the first 2 years of data to initialize the Seasonal Model (without trend). b. Use Seasonal Model (without trend), (with = 0.3, = 0.4) to update the forecasts in 2005. c. Use Seasonal Model (without trend), (with = 0.3, = 0.4) to make forecasts for 2006. 5. Given the following actual sales, A(t) Spring 8 Summer 14 Fall 12 Winter 29 2004 Spring 11 Summer 19 Fall 13 Winter 32 2005 Spring 17 Summer 19 Fall 15 Winter 36 a. Use the first 2 years of data and the Decomposition Forecasting method to initialize the Winter’s Model. b. Use Winter’s Model, (with = 0.3, = 0.4, = 0.2) to update the forecasts in 2005. c. Use Winter’s Model, (with = 0.3, = 0.4, = 0.2) to make forecasts for 2006. 2003 6. Given the following actual sales, t A(t) 1 12 2 17 3 14 4 19 5 16 6 12 7 23 a. Use the first 2 data sets to initialize the Exponential Smoothing forecasting model. b. Use Exponential Smoothing method (with = 0.3) to update the forecasts in periods 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. c. Calculate the bias and MAD using the actual and forecast sales in periods 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. d. Use Exponential Smoothing method (with = 0.8) to update the forecasts in periods 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. e. Calculate the bias and MAD using the actual and forecast sales in periods 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. f. Comparing the bias and MAD from the two forecasting models, what conclusion can you make? 7. Continued from the previous problem, a. Calculate the MPE and MAPE using the actual and forecast sales (Exponential Smoothing method with = 0.3) in periods 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. b. Calculate the MPE and MAPE using the actual and forecast sales (Exponential Smoothing method with = 0.8) in periods 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. c. Comparing the MPE and MAPE from the two forecasting models, what conclusion can you make? 8. Given the following actual and forecast sales, t A(t) F(t) 1 4.0 2 8.0 6.0 3 7.0 6.8 4 9.0 6.8 5 12.0 7.6 6 11.0 9.3 7 13.0 9.9 8 12.0 11.1 a. Calculate the tracking signals starting from period 3. b. When will the tracking signal exceed 5.0?