Document 7289599
advertisement

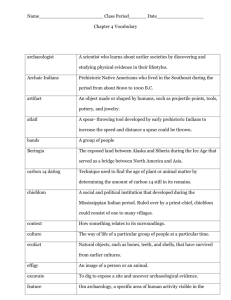
Prehistoric Indian Civilizations Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Which was not a part of the prehistoric Indian culture in Georgia? a. Mississippian b. Woodland c. Paleo d. Creek 2. Native Americans used plants a. to fight diseases. b. as cooking, storing, and serving containers. c. as clothing decorations. d. as trade goods. 3. Which definition best describes a barter economy? a. Trading items for other items within a family b. Trading items or services without the use of money c. Buying and selling items for cash d. Buying and trading items with coins 4. Which statement does not give a probable reason for the disappearance of the Mississippian tribes? a. English settlers killed them. b. Disease or starvation killed them. c. They moved away in search of food. d. They died out because of tribal warfare. 5. Which statement best explains why there are so few Paleo sites in Georgia? a. Remains from the “Old Stone Age,” when Paleo Indians lived, have been destroyed by natural forces such as erosion and changes in Earth’s surface. b. Because the Paleo Indians were nomadic, they did not leave many artifacts in one place. c. Because the Paleo Indians were concentrated primarily in western states, few would have been in Georgia. d. As the oldest prehistoric civilization, most Paleo archaeological sites have been destroyed. 6. Which factor resulted in prehistoric Indians settling in groups in a permanent area? a. Large game was abundant. b. The Indians began to cultivate plants as foods. c. Prehistoric Indians followed herds of large animals. d. Prehistoric Indians wanted to band together for protection. 7. Which statement best explains why archaeologists claim that learning to make and use pottery was one of the greatest contributions of the Archaic Indians? a. Pottery was used to hold water for the tribe. b. Pottery allowed the prehistoric Indians to record their culture for future generations through drawings and symbols on the pots. c. The Archaic Indians learned to decorate their pottery. d. Pottery could be used to store food, allowing prehistoric Indians to survive living in one area. 8. Which statement explains why archaeologists consider prehistoric Indians to have believed in some form of life after death? a. The legends of an afterlife were passed down from generation to generation until today. b. Burial mounds for the dead contained items such as tools, tobacco pipes, and weapons. c. Their pictographs and cave drawings depicted a spiritual world after the living world. d. Their tribal centers had churches for worship. ____ 9. Which statement is not an indication that the Mississippian people were an advanced civilization? a. From archaeological sites, we know they had sophisticated farming methods and used farming tools. b. From archaeological sites, we know that they lived in villages. c. From archaeological sites, we know that they were nomadic, following herds of large animals that were their primary food source. d. From archaeological sites, we know that their dress and fashion styles became more complex and sophisticated. ____ 10. The Creek Indians were like modern-day Georgians in that a. their large villages were surrounded by smaller villages and large farm areas. b. religious and government buildings or facilities were in the center of their communities. c. when their villages became too large, they split and established a new village. d. their homes or residences were built of nearby materials. ____ 11. Cherokee family life was similar to the lives of modern-day Georgians because a. the tribe was the focal point for the organization of society. b. children played at games that helped them learn their adult roles. c. at different times, many different family members lived and worked together helping each other. d. it was a matrilineal society, with family blood lines traced through the mother. ____ 12. Which statement best explains the information on the map? a. The east coast of the United States has not changed in 20,000 years. b. There is less land in the world today than 20,000 years ago. c. Florida was a peninsula 20,000 years ago. d. The British Isles were islands 20,000 years ago. ____ 13. According to the map, the people who came to North America via the Bering land bridge moved as far south as the present country of a. b. c. d. the United States. Canada. Mexico. Guatemala. ____ 14. According to the map, which section of Georgia has no mounds? a. Northwest b. Southwest c. Northeast d. Southeast ____ 15. What does the information on the map tell you about the moundbuilders? a. The moundbuilders lived throughout Georgia. b. The moundbuilders mostly settled along the coast. c. The moundbuilders built cone-shaped mounds. d. The moundbuilders believed in an afterlife. ____ 16. Which county does not have any mounds? a. Bartow b. Dade c. Greene d. White ____ 17. Mounds are found in a. Bartow County. b. Gwinnett County. c. Lamar County. d. Polk County. Matching Match each prehistoric period to the statement that describes it. You may use each letter more than once. a. Woodland period c. Paleo period b. Mississippian period d. Archaic period ____ ____ ____ ____ 18. 19. 20. 21. Some villages were protected by moats, guard towers, and wooden fences. Nomadic hunters followed herds of large animals. People began to turn from large game to smaller animals for food. People began to band together in groups called tribes. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. People painted or tattooed their bodies and often wore feather headdresses. People hunted primarily with long wooden spears. People developed drills, choppers, and chipping tools made from deer antlers. The highest prehistoric culture in Georgia’s history lived during this period. People first used the bow and arrow for hunting. People first used a grooved axe on a wooden handle. This period is also known as the Temple Mound period. People built cone-shaped burial mounds for their dead. Evidence indicates that people moved each season in search of food. People started horticulture, the cultivating of plants and trees. People first baked pottery to make it last longer. Indians in this period grew most of their own foods. Evidence indicates that several small groups banded together to form camps. This was the oldest known prehistoric Indian period. People first used clay containers to store, cook, and serve their foods. People hunted with long weighted spears with hooks on the end. Prehistoric Indian Civilizations Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: TOP: 2. ANS: TOP: 3. ANS: TOP: 4. ANS: TOP: 5. ANS: TOP: 6. ANS: TOP: 7. ANS: TOP: 8. ANS: TOP: 9. ANS: TOP: 10. ANS: TOP: 11. ANS: TOP: 12. ANS: TOP: 13. ANS: TOP: 14. ANS: TOP: 15. ANS: TOP: 16. ANS: TOP: 17. ANS: TOP: D DIF: Easy Prehistoric Indians A DIF: Average Georgia Indian Tribes B DIF: Average Georgia Indian Tribes A DIF: Hard Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Hard Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Hard Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Hard Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Average Prehistoric Indians C DIF: Average Prehistoric Indians A DIF: Hard Georgia Indian Tribes C DIF: Hard Georgia Indian Tribes B DIF: Hard Using Maps C DIF: Average Using Maps D DIF: Easy Using Maps A DIF: Average Using Maps C DIF: Average Using Maps A DIF: Average Using Maps REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 2 STO: QCC 9 REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 2 STO: QCC 9 REF: Section 2 STO: QCC 9 REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a B DIF: Average Prehistoric Indians C DIF: Average Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a MATCHING 18. ANS: TOP: 19. ANS: TOP: 20. ANS: TOP: 21. ANS: TOP: 22. ANS: TOP: 23. ANS: TOP: 24. ANS: TOP: 25. ANS: TOP: 26. ANS: TOP: 27. ANS: TOP: 28. ANS: TOP: 29. ANS: TOP: 30. ANS: TOP: 31. ANS: TOP: 32. ANS: TOP: 33. ANS: TOP: 34. ANS: TOP: 35. ANS: TOP: 36. ANS: TOP: 37. ANS: TOP: Prehistoric Indians A DIF: Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Prehistoric Indians C DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Prehistoric Indians A DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Prehistoric Indians A DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians A DIF: Prehistoric Indians B DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians C DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians D DIF: Prehistoric Indians Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Easy REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Average REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a Hard REF: Section 1 STO: QCC 6, GPS SS8H1a