The Big Bang - Tasker Milward Physics Website
advertisement

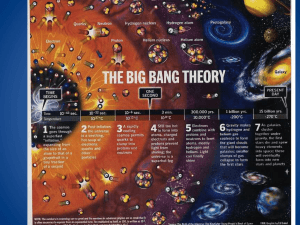
PISA Style Question The Big Bang Theory Read the text about the Big bang Theory. In the 1920s, astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered the universe was not static. Rather, it was expanding, a find that revealed the universe was apparently born in an event we call the Big Bang. The Big Bang is thought to have happened around 13.8 billion years. It is thought to have begun as an unimaginably hot, dense point which rapidly expanded outwards. As space expanded, the universe cooled and matter formed. One second after the Big Bang, the universe was filled with neutrons, protons, electrons, anti-electrons, photons and neutrinos. During the first three minutes of the universe, the light elements were born. Temperatures cooled from 1032 oC to 109 oC, and protons and neutrons collided to make deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen. Most of the deuterium combined to make helium, and trace amounts of lithium were also generated. Roughly 380,000 years after the Big Bang, matter cooled enough for atoms to form, resulting in a transparent, electrically neutral gas. This set loose the initial flash of electromagnetic radiation created during the Big Bang, which is detectable today as cosmic microwave background radiation. About 400 million years after the Big Bang, clumps of gas collapsed enough to form the first stars and galaxies. A little after 9 billion years after the Big Bang, our solar system was born. Question 1 : BIG BANG In the text, the beginning of the universe is described. Which of the following statements best describe how the universe evolved? A B C D The temperature and density increased as the universe expanded. The temperature and density decreased as the universe expanded. The temperature increased and the density decreased as the universe expanded. The temperature decreased and the density increased as the universe expanded. Question 2 : BIG BANG By what factor did the temperature of the universe decrease in the first three minutes after the Big Bang? A B C D A factor of 32 A factor of 23 A factor of 1023 A factor of about 3.5 Question 3 : BIG BANG Which of these statements best describes the composition of the universe after one second? A B C D Positive and negative particles and electromagnetic radiation Positive, negative and neutral particles Neutral particles and electromagnetic radiation Positive, negative and neutral particles and electromagnetic radiation. Question 4 : BIG BANG After 380,000 years atoms began to form. Circle ‘yes’ or ‘no’ for each statement that describes the formation of atoms: The formation of atoms There are equal numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus in order that the atom is neutral Yes or No ? Yes / No There are equal numbers of protons and electrons in the nucleus in order that the atom is neutral Yes / No There are equal numbers of protons and neutrons in the atom in order that the atom is neutral Yes / No There are equal numbers of protons and electrons in the atom in order that the atom is neutral Yes / No Question 5 : BIG BANG Which of the following is the best estimate for the age of our solar system? A B C D 4.5 billion years 13.8 billion years 9 billion years 400 million years Look at the diagram that represents the development of the universe Question 6 : BIG BANG Which of the following statements best describes the scales shown on the diagram? A B C D The horizontal and vertical scales are both linear. The horizontal scale is non-linear, the vertical scale is linear. The horizontal scale is non-linear, we do not know whether or not the vertical scale is linear. Both scales are non-linear. Question 7: BIG BANG Which of the following is the closest estimate to the duration of the ‘Quark Soup’ era? A B C D 1 second 10-12 seconds 10-11 seconds 0.1 seconds Question 8: BIG BANG Use information from the diagram and from the text on page 1 to explain the likely meaning of the term ‘parting company’ on the diagram. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… SCORING : BIG BANG Question 1 Full credit B The temperature and density decreased as the universe expanded. No credit Other responses Missing Narrative : The text says that the universe began as ‘an unimaginably hot, dense point which rapidly expanded outwards. As space expanded, the universe cooled and matter formed.’ The question basically tests the candidate’s ability to relate cooling to a decrease in temperature and expansion to a decrease in density. Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Low Question 2 Full credit C A factor of 1023 No credit Other responses Missing Narrative : The factor by which the temperature decreases is arrived at by subtracting the powers of ten (the difference between oC and K is negligible for such large temperatures – and few GCSE candidates will be familiar with the Kelvin scale). Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Medium Question 3 Full credit D Positive, negative and neutral particles and electromagnetic radiation. No credit Other responses Missing Narrative : The passage states that ‘the universe was filled with neutrons, protons, electrons, anti-electrons, photons and neutrinos’. It would be reasonable to expect a GCSE candidate to recognise that protons are positive, electrons are negative, neutrons are neutral and photons are electromagnetic radiation. This can be deduced without knowing anything about neutrinos or anti-electrons. Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Medium Question 4 Full credit No No No Yes No credit Other responses Missing Narrative : This requires a basic knowledge of atomic structure and the ability to recall that the majority of elements in the periodic table have more neutrons than protons in the nucleus. Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Question 5 Full credit A 4.5 billion years No credit Other responses Missing Low Narrative : The candidate is required to extract the information that ‘A little after 9 billion years after the Big Bang, our solar system was born’ and subtract it from the estimated age of the universe of 13.8 billion years. This gives 4.5 billion years as the closest answer. The other responses would typically be extracted directly from the text without understanding what is required to arrive at the age of our solar system. Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Medium Question 6 Full credit C The horizontal scale is non-linear, we do not know whether or not the vertical scale is linear. No Credit Other responses Missing Narrative : The question tests the candidate’s ability to recognise what is meant by a linear and non-linear scale. The horizontal scale is clearly non-linear. Most readers may tend to assume that the vertical scale is linear and that the gradient indicates the relative rate of expansion, but there is nothing on the diagram to confirm that this is the case. Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Medium Question 7 Full credit A 1 second No credit Other responses Missing Narrative : According to the diagram the Quark Soup era is between 10-12 seconds and 1 second. Since the difference between these two values is basically 1 second (a standard scientific calculator returns an answer of 1 for this calculation) then A is the best estimate. Answer D (0.1 seconds) demonstrates an understanding that the difference between the values at the start and end of the Quark Soup era need to be subtracted but a lack of understanding of what is meant by 10-12 and the nonlinearity of the scale. Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand Medium Question 8 : BIG BANG Full credit Reference to the formation of atoms and a link to protons and neutrons already having formed nuclei of simple elements and electrons beginning to orbit these nuclei – hence ‘parting company’ of protons, neutrons and electrons from the ‘soup’ of the earlier era. OR Reference to the formation of atoms as described, and the ‘parting company’ of protons/neutrons/electrons from the electromagnetic radiation which was then ‘let loose’. Partial credit A partially correct attempt to explain either of the above ideas – perhaps with a lack of clarity or some minor errors. No credit Other responses Missing Narrative : Framework Categories Knowledge type 2015 Framework Competency Context Cognitive demand High