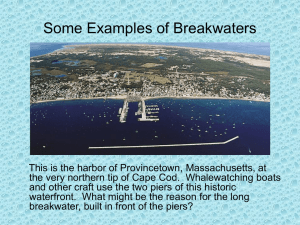
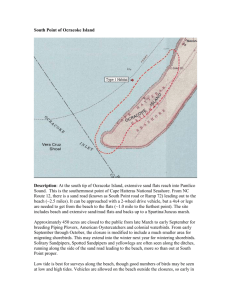
File
advertisement

Review 8 – Deserts, Glaciers, Oceans, and Climate These questions are a selection pulled from the Tarbuck and Lutgens Earth text. As a result, they may not by in numerical order. To get credit, highlight/bold/italic/mark your answer and uploaded the saved file into the D2L dropbox. As long as you turn in your own copy and actively participate in doing the work, you may do these homeworks in small groups (I reserve the right to change this policy if it looks like people are turning in work that they had no involvement in). Chapter 18 Glaciers and Glaciation Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology, 9e (Tarbuck/Lutgens) 18.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 4) Where is the world's largest ice sheet located today? A. Greenland B. Russia, Siberia C. Iceland D. Antarctica 5) Approximately how long ago did the last of the great North American ice sheets melt? A. 1500 yrs B. 1.5 million yrs C. 15,000 yrs D. 150,000 yrs 8) Which one of the following applies to a valley glacier that lengthens (extends its terminus downslope) over a period of many years? A. Wastage exceeds accumulation. B. Accumulation exceeds wastage. C. Accumulation and wastage are about equal. D. none of the above 9) Abrasion and plucking generally involve what part of a glacier? A. the internal, flowage zone B. the snout zone C. the surface, brittle zone D. the basal, sliding zone 10) A ________ cross-valley profile is typical of canyons and valleys eroded and deepened by alpine or valley glaciers. A. U B. Y C. V D. S 30) Which process occurs where a glacier enters the sea? A. kaming B. calving C. surging D. drowning 31) The ________ of the geologic time scale represents the time of the most recent "Ice Age." A. Pleistocene era B. Pliocene epoch 1 C. Pleistocene epoch D. Pliocene era 34) A ________ is an erosional feature specifically produced by alpine glaciation. A. lateral moraine B. drumlin C. crevasse spur D. U-shaped valley 37) A drumlin is a ________. A. smooth, tapering ridge of till; formed and shaped beneath a continental ice sheet B. bowl-shaped depression eroded largely by frost action and glacial plucking C. till mound of outwash deposited by meltwater streams at the snout of a glacier D. smooth, striated, bedrock ridge shaped and polished by a glacier 42) Which one of the following statements concerning glacial deposits is not true? A. Till is deposited directly from the ice; outwash is deposited by meltwater streams. B. Glacial erratics are blocks of rock that are too large for the glacier to move. C. Tills are poorly sorted and the fragments are mostly angular. D. Outwash is mainly stratified sand and gravel. 18.3 True/False Questions 2) T or F: Crevasses are short, narrow cracks in the plastic flow zone of a glacier that alternately open and close as the ice flows along. 4) T or F: Till is an unsorted sediment deposited directly from the melting glacial ice; stream action is not involved. 19) T or F: Rock flour consists of silt-sized, rock and mineral particles produced by glacial abrasion. Chapter 19 Deserts and Winds Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology, 9e (Tarbuck/Lutgens) 19.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which one of the following statements is true? A. Desert landscapes are monotonous, relatively flat areas covered to various depths with sand. B. Deserts and dry lands are concentrated in areas of ascending air masses and relatively low atmospheric pressures. C. Despite infrequent rainfalls, erosional and depositional features of running water are important in desert landscapes. D. Rainshadow deserts occur where air masses descend after first having risen to cross a mountain range. 3) Most dry lands lie between ________ degrees north and south of the equator. A. 40 and 50 B. 20 and 30 C. 5 and 10 D. 0 and 5 4) Which one of the following statements concerning rock weathering is true? A. Warm temperatures and high soil moisture contents accelerate chemical weathering. B. Low temperatures and high soil moisture contents accelerate chemical weathering but inhibit mechanical weathering. C. Warm temperatures and low soil moisture contents both promote rapid rates of mechanical weathering. D. Temperature has no effect on rock weathering. 6) ________ refers to the "bouncing" mode of sand transport in a windstorm or stream. A. Saltation B. Ventifaction C. Siltation D. Deflation 2 9) In which area would surface water most effectively infiltrate into the local groundwater system? A. a stream in a steep-sided, bedrock canyon in the mountains B. streams flowing in the numerous channels of an alluvial fan C. a playa lake with a thick mud bottom D. All of the above would promote infiltration. 11) How is desert pavement formed? A. Deflation removes the coarse fragments leaving behind a layer of loess. B. Alluvial fans are eroded to form inselbergs with rocky surfaces. C. Groundwater in an alluvial fan evaporates, leaving behind a surface layer of hard-baked mud. D. Runoff and deflation carry off the silt and clay, leaving coarser particles behind. 18) Which of the following statements concerning dry lands is not true? A. Precipitation totals are low; dew points are lower in the summer than winter. B. Evaporation potential exceeds actual precipitation. C. Storms are infrequent and rainfall amounts are highly variable. D. Wind is the dominant agent of erosion and sediment transport. 19) How are sand grains transported by the wind? A. high in the moving air column as suspended load B. by saltation in the first few meters above the land surface C. by deflation of abraded desert pavement D. by being picked up in swirling dust clouds and carried to distant blowouts 20) Which of the following best describes the climatic factors that cause low latitude deserts like the Sahara in Africa? A. Cool, dry air aloft is descending; surface winds are blowing toward the equator. B. Warm, humid air aloft is descending; surface winds blow away from the equator. C. Warm, humid air is rising; surface winds are calm. D. Cool, dry air at the surface is rising causing winds to blow away from the equator. 26) A ________ is formed by abrasion of rocks by windblown sand. A. playa B. ventifact C. pediment D. desert pavement 31) Rainshadow deserts are common in ________. A. vast, dry, steppe lands like the Great Plains B. north central Africa C. the dry valleys of eastern California and Nevada D. Europe north of the Alps 19.3 True/False Questions 1) T or F: Running water is an important erosional agent in many arid lands despite infrequent rainfalls. 13) T or F: Sand is transported by saltation in running water and blowing winds. 18) T or F: Saltation refers to evaporation of shallow, muddy waters from a playa lake. Chapter 20 Shorelines Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology, 9e (Tarbuck/Lutgens) 20.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 3) Water movement and sand transport parallel to the beach are fundamentally caused by ________. A. strong, offshore winds creating a pileup of water along the beach front B. deep-water waves breaking offshore C. waves impinging obliquely onto a beach 3 D. a long fetch parallel to the beach 6) ________ are built more or less parallel to the beach. A. Jetties B. Seawalls C. Groins D. Breakers 17) Which of the following is true regarding the gravitational forces affecting Earth? A. The lunar force is stronger that of the Sun. B. The solar and lunar gravitational forces are about the same magnitude. C. The solar force is stronger that of the Moon. D. The gravitational forces of each vary depending upon seasons on Earth. Match the policy options with expected costs and long-term effectiveness, assuming that sea level will continue to slowly rise in the future. A. promote coastal development; build massive, hardened structures to stop all but the most powerful storm waves B. prohibits coastal development; build nothing, declare victory over the sea and retreat from the coastline C. allow coastal development; make a long-term commitment to beach nourishment 20) ___B_____ low initial costs and modest maintenance costs; high potential for storm damages and low to moderate potential for negative environmental effects 21) ___A_____ high initial costs and eventually high maintenance costs; high potential for storm damage and negative environmental consequences 22) ___C_____ low initial costs and low maintenance costs; low potential for storm damages and for negative environmental consequences 24) ________ are currents that move sand and water parallel to the beach. A. Reflected B. Longshore C. Translational D. Ebb tide 28) Which one of the following is an artificial coastal feature? A. breakwater B. sand spit C. sea arch D. barrier island 34) Which one of the following would not be a likely effect of a breakwater? A. increased, longshore current velocities between the breakwater and the beach B. dissipation of storm wave energy on the seaward side of the breakwater C. increased sand deposition between the beach and the breakwater D. increased erosion of the beach on one side of the breakwater 37) ________ not the direct result of longshore current action. A. Building and extension of spits are B. Closing off of small estuaries by baymouth bars is C. Transport of sand along the beach is D. Cracking and abrasion of rock at the base of a wave-cut cliff are 39) ________ are coastal structures designed to keep tidal inlets from shifting location or filling with sand. A. Breakwaters B. Seawalls C. Jetties D. Groins 40) Which one of the following statements concerning sea level is correct? 4 A. B. C. D. It has dropped since 900 A.D., but will probably rise for the next few hundred years. It dropped during the past few centuries and that trend will continue. It rose over past centuries but will probably drop in the next hundred years. It rose for the past few centuries and will continue to rise. 20.3 True/False Questions 7) T or F: Because the land is rising faster than sea level, storm damage and erosion along emergent coastlines are relatively unimportant. 8) T or F: Massive seawalls and groins, financed by the average taxpayer, are very cost-effective methods for protecting expensive, privately owned, beach front properties. 13) T or F: Groins are constructed perpendicular to the beach; they are designed to trap sand that might otherwise keep moving along the beach. 15) T or F: Over the past few centuries, sea level has been gradually falling. 20) T or F: Longshore sand transport and longshore currents depend on waves impinging parallel to a shoreline. Chapter 21 Global Climate Change Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology, 9e (Tarbuck/Lutgens) 21.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 7) Which one of the following is NOT a component of the climate system? A) biosphere B) solid Earth C) exosphere D) cryosphere E) hydrosphere 15) Which one of the following is NOT a trace gas contributing to a future global increase in temperature? A) nitrous oxide B) methane C) water vapor D) chlorofluorocarbons 17) The most realistic models of atmospheric warming predict that mean global surface temperature will increase about ________˚C during the second half of the 21st century. A) 2.5 B) 3.5 C) 4.5 D) 5.5 E) 6.5 27) The combustion of ________ has added great quantities of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. A) fossil fuels B) wood C) paper D) oxygen E) none of the above 30) The magnitude of a temperature increase due to greenhouse warming will probably be smallest in the ________. A) polar regions B) lower middle-latitudes C) higher middle-latitudes D) subtropics 5 E) tropics 21.3 True/False Questions 8) The climate system involves only Earth's atmosphere and solid surface. False 10) Positive feedback mechanisms produce results that are opposite of the initial change and tend to offset it. False 16) As a result of global warming, a significant melting of major ice sheets is expected during the next century. True 18) The hydrosphere refers to the snow and ice that exist at Earth's surface. True 6