Warm-up Problems - McGraw-Hill
advertisement

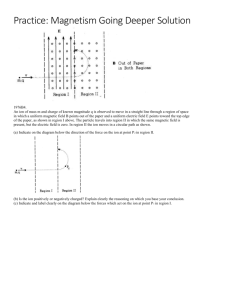
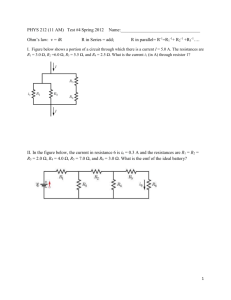
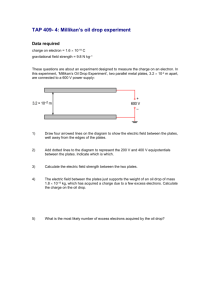
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 8 Section 8.1 Warm-up Problems Warm-up problems for student textbook pages 329–330 1. Two parallel, insulated, oppositely charged metal plates are separated by 2.5 cm. A test charge of 1.5 C is placed 1 cm from one of the plates, and experiences a force of magnitude 835 N. (a) Determine the magnitude of the electric field intensity at the location of the test charge. (b) Determine the magnitude of the electric field intensity at the midpoint between the plates. 2. In question 1, suppose the area of the plates is doubled. How does the magnitude of the electric field intensity change? 3. In question 1, suppose the charge on each plate is doubled. How does the magnitude of the electric field intensity change? 4. In question 1, suppose the separation between the plates is reduced to 1.0 cm. Determine the new electric field intensity between the plates. Warm-up problems for student textbook page 333 1. The potential difference between two parallel plates separated by 5 cm is 46 V. Determine the electric field intensity between the plates. 2. The electric field intensity between two parallel plates separated by 3 cm is 254 N/C. Determine the potential difference between the plates. 3. The electric field intensity between two parallel plates is 55 N/C and the potential difference between them is 148 V. Determine the distance between the plates. 4. (a) In question 1, determine the force on a test charge of 0.03 C placed between the plates. (b) Repeat part a) for question 2. (c) Repeat part a) for question 3. Warm-up problems for student textbook page 338 1. Two horizontal plates are separated by 3.5 cm and have an electric potential difference of 275 V. A large oil drop of mass 3.5 1012 kg is balanced between the plates. (a) Determine the weight of the oil drop. (b) Determine the electrostatic force exerted by the plates on the oil drop. (c) Determine the charge on the oil drop. 2. Repeat question 1 if the mass of the oil drop is 2.6 1013 kg. 3. Two horizontal plates are separated by 1.9 cm and have an electric potential difference of 48 V. An oil drop of charge 4.8 1019 C is balanced between the plates. (a) Determine the electric field intensity between the plates. (b) Determine the electrostatic force exerted by the plates on the oil drop. (c) Determine the weight of the oil drop. (d) Determine the mass on the oil drop. 4. Repeat question 3 if the charge on the oil drop is 6.4 1019 C. Copyright © 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 8 Section 8.3 Warm-up Problems Warm-up problems for student textbook page 352 1. A proton (charge 1.6 1019 C) with a velocity of 1.1 105 m/s to the right experiences a magnetic field of magnitude 0.55 T directed upwards. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the magnetic field on the proton. 2. An electron (charge 1.6 1019 C) with a velocity of 1.24 106 cm/s upwards experiences a magnetic field of magnitude 0.55 T directed to the right. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the magnetic field on the electron. 3. A magnetic field exerts a force of 4.7 1014 N to the right on an electron with a velocity of 5.1 106 cm/s downwards. Determine the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic field. 4. A magnetic field of 0.46 T upwards exerts a force of 8.76 1013 N to the left on an electron. Determine the initial speed and direction of the electron. Warm-up problems for student textbook page 355 1. A wire 3.2 m long carrying a current of 4.1 mA runs parallel to a magnetic field of strength 0.4 T. Determine the force that the magnetic field exerts on the wire. 2. A wire 4.76 m long carrying a current of 2.9 A runs perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 0.71 T. Determine the force that the magnetic field exerts on the wire. 3. A wire 48 m long runs perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 0.55 T. The magnetic field exerts a force of 31 N on the wire. Determine the current in the wire. 4. A wire 27.8 cm long runs perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 1.8 T. The magnetic field exerts a force of 129 N on the wire. Determine the current in the wire. Warm-up problems for student textbook page 359 1. A negative ion with a charge of 1.6 1019 C is accelerated through an electric potential difference of 245 V. Determine the final kinetic energy of the ion. 2. A particle of mass 8.3 1026 kg and charge 3.2 1019 C moves at a speed of 4.4 104 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 1.6 T. Determine the radius of the particle’s resulting circular orbit. 3. An electron moves in a circular orbit of radius 3.8 cm at a speed of 7.8 106 m/s in a plane perpendicular to a magnetic field. Determine the strength of the field. 4. A particle of charge 4.4 1017 C moves at a speed of 1.7 103 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 0.57 T. Determine the mass of the particle if the radius of the particle’s orbit is 7.1 cm. Copyright © 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Review Warm-up Problems Warm-up problems for student textbook pages 366–369 1. The electric field intensity between two parallel plates separated by 5.5 cm is 338 N/C. Determine the potential difference between the plates. 2. Two horizontal plates are separated by 5.3 cm and have an electric potential difference of 572 V. A large oil drop of mass 2.1 1013 kg is balanced between the plates. (a) Determine the weight of the oil drop. (b) Determine the electrostatic force exerted by the plates on the oil drop. (c) Determine the charge on the oil drop. 3. A particle of charge 5.2 1018 C and a velocity of 4.4 104 m/s to the right experiences a magnetic field of magnitude 0.78 T directed downwards. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the magnetic field on the particle. 4. A wire 6.1 m long carrying a current of 1.92 A runs perpendicular to a magnetic field of strength 1.38 T. Determine the force that the magnetic field exerts on the wire. Copyright © 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited DATE: NAME: CLASS: Unit 3 Review Warm-up Problems Warm-up problems for student textbook pages 372–377 1. Determine the mass of a group of electrons whose total charge is 1 C. 2. Determine the magnitude of the force between two electrons that are 2.0 108 m apart. 3. The electric field intensity between two parallel plates 4.3 mm apart is 42 N/C. Determine the electric potential difference between the plates. 4. An electron moves at a speed of 3.0 104 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field intensity of 0.83 T. Determine the radius of the electron’s orbit. Copyright © 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Answers Chapter 8 Section 8.1 Warm-up problems for student textbook pages 329–330 1. 2. 3. 4. (a) 5.6 108 N/C half as intense doubled 5.6 108 N/C (b) 5.6 108 N/C Warm-up problems for student textbook page 333 1. 2. 3. 4. 9.2 N/C 7.6 V 2.7 m (a) 2.8 107 N (b) 7.6 106 N (c) 1.7 106 N Warm-up problems for student textbook page 338 1. 2. 3. 4. (a) 3.4 1011 N (a) 2.5 1012 N (a) 2.5 103 N/C (a) 2.5 103 N/C (b) 3.4 1011 N (c) 4.4 1015 C (b) 2.5 1012 N (c) 3.2 1016 C (b) 1.2 1015 N (c) 1.2 1015 N (d) 1.2 1016 N (b) 1.6 1015 N (c) 1.6 1015 N (d) 1.6 1016 N Section 8.3 Warm-up problems for student textbook page 352 1. 2. 3. 4. 9.7 1015 N [out of the page] 1.1 1015 N [out of the page] 5.8 T [out of the page] 1.2 107 m/s [into the page] Warm-up problems for student textbook page 355 1. 2. 3. 4. 0 9.8 N 1.2 A 260 A Warm-up problems for student textbook page 359 1. 2. 3. 4. 3.9 1015 J 7.1 103 m 1.2 103 T 1.0 1021 kg Chapter 8 Review Warm-up problems for student textbook pages 366–369 1. 2. 3. 4. 19 V (a) 2.1 1013 kg (b) 2.1 1012 N (c) 1.9 1016 C 13 1.8 10 N [in to the page] 16 N Copyright © 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Unit 3 Review Warm-up problems for student textbook pages 372–377 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.7 1012 kg 5.8 1013 N 0.18 V 2.1 107 m Copyright © 2002 McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited