linear perspective - Northern Secondary School
advertisement

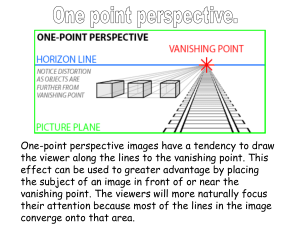
Northern Secondary School Art Department Art Comprehensive Mr. S. Macnaughton LINEAR PERSPECTIVE Grade 9 Definitions of Perspective Terms Horizon Line: The eye level of the spectator A line drawn horizontally across the picture plane at the point of intersection with the line of sight. Construction Lines: (Perspective Lines) (Vanishing Lines) Help you to draw an object accurately in perspective. Vanishing Points: The point of convergence on the Horizon Line where Perspective Lines meet. Picture Plane: A flat vertical surface that can be imagined as a sheet of glass in front of the spectator through which the object is being viewed. One Point Perspective: (Parallel Perspective) All convergent lines meet on the horizon at a single vanishing point. Two Point Perspective: (Angular Perspective) Convergent lines meet at a vanishing point to the left and to the right along the horizon line. Drawn lightly as a guide for creating the object to be drawn. Perspective lines are also drawn lightly and will convergence at the vanishing point(s). Horizontal Lines that are directly facing the spectator are drawn as parallel lines to the horizon. Vertical Lines are drawn parallel to each other and are perpendicular to the horizon. Vertical Lines still remain vertical. Reflections: Form a mirror-like image of the object in perspective drawn directly below the object on a surface such as water or wet pavement. Ellipse: This is the term given to the appearance of a circle when it is drawn or viewed in perspective. -2- Other Methods of Creating the Illusion of Depth in a Perspective Drawing are: The use of overlapping objects: Objects in front appear closer while those objects behind appear further away. Position of the Spectator: The closer the spectator stands to the object the greater the appearance of foreshortening will be on the picture plane. Position of the Picture Plane: The further away the object is from the picture plane the smaller it will appear. This is of course providing that the spectator remains in a fixed position relative to the object. Size: Objects that are closer appear larger while objects that are further away from the spectator will appear smaller. Detail: More detail and greater clarity will appear on objects drawn as being closer to the spectator. Intensity: Objects closer to the spectator appear brighter in colour while those objects further away begin to diminish in colour to the point of appearing gray. 9-Art Comprehensive-Linear Perspective