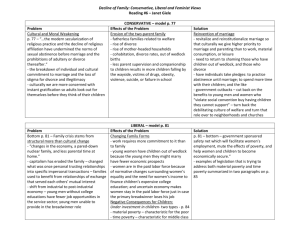
Marriage and Intimate Relationships
Marriage is the legally sanctioned union of
sexually intimate adults. Included in this
arrangement is common residence, sexual
fidelity, economic interdependence, shared
responsibilities for children.
Social trends that are affecting marriage today.
1) Increased acceptance of single lifestyle.
2) Increased acceptance of cohabitation
(living together without legal bonds of
marriage.)
3) Reduced expectation of permanence.
There is increased expectation of
personal growth and marriage as
facilitating that. Otherwise, divorce is
seen as a reasonable alternative.
4) Transitions in gender roles. Roles are
more varied, flexible & ambiguous.
5) Increased voluntary childlessness
6) Decline of nuclear family. Traditional
values have declined in favor of more
individualistic values.
So what motivates people to still marry?
1) Desire to have a dependable
relationship, sanctioned by society.
2) Social pressure comes at a certain age.
3) Romanticized view of love.
What influences our choice of mate?
1) Endogamy- people tend to marry within
their own social group. Common norms
foster attraction.
2) Homogamy- tendency to marry those
with similar personal characteristics. If
we divert from that, it is in favor of
older men, more educated than wives.
3) Gender preferences- men emphasize
women’s youth and attractiveness,
women emphasize men’s SES, IQ,
ambition and financial prospects.
4) Stimulus-Value role theory- 3 stages:
a. Stage 1- focus on easily identifiable
surface characteristics of the other. If
both have “even” characteristics (even
if not the same ones) in value, then
they proceed.
b.Stage 2- value comparisonscomparing their values to see how
compatible they are- religion, politics,
sex, gender roles, leisure activities.
c. Stage 3- role stage- if values are
deemed compatible, they begin to
think about marriage. Now they assess
power differential, nature of emotional
support, sexual satisfaction.
Predictors of marital success- is success
measured by longevity? Mutual satisfaction?
Passion? Lack of conflict?
1) Family background and marital
stability- satisfaction of a couple directly
correlates to satisfaction of parents’
marriage. Parents’ divorce relates to
children’s rate of divorce.
2) Age at marriage- older or younger than
the norm have higher risk of divorce.
3) Length of courtship- longer courtship
relates to more stable marriage.
4) SES- divorce is more common in working
and lower classes (financial stressors)
5) Personality- worse outcome if one partner
is higher in neuroticism. Better if partners
score higher in agreeableness/
Conscientiousness.
Family Life Cycle- an orderly sequence
of developmental stages that families
progress through over time. Satisfaction in
marriage generally dips as families become
immersed in raising children. It increases as
children leave the nest. It is almost equally
high at the very beginning and very end.
While raising adolescents, adults are often
also responsible for aging parents- the
sandwich generation. The empty nest is
not as difficult for parents as thought in the
past. Most mothers enjoy branching out into
new areas of interest. It may be a problem if
the new adults decide to return home,
though.
Areas of challenge in marriage1) Role expectations-roles are molded
by what partners observed in their
own homes. These may be very
different for the two partners. Roles
today are much more ambiguous
than in the past. All these
differences need to be negotiated.
Even so, men’s careers take
precedence over women’s. Women
carry most responsibility for
children’s needs. Chores are broken
down inequitably with women
doing the more chronic chores.
There is a common perception of
inequality in this area.
2) Work/ career issues- work
responsibilities often get in the way
of home commitments. Work stress
can impact home satisfaction. Dual
career couples are no less satisfied
with marriage, however.
Effects of work on childrenmothers working does not have a
detrimental effect on children or
their attachment. It enhances
daughters’ achievement.
3)Financial issues- poverty has a negative
impact on marital success, but wealth
doesn’t guarantee happiness. Risk of divorce
increases as husband’s income drops.
Children raised in poverty show problems
with health, academic achievement,
delinquency, mental health.
4) Inadequate communication- most
often cited as a cause of divorce. The
more partners withdraw and refuse to
communicate, the lower satisfaction
becomes. Specific problems include:
few positive messages, feeling
misunderstood, more intense negative
messages, differing self-disclosure.
Gottman has defined 4 patterns that are
most associated with risk for divorce:
a) Contempt (communicating
that spouse is inferior)
b) Criticism (negative
evaluations of partner)
c) Defensiveness (responding
to C&C with obstructions
that escalate conflict)
d) Stonewalling (refusing to
listen to partners’
complaints)
e) Belligerence was added
later (provocative,
combative challenges to
partners’ power/authority)
Divorce-legal dissolution of marriage. Usually
due to a gradual disintegration of the marriage.
Rates have increased since the 70s but have
leveled out recently. Current risk is 50% (much
higher for second+ marriages). People usually
divorce after hesitating for awhile, making a
variety of accommodations before giving up.
Recent studies have shown that couples who did
not divorce, but contemplated it, are much
happier 5 years later, than those who did
divorce. Divorce is no solution to personal
problems.
The process of divorce is stressful for everyone
involved. 1 million children experience
parents’ divorce every year. It has a negative
effect on children, especially in the short-term,
but if the parents’ marriage was violently
conflicted, it is better for children.
Symptoms children experience: depression,
nightmares, dependency, aggression, lower
academic performance, poorer health, substance
abuse, early sexual behavior. All these
symptoms are heightened if the parents push
through an acrimonious divorce and put children
in the middle.
Long-term effects on children:
emotional maladjustment, antisocial
behavior, marital instability, poorer career
prospects. Parents who have good emotional
skills can moderate these problems for the
child.
Effects on partners: divorce costs
women more financially and they usually
carry most responsibility for children.
Fathers lose contact with children ½ the
time.
Custodial mothers experience 36% decrease
in standard of living, and noncustodial
fathers experienced a 28% increase.
Emotional impacts are similar for M/W. It is
easier for the partner who initiates the
divorce.
Remarriage- 75% of divorced remarry,
generally in less than 4 years. It is a difficult
adjustment for most children.
Staying single- people are marrying later
and deciding not to marry more today. Even
so, most people expect to marry. Single
women are more satisfied with their lives
than single men.
Even so, being married is associated with
greater health and happiness. Spouses
provide emotional and social support that
buffers the effects of stress. Couples have
higher incomes and better health.
Cohabitation- 4.2 million people today- 7%
of couples. It is generally a short experienceeither they marry or break up in 12 months.
It’s more common in lower-income, lesseducated groups. 35% have children.
75% expect to marry their partner. They
report less satisfaction than married couples.
29% of those cohabiting break up in 2 years.
Cohabitation does not improve chances of
marital success. It’s related to a higher
divorce rate. (Maybe because these people
are more liberal in general, with less sense
of commitment and fewer qualms with
divorce.)
Gay relationships- 5-8% of population.
They can’t legalize their relationship (except
in VT) and they can’t benefit from most
advantages of marriage- insurance, legal
protections. They do tend to be shorter due
to fewer problems in dissolution. They
report similar levels of sexual and overall
satisfaction. Roles are more flexible than in
heterosexual unions. There is a more
equitable balance of power for gays.
Lesbians generally have committed
relationships (45-80%) although 40-60% of
gay males describe being in a committed
relationship (although half describe their
unions as ‘open’ sexually) Gays are more
often considered single rather than part of a
family, though. More gays are opting to
have children. They parent in a similar way
to heterosexual parents and children
generally grow up heterosexual and welladjusted.
Domestic abuse- intimate violence is
aggression directed at those in close
relationship to the aggressor.
1) Date rape- occurs to 13-25% of
women at some point. Most rapists
are known to the victim, which
increases the trauma associated with
the violence. Effects can be as
serious as PTSD, and may continue
for some time. Testifying in court
can contribute to traumatization.
Factors: Alcohol or date rape drugs
(rohypnol, GHB) are often involved.
Aggressive pornography
desensitizes users to the effects of
sexual violence on the victim &
fosters the myth that women enjoy
being raped. The double standard
for sexual behavior of men/women
can promote sexual aggression by
men. Miscommunication in the
nature of flirtatious behavior and its
meaning. Men who have a
suspicious schema about women’s
interest in sex.
Four warning signs of a date rapist:
feelings of sexual entitlement, need
to exert power, high hostility/ anger,
acceptance of interpersonal violence
as the norm.
2) Partner abuse- comes in many
forms- physical, emotional,
psychological. 25% of women and
7% of men have been battered. Most
women’s violence is a retaliation
for abuse. Women are the victims
in 75% of murders by spouses.
Women are the perpetrators of
spousal murders 25% of the time.
Beyond the physical effects, other effects are
anxiety, depression, feelings of helplessness,
humiliation, stress-related illness, suicide.
Children who witness abuse suffer similar
effects, including delinquency.
Other factors that contribute to battering:
unemployment, drug use, low self-esteem, sense
of entitlement, childhood abuse or witness of
abuse. Battering is a tool to exert control over
the victim.
Why do women stay in abusive relationships?
Many do leave, but leaving increases one’s
risk of being murdered 75%. Financial
dependency is a big issue, as is the feeling the
woman can’t provide as well for her children.
Staying is a way of taking care of her children.
Others have nowhere to go, no family support
(as the abuser has usually cut off family contact)
Abuse shelters have only been available for a
few years. Women have been intermittently
reinforced in the honeymoon cycle of abuse.
3) Child abuse-intentional acts of harm to a
child physically, sexually or
psychologically, including neglect. 3 million
children/ year. Boys are more likely to be
physically abused, girls sexually. Our
culture has accepted violence against
children as legitimate discipline until
recently. More common with parents who
were abused themselves as children.
Effects: low self-esteem, depression,
aggressiveness, poor school
achievement. In adulthood it’s linked to
substance abuse, emotional problems,
self-injurious behavior, suicide,
violence.
Child sexual abuse: 400,000 reported
per year. Incest is sexual activity
between close relatives. Girls are most
often the victims; fathers, stepfathers,
older brothers most often the
perpetrators. These relationships usually
start when the girl is 6-11 and last about
2 years. It occurs most in families that
are socially isolated, have a strong,
dominating father, with a wife who is
financially/ emotionally dependent on
husband, or sick, absent, mentally ill.
Victims usually feel very guilty because
they don’t feel they resisted effectively
enough or they enjoyed the affection/
attention even though they disliked the
form it came in. Some cooperate
because they feel they have to in order
to keep the family together, or keep
father from going to jail, or their mother
will blame them.
Effects: all the effects of physical abuse
plus eating disorders, sexual problems,
reckless behavior, PTSD, emotional
numbing, flashbacks, problems in
intimate relationships trusting another.
Marriage and Intimate Relationships
Marriage is the legally sanctioned
union of sexually intimate adults.
Social trends that are affecting marriage today.
1) Increased acceptance of single lifestyle.
2) Reduced expectation of permanence.
3)Transitions in gender roles.
4) Increased voluntary childlessness
5)Decline of nuclear family.
So what motivates people to still marry?
1)Desire to have a dependable relationship,
sanctioned by society.
2)Social pressure
3)Romanticized view of love.
What influences our choice of mate?
1) Endogamy- people tend to marry within
their own social group.
2) Homogamy- tendency to marry those
with similar personal characteristics. If
we divert from that, it is in favor of
older men, more educated than wives.
3) Gender preferences- men emphasize
women’s youth and attractiveness,
women emphasize men’s SES, IQ,
ambition and financial prospects.
4) Stimulus-Value role theory- 3 stages:
a. Stage 1- focus on easily identifiable
surface characteristics of the other. If
both have “even” characteristics (even
if not the same ones) in value, then
they proceed.
b.Stage 2- value comparisonscomparing their values to see how
compatible they are- religion, politics,
sex, gender roles, leisure activities.
c. Stage 3- role stage- if values are
deemed compatible, they begin to
think about marriage. Now they assess
power differential, nature of emotional
support, sexual satisfaction.
Predictors of marital success- is success
measured by longevity? Mutual satisfaction?
Passion? Lack of conflict?
1) Family background and marital
stability- satisfaction of a couple directly
correlates to satisfaction of parents’
marriage. Parents’ divorce relates to
children’s rate of divorce.
2) Age at marriage- older or younger than
the norm have higher risk of divorce.
3) Length of courtship- longer courtship
relates to more stable marriage.
4) SES- divorce is more common in working
and lower classes (financial stressors)
5) Personality- worse outcome if one partner
is higher in neuroticism. Better if partners
score higher in agreeableness or
conscientiousness.
Family Life Cycle- an orderly sequence
of developmental stages that families
progress through over time. Satisfaction in
marriage generally dips as families become
immersed in raising children. It increases as
children leave the nest. It is almost equally
high at the very beginning and very end.
While raising adolescents, adults are often
also responsible for aging parents- the
sandwich generation. The empty nest is
not as difficult for parents as thought in the
past.
Areas of challenge in marriagea. Role expectations-roles are molded by
what partners observed in their own
homes. There is a common perception of
inequality in this area.
b. Work/ career issues- work
responsibilities often get in the way of
home commitments.
Effects of work on childrenmothers working does not have a
detrimental effect on children or
their attachment. It enhances
daughters’ achievement.
3)Financial issues- poverty has a negative
impact on marital success, but wealth
doesn’t guarantee happiness. Risk of divorce
increases as husband’s income drops.
4)Inadequate communication- most
often cited as a cause of divorce. The
more partners withdraw and refuse to
communicate, the lower satisfaction
becomes.
Gottman has defined 4 patterns
that are most associated with risk for
divorce:
1. Contempt (communicating that
spouse is inferior)
2. Criticism (negative evaluations
of partner)
3. Defensiveness (responding to
C&C with obstructions that
escalate conflict)
4. Stonewalling (refusing to listen
to partners’ complaints)
5. Belligerence was added later
(provocative, combative
challenges to partners’
power/authority)
Divorce-legal dissolution of marriage. Usually
due to a gradual disintegration of the marriage.
Rates have increased since the 70s but have
leveled out recently. Current risk is 50% (much
higher for second+ marriages).
The process of divorce is stressful for everyone
involved. 1 million children experience
parents’ divorce every year. It has a negative
effect on children, especially in the short-term,
but if the parents’ marriage was violently
conflicted, it is better for children.
Symptoms children experience:
depression, nightmares, dependency, aggression,
lower academic performance, poorer health,
substance abuse, early sexual behavior.
Long-term effects on children:
emotional maladjustment, antisocial
behavior, marital instability, poorer career
prospects.
Effects on partners: divorce costs
women more financially and they usually
carry most responsibility for children.
Fathers lose contact with children ½ the
time.
Custodial mothers experience 36% decrease
in standard of living, and noncustodial
fathers experienced a 28% increase.
Remarriage- 75% of divorced remarry,
generally in less than 4 years. It is a difficult
adjustment for most children.
Staying single- people are marrying later
and deciding not to marry more today. Even
so, most people expect to marry. Single
women are more satisfied with their lives
than single men.
Even so, being married is associated with
greater health and happiness. Spouses
provide emotional and social support that
buffers the effects of stress. Couples have
higher incomes and better health.
Cohabitation- 4.2 million people today- 7%
of couples. It is generally a short experienceeither they marry or break up in 12 months.
29% of those cohabiting break up in 2 years.
Cohabitation does not improve chances of
marital success. It’s related to a higher
divorce rate.
Gay relationships- 5-8% of population.
They can’t legalize their relationship (except
in VT) and they can’t benefit from most
advantages of marriage- insurance, legal
protections. They do tend to be shorter due
to fewer problems in dissolution. They
report similar levels of sexual and overall
satisfaction. Roles are more flexible than in
heterosexual unions. There is a more
equitable balance of power for gays.
Lesbians generally have committed
relationships (45-80%) although 40-60% of
gay males describe being in a committed
relationship (although half describe their
unions as ‘open’ sexually)
More gays are opting to have children.
They parent in a similar way to heterosexual
parents and children generally grow up
heterosexual and well-adjusted.
Domestic abuse- intimate violence is
aggression directed at those in close
relationship to the aggressor.
1)Date rape- occurs to 13-25% of women at
some point. Most rapists are known to the
victim, which increases the trauma associated
with the violence.
Effects can be as serious as PTSD, and
may continue for some time. Testifying in
court can contribute to traumatization.
Factors: Alcohol or date rape drugs
(rohypnol, GHB) are often involved.
Aggressive pornography desensitizes
users to the effects of sexual violence on
the victim & fosters the myth that
women enjoy being raped. The
double standard for sexual behavior of
men/women can promote sexual
aggression by men.
Miscommunication in the nature of
flirtatious behavior and its meaning.
Men who have a suspicious schema
about women’s interest in sex.
Four warning signs of a date rapist:
feelings of sexual entitlement, need
to exert power, high hostility/ anger,
acceptance of interpersonal violence
as the norm.
2)Partner abuse- comes in many formsphysical, emotional, psychological. 25% of
women and 7% of men have been battered. Most
women’s violence is a retaliation for abuse.
Women are the victims in 75% of murders by
spouses. Women are the perpetrators of
spousal murders 25% of the time.
Beyond the physical effects, other effects are
anxiety, depression, feelings of helplessness,
humiliation, stress-related illness, suicide.
Children who witness abuse suffer similar
effects, including delinquency.
Other factors that contribute to battering:
unemployment, drug use, low self-esteem, sense
of entitlement, childhood abuse or witness of
abuse. Battering is a tool to exert control over
the victim.
Why do women stay in abusive relationships?
Many do leave, but leaving increases one’s
risk of being murdered 75%. Financial
dependency is a big issue, as is the feeling the
woman can’t provide as well for her children.
Staying is a way of taking care of her children.
Others have nowhere to go, no family support
(as the abuser has usually cut off family contact)
Abuse shelters have only been available for a
few years. Women have been intermittently
reinforced in the honeymoon cycle of abuse.
3) Child abuse-intentional acts of harm to a
child physically, sexually or
psychologically, including neglect. 3 million
children/ year. Boys are more likely to be
physically abused, girls sexually.
Effects: low self-esteem, depression,
aggressiveness, poor school
achievement. In adulthood it’s linked to
substance abuse, emotional problems,
self-injurious behavior, suicide,
violence.
Child sexual abuse: 400,000 reported
per year. Incest is sexual activity
between close relatives. Girls are most
often the victims; fathers, stepfathers,
older brothers most often the
perpetrators.
Effects: all the effects of physical abuse
plus eating disorders, sexual problems,
reckless behavior, PTSD, emotional
numbing, flashbacks, problems in
intimate relationships trusting another.