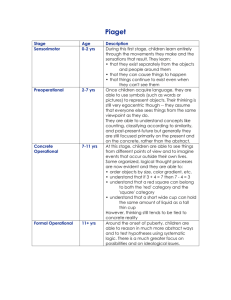
How many gas stations are there in the US

Why Professor
Can't Teach
Traditional Instruction vs. Interactive Engagement
Michael Dubson
Dept. of Physics
University of Colorado at Boulder dubson@spot.colorado.edu http://spot.Colorado.EDU/~dubson
What is your age?
Pink: less than 10 yrs old
Yellow: 10-20 yrs
Green: 20-30 yrs
Blue: 30-40 yrs
Blue: 40-50 yrs
Blue: 50 - 60 yrs
Blue: greater than 60 yrs
How many gas stations are there in the US?
Pink: Less than 1,000
Green: Between 1000 and 5000
Yellow: Between 5000 and 50,000
Purple: Between 50,000 and 500,000
Blue: Between 500,000 and 5 million
Hold up all colors: More than 5 million
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Problems
Quantitative:
In the circuit below, V = 25V, R
1
= R
2
= 10
, R
3
= R
4
= R
5
= 15
, R
6
= 50
.
What is the current through resistor R
3
?
Qualitative.
Consider the behavior of the circuit when various values increase or decrease.
For each question, answer I (increases), D (decreases), or S (stays the same).
When R
6
increases, the current through R
2
____________.
When R
3
increases, the current through R
4
____________.
When R
1
decreases, the current through the battery _________.
Interactive Engagement,
Peer Instruction,
Concept Tests
Eric Mazur
Prentice Hall
1997
Concept Test 1.
An astronaut in intergalactic space is twirling a rock on a string.
Suddenly the string breaks when the rock is at the point shown:
Snap!
purple yellow green pink
Which path (pink, green, yellow, or purple) does the rock follow after the string breaks?
Concept Test 2.
A moving van collides with a sports car in a high-speed head-on collision. Crash!
During the impact, the van exerts a force F van on the car and the car exerts a force F car on the van. Which one of the following statements about these forces is true:
Pink: The force exerted by the van on the car is the same size as the force exerted by the car on the van: F van
= F car
Yellow: F van
> F car
Green: : F van
< F car
Some variation in student attitudes towards Concept
Tests, but overwhelmingly positive.
Professor A Professor B
Concept Tests Student Attitudes
Calc-based Intro Physics
Like
20%
Neutral
0%
Hate
0%
Dislike
0%
Concept Tests Student Attitudes
Algebra-based Intro Physics
Neutral
18%
Hate
1%
Love
39%
Love
80%
Like
42%
Dislike
0%
Professor C
Concept Tests Student Attitudes
"Physics for Poets" Course
Hate Love
5% 8%
Dislike
25%
Like
25%
Neutral
37%
Concept Test 3
Brass has a positive coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning brass expands when heated. A ring (annulus) of brass is heated.
Does the hole in the middle of the ring get larger or smaller?
Pink: larger
Yellow: smaller
Green: stays the same
Concept Test 4
When an jet flies faster than the speed of sound, there is...
Red: a sonic boom occurring only at the moment that the jet exceeds the speed of sound.
Green: a continuous sonic booming occurring all the time that the jet is going faster than Mach 1.
Boom!
Summer/Winter Concept Test 5
Here in the northern hemisphere, it is cold in the winter and warm in the summer. Why? Which explanation below is the most accurate?
Pink: In the winter, there is less solar radiation per unit area of the ground.
Yellow: The Sun is further from the Earth in the winter.
Blue: Because of climate patterns, it is more cloudy than average in the winter, therefore less solar radiation than average reaches the ground.
Green: Because the Sun is lower in the sky in the winter, the sunlight travels through more air before it reaches the ground and the air absorbs heat, leaving less heat reaching the ground.
Taylor's Top Ten Tips for T.A.'s
(Actually, it's fifteen, and slightly edited by Mike Dubson)
1. Never, ever, be late.
2. Come prepared.
3. Never demean students; never show irritation or condescension. Every question is a good question.
4. Don't be afraid to repeat yourself.
5. Speak clearly and LOUDLY. (You cannot speak in a normal tone of voice to
30 people in a classroom. You must "boom" your voice.)
6. Write clearly on the chalkboard.
7. Try to know your students' names.
8. Grade promptly.
9. Accumulate lots of scores with a good spread.
10. Time office hours thoughtfully and encourage attendance.
11. Keep in touch with lectures and course rules.
12. Don't sit in the back grading.
13. Get students involved. The less you talk, the more they talk, the better the class.
14. Show enthusiasm.
15. Make class enjoyable.
The Golden Rules of Lecturing:
Rule #1:
If they learned something, but they leave hating the subject, you have failed.
Morale is vital.
Talk to/listen to students, especially during office hours.
Rule #2:
It's OK to lecture less, ... because they're not listening anyway.
Use Concept Tests –
Active learning works, passive learning does not.
Lots of Demos
Few or no derivations
Put lecture notes (+ everything else) on the Web.
Rule #3:
Emphasize qualitative reasoning and conceptual understanding.
in lecture
on homeworks
on exams
It doesn't matter if they can compute the acceleration, if they don't know what acceleration is.