Lectures 06t
advertisement

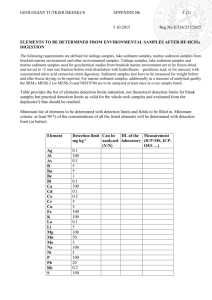
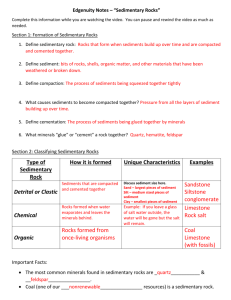
Practice Questions for Lectures 6 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture 6. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will have more questions total. A. Short answer: 1. In a breccia, the coarse particles are ________ . 2. A rounded pebble would be a type of particle found in a ________. 3. Salt and other sediments that form when a body of water dries up are called ______________. 4. The sand grains in an ancient dune deposit are frosted and well ______ . 5. Sediments that were transported by glacial ice are ______ sorted and unstratified. 6. Shallow marine sediments often consist of _________-rich sands and mud. 7. Where the sea meets a river, a tidal _______ forms. 8. In ________ bedding, the coarsest grains settle to the bottom first, and grain size decreases gradually toward the top of a layer. 9. Sediment may undergo _____________, the process of compaction and cementation that turns it to rock. 10. As sea-level rises, a freshwater facies such as a river deposit can be covered with a marine facies, for example ________ sediments. B. Match the terms 1. Chalk _____ a. gypsum and salt 2. Cementation ______ b. mud 3. Beach sediment____ c. plants fall in a swamp 4. Evaporite minerals____ d. rounded coarse particles > 2 mm 5. Still water sediment ____ e. Size interval for sand particles 6. Coal _____ f. coarsest below, getting finer upward 7. Conglomerate _____ g. glue grains together 8. 0.06 mm to 2 mm ______ h. quartz arenite sandstone 9. Deep marine sediments ___ i. biogenic limestone 10. Graded bed. _______ j. carbonate and silica skeletons of plankton C. True or False? 1. Chalk is a biogenic limestone formed from carbonate secretions of microorganisms. True or False? 2. Mudcracks and graded bedding are useful for "right-side-up" determinations. True or False? 3. The most abundant types of sedimentary rock are conglomerates. True or False? 4. Mudcracks can form on a floodplain. True or False? 5. The degree to which sediment particles become rounded depends on their hardness, how far they are transported, and the energy of their collisions with other particles. True or False? 6. Deep lagoons are more effective in rounding sediment particles than swiftly flowing rivers. True or False? 7. Wind generally results in the most well-sorted sediments. True or False? 8. Sediments are classified as either detrital sediment or chemical sediment on the basis of the source of the sediments 9. Symmetrical ripples can reveal the direction of current flow. True or False? 10. Detrital sedimentary rocks are classified on the basis of their particle sizes. True or False? D. Multiple choice: 1. The vertical sequence of preserved sedimentary environments ("Facies") indicating a rising sea level would be: (a) river, beach, shallow marine, deep marine. (b) beach, shallow marine, deep marine, river. (c) shallow marine, deep marine, beach, river. (d) deep marine, shallow marine, beach, river. 2. Which of the following statements concerning the formation of coal is NOT true? (a) The environment for deposition of coal is usually a swamp. (b) Coal is composed primarily of the remains of microorganisms such as bacteria and plankton. (c) Coal forms from the decomposition of plant leaves and wood and other organic materials deposited in waters containing little oxygen. (d) Organic matter changes from peat, to lignite, to bituminous coal, and finally into anthracite coal. 3. The main difference between a breccia and a conglomerate is: (a) particle size. (b) particle shape. (c) color. (d) mineral composition. 4. A sandstone with more than 25% feldspar and poorly sorted, angular grains is called: (a) quartz arenite. (b) arkose. (c) graywacke. (d) quartzite. 5. Of the following, the most likely environment of deposition for a pure quartz sandstone (quartz arenite) would be: (a) an ocean shoreline. (b) at the end of a glacier. (c) beneath a landslide. (d) the bottom of an alluvial fan. 6. All of the following colors are common in mudstones EXCEPT: (a) red shales containing iron oxides derived from an oxygen-rich environment. (b) green shales containing iron minerals derived from an oxygen-poor environment. (c) black shales indicating abundant organic matter. (d) bright yellow shales containing much pyrite. 7. Ripple marks in sediments that were transported by water (in crosssection they appear as "cross-beds"), can tell us: (a) the direction of flow. (b) the current velocity (c) whether tides were important there. (d) All of the above 8. Of the following, the most likely environment of deposition for shale is: (a) an ocean shoreline. (b) at the end of a glacier. (c) the bottom of a river. (d) the bottom of a lagoon. 9. Which of the following sedimentary structures would indicate deposition had occurred in shallow water with cycles of drought? (a) Graded bedding. (b) Ripple marks. (c) Mudcracks. (d) Cross-bedding. 10. All of the following statements about cross-bedding are true EXCEPT: (a) cross-beds are formed when a sedimentary layer is deposited at an angle to the underlying bed. (b) cross-bedding is usually formed by deposition of sediments from wind or water. (c) changes in direction of wind or water currents are recognizable within cross-beds. (d) cross-beds form when particles drop from still water. E. Short answers, no more than one sentence. 1. Name an environment in which muds are being deposited today. 2. Name an environment in which sands are being deposited today, and explain why sands are deposited there. 3. How do the particles of detrital sedimentary rocks become cemented together? 4. Explain how graded beds form. 5. Describe the appearance of graded beds in an outcrop. 6. How could a geologist use graded beds to tell if sedimentary strata were "right side up" or overturned? 7. Give one example of a situation where a graded bed forms.