Purification of antibodies by zeolite A References and further
advertisement

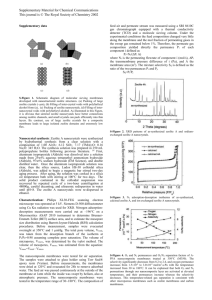
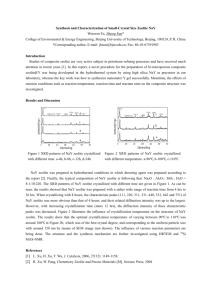
Purification of antibodies by zeolite A Y. C. Huang, Y. C. Yu and T. Y. Lee Department of Chemical Engineering, National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan, Republic of China Received 20 December 1993; accepted 24 October 1994. Available online 28 December 1999. Abstract Zeolite A and its modified forms can be used to separate immunoglobulin G from a mixture of plasma proteins and mouse ascites fluid. The separation was achieved by adjusting the pH of buffers according to the isoelectric points of proteins in the mixture. Zeolite A with potassium cations (K-A) and its calcium phosphate modified from (CaP-A) performed better than those with sodium, ammonium cations, and dealuminated zeolite X, respectively. Antibody fractionation eluted from zeolite A columns showed high activity and purity, which were verified by sodium dodecyl sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. A summary of the physical characteristics of zeolite A in comparison with conventional materials is presented. Zeolite is a promising new material as an ion exchanger or column packing support for large-scale bioseparation. Author Keywords: Antibodies; purification; zeolite; ion-exchange