Emission of molecular fragments synthesized in hypervelocity nanoparticle impacts
Ecole Polytechnigue
Author(s): Guillermier C (Guillermier, C.)1, Della-Negra S (Della-Negra, S.)2, Schweikert EA (Schweikert, E. A.)1, Dunlop A (Dunlop, A.)3, Rizza G
(Rizza, G.)3
Source: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MASS SPECTROMETRY
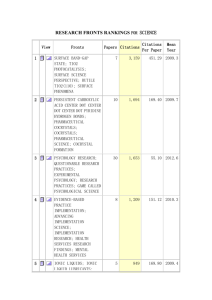
Times Cited: 1
References: 20
Volume: 275
Issue: 1-3
Pages: 86-90
Published: AUG 1 2008
Citation Map
Abstract: We report on experiments with Au-n nanoparticles (100 <= n <= 400) at velocities of 10-60 km/s. They are implanted virtually intact via
hydrodynamic penetration. The products of the extreme pressure transient are observed by mass analyzing the ionized ejecta. Targets of labeled
molecules (C-13-, N-15-glycine) reveal fragmentation-recombination processes, producing CN- and CCN- with high efficiency (45%). This value is
over two orders of magnitude larger than that obtained with atomic and small cluster projectiles. The experiments could simulate collisions of
nanosized dust particles in interstellar space. (C) 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Document Type: Article
Language: English
Author Keywords: nanoparticle impact; extreme chemistry; secondary ions; hydrodynamic penetration; surface analysis
KeyWords Plus: ION MASS-SPECTROMETRY; PROJECTILE SIZE; CLUSTERS; ENERGY; DUST; COLLISIONS; SURFACES; SOLIDS; EARTH
Reprint Address: Schweikert, EA (reprint author), Texas A&M Univ, Ctr Chem Characterizat & Anal, College Stn, TX 77843 USA
Addresses:
1. Texas A&M Univ, Ctr Chem Characterizat & Anal, College Stn, TX 77843 USA
2. Univ Paris 11, Inst Phys Nucl, UMR8608, F-91406 Orsay, France
3. Ecole Polytech, CEA DRECAM, Solides Irradies Lab, F-91128 Palaiseau, France
E-mail Addresses: schweikert@mail.chem.tamu.edu
Publisher: ELSEVIER SCIENCE BV, PO BOX 211, 1000 AE AMSTERDAM, NETHERLANDS
IDS Number: 338OV
ISSN: 1387-3806
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijms.2008.05.023