EAST LOS ANGELES COLLEGE - Respiratory Therapy Files
advertisement

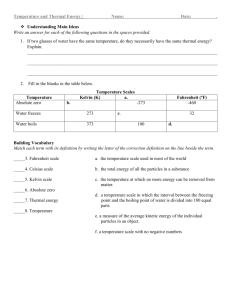
EAST LOS ANGELES COLLEGE RESPIRATORY THERAPY 21 STUDY GUIDE # 1 -- ABSOLUTE UNITS FOR TEMPERATURE & PRESSURE When temperature and pressure units are used in gas law calculations, absolute units must be used or the result will be inaccurate. TERMS 1. Temperature: the amount of heat energy in matter expressed in terms of a specific scale. 2. Absolute Temperature Scale: A temperature measurement scale in which the 0 point is absolute 0 or the temperature at which all molecular motion ceases. Absolute 0 temperature is about -273 Celsius. The absolute temperature scale for Celsius is called the Kelvin temperature scale. Celsius temperatures can be converted to Kelvin temperatures by adding 273 degrees to the Celsius temperature as shown below: Kelvins = Celsius + 273 Example: Convert 37 C to Kelvins Kelvins = 37 + 273 = 310 Kelvins To convert Kelvin temperatures to Celsius, subtract 273 as shown below: Celsius = Kelvins - 273 Example: Convert 298 Kelvins to Celsius Celsius = 298 K - 273 = 25 Celsius 3. "Gauge" Temperature Scale: A temperature measurement scale in which the 0 point is something other than absolute 0. For example, in the Celsius temperature scale, the 0 point is the freezing point of water and in the Fahrenheit temperature scale the 0 point is 32 degrees below the freezing point of water. In the hospital, the Celsius scale is used to report patient temperatures. This is somewhat confusing for patients who are used to ambient temperatures that are usually reported in Fahrenheit temperatures. For this reason, it is important for you to be able to convert temperatures from one scale to the other. 4. Temperature Conversion: To convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, use the following formula: C = .55 x (F - 32) Example: Convert 60 Fahrenheit to Celsius C = .55 (60 - 32) = .55 x 28 = 15 Celsius To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, use the following formula: F = (1.8 x C) + 32 Example: Convert 20 Celsius to Fahrenheit F = (1.8 x 20) +32 = 36 + 32 = 68 Fahrenheit 5. Pressure: A measurement of force per unit area, ie: pounds per square inch (PSI) 6. Absolute Pressure Scale: A pressure scale in which the 0 point is a complete vacuum or the pressure at which all molecular motion ceases. Absolute pressure includes atmospheric pressure. 7. Gauge Pressure Scale: A pressure scale in which the 0 point is atmospheric pressure or the pressure of the atmosphere pushing down on a given point on the earth. Pressure measurement scales can be either gauge or absolute and a different conversion factor is needed for each scale: PSIA = PSIG + 14.7 cmH20 (absolute) = cmH2O (gauge) + 1034 torr (absolute) = torr (gauge) + 760 With cm H2O and torr it is sometimes difficult to determine whether the reading is gauge or absolute. You must know if a certain parameter such as blood pressure is generally reported in torr absolute or gauge. As a general rule, if the reading is obtained from a "gauge" or manometer, then it is a gauge pressure reading. 8. "Negative Pressure:" negative or minus gauge pressure is frequently used in respiratory care to describe gauge pressure conditions that are lower or less than 0 or atmospheric pressure. Example: Chest tube drainage pressure is usually set at -15 cm H2O or 15 cm H2O below atmospheric pressure. Example: -15 cm H2O gauge = 1019 cm H2O absolute. 1034 cmH2O - 15 cmH2O = 1019 cm H20 Negative absolute pressure is not possible because 0 absolute pressure represents a complete vacuum or the complete absence of pressure. 9. Conditions of measurement: specific temperature, pressure and humidity conditions that are used to measure gases so that we can compare measurements, usually of gases, made by different people at different times. Conditions of measurement are abbreviated with upper case letters, ie: STPD. In respiratory care we commonly use three different conditions of measurement: STPD: 0 Celsius, 1 atmosphere (760 torr), dry -- used mainly in chemistry, used in respiratory care to measure metabolic and nutritional values. BTPS: 37 Celsius, 1 atmosphere (760 torr), saturated -- the conditions in the body, used in respiratory care to measure lung volumes. ATPS: room temperature, room pressure, saturated -- ambient or room conditions, the temperature and pressure vary with the conditions in the environment or room. Used in respiratory care to convert room conditions to body conditions. There are conversion equations and charts that can be used to convert from one set of conditions to another, ie: ATPS to BTPS. You will not be required to convert these conditions in this course. MT: 08/2000 RT 21

![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)