Responsibilities for chemical safety - Academic lab pages
advertisement

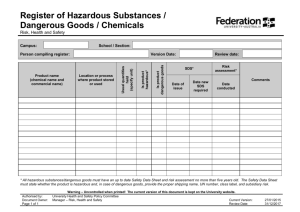
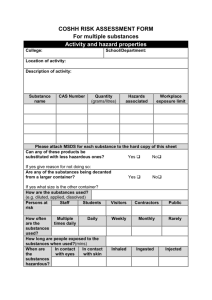
Responsibilities for chemical safety All staff including postgraduate research students will be expected to attend the appropriate chemical safety training courses (details are given in the Graduate School Resource File) and will have access to safety information on the University Health and Safety web page. All undergraduate and taught MSc students must attend a course on Safety and Laboratory practice (details provided in intoductory packs and included in timetables). Laboratories are designated work areas and are not to be adapted into living space or recreation areas. All work should be to the standard of Good Chemical Practice (GChP). GChP sets the minimum standard for ensuring the protection of people against the adverse effects of chemical substances encountered at work. Details of GChP can be found on UHSP/15/HS/03. The main points of GChP are as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Food, drink, cosmetics and cigarettes must not be taken into or used in the laboratory. Pipetting by mouth is prohibited. Laboratories and communal areas are designated as NO SMOKING. Benches should be cleaned and tidied regularly, surplus apparatus and chemicals returned to the stores or cupboards. Laboratory coats must be worn when working in the laboratory. Laboratory coats should be removed on leaving the laboratory area and MUST NOT be worn in coffee rooms, common rooms etc. As a minimum, Safety spectacles or face visors must be worn to protect the eyes from splashes when handling hazardous liquids. When the risk from splashing is high, especially from toxic or corrosive liquids, a visor or goggles must be worn. Work must be carried out cleanly with the minimum of spilling and splashing to minimize contamination. Contaminated areas should be cleaned as soon as possible. The work area must be kept tidy and chemicals returned to the approved storage areas when not in use. Where it is necessary to avoid the inhalation of fumes and vapours or the build up of an explosive atmosphere (from highly flammable liquids or gases) a fume cupboard must be used. Fume cupboards should not be used for storage of chemicals. Flammable substances must be kept well away from sources of ignition - naked flames, hot plates etc. Minimise exposure to fumes and vapours by covering vessels and by prompt replacement of caps and stoppers to bottles when handling volatile or dusty chemicals. Winchester bottles and liquid nitrogen must be carried in the special carriers. Hands must be washed before leaving the laboratory area. Highly toxic chemicals must be stored in a locked container and a record of this store maintained. All work with carcinogens must be in accord with the guidelines provided at UHSP/15/HS/03 Schedule 3.3. Containers must be adequately labelled to identify contents and to identify risk phrases. There are nine specific hazards associated with chemicals, each having its own warning symbol on a bright orange background. These symbols are given on bottles and in catalogues. The following protective equipment etc. are available from Stores : Laboratory coats Gloves, of various types, and barrier creams Goggles and spectacles Dust masks Winchester carriers All accidents involving chemicals must be reported immediately to the Deputy School Manager (Tel. 46551). Supervisors have a responsibility for assessing the risk to health and safety from any chemical hazard and for ensuring that working procedures are assessed and designed to minimise risk. They are responsible for ensuring that all activities involving chemicals or that may release chemicals have been assessed as required by University Hazardous Substances Policy. The Law and University Hazardous Substances Policy The Health and Safety at Work Etc Act 1974 and regulations made under it such as the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations and the Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) Regulations impose legal requirements on work involving hazardous substances. The law requires: Assessment of the hazard (potential to cause harm) and risk (likelihood of harm under conditions of use) to the health and safety of people at work (and visitors) of the substances with which they are working. 1. Prevention or adequate control of exposure to or risks from such substances. 2. Adequate maintenance of plant and personal protective equipment needed for prevention or control. 3. Monitoring exposure at the workplace if prevention cannot be achieved. 4. Health surveillance where necessary. 5. The provision of information, instruction and training for staff. The over-riding requirement of the law is that work involving hazardous substances is prohibited unless a suitable and sufficient risk assessment has been made and the controls and other findings of the assessment put in place. University Health and Safety Policy, including Hazardous Substances Policy, is based on the legal requirements. Compliance with University Policy should ensure compliance with the law. 1 Forms for Chemical Hazard and Risk assessments and associated guidelines are available from the School Safety Office (Room SG23 tel.46557; s.ward@bham.ac.uk) and from the School server (http://www.biosciences.bham.ac.uk/safety/index.htm). Advice can also be obtained from the School Safety Office. All assessments will be given an accession number. The accession numbers should be noted on all order forms for chemical purchase. A database of School assessments has been initiated and can be accessed via http://www.biosciences.bham.ac.uk/safety/index.htm. All assessments will be kept by the Safety Office and should also be available as a hard copy in the relevant laboratory. HAZARDOUS WASTE DISPOSAL Procedures for the disposal of hazardous wastes a. carcinogens b. phenol c. mercury d. ethidium bromide e. cyanogen bromide f. acrylamide are all given on http://www.biosciences.bham.ac.uk/safety/index.htm WASTE SOLVENTS At the point of production, waste solvents must be collected in securely closed screwcapped 2 litre Winchester bottles (partially filled) in two categories: Halogenated (ie. Those that contain chlorine, bromine, fluorine or iodine) Non-Halogenated (not containing halogens in any form) These should be labelled (remove or cover the original label) with a waste solvent label available from Stores. Waste solvents should be taken to Stores. TRANSPORT OF LIQUID NITROGEN All transport of liquid nitrogen should be with the use of special containers (dewars) designed for this purpose. A barrier system must be used when transporting by lift to ensure that no personnel travel with it. The barrier system is available from the Stores and should be positioned inside the lift doors with the dewar during transport. The barrier includes a sign indicating DANGER/DO NOT ENTER. 2 Glossary of Laboratory Safety ACID storage - stand bench bottles in a tray. Keep Winchesters in trays to contain breakages within the bin. ACID PERCHLORIC - stand bench bottle in a full - size beaker. CARCINOGENS- All work with carcinogens must be in accord with University Guidelines provided at UHSP/15/HS/03 Schedule 3.3 (Replaces USP/80/CR/2) . The Health and Safety Unit must be informed. COLD ROOMS need a grand clear-out every six months. DECONTAMINATE work areas and apparatus after using hazardous chemicals. DISPOSAL- Certain toxic chemicals require special disposal procedures (refer to http://www.biosciences.bham.ac.uk/safety/index.htm for guidelines and procedure documents for hazardous wastes including carcinogens). FLAMMABLE SOLVENTS - do not heat on hot plate or naked flame. FLAMMABLE SOLVENTS - store in solvent bins, limit 50 litres/ lab. Segregate from nonflammable do not store in standard refrigerators (fire risk). FOOD AND DRINK to be stored in approved areas only. A GLOVE BOX or custom balance enclosure, such as Waysafe, are the places to weigh out hazardous chemicals. GAS CYLINDERS must be secured, e.g. by stout chain, to workbench. GAS CYLINDERS are transported by cylinder trolley. GAS CYLINDERS must not be retained beyond immediate use. GLASS APPARATUS subjected to vacuum or gas pressure could implode, net it. HAZARD WARNING LABELS obtainable from Stores. IMPLOSION RISK - vacuum desiccators, freeze driers, distillations. LIQUID NITROGEN –store and transport in special containers NB Transport in the lift must not be accompanied by any person. Refer to the School Safety Office or Stores for details of the accepted procedure. MICROWAVE OVENS can leak radiation if the door or seal are damaged and ill-fitting. Damaged ovens should be checked by the Health and Safety Unit. PEROXIDE-FORMING SOLVENTS - e.g. ethers, dioxan, tetrahydrofuran - require periodic testing and possible disposal. SAFETY CABINETS for microbiological work to be regularly maintained. SHARPS e.g. used needles, scalpel blades, this includes tips!- store in sharps boxes in labs. Disposal via the special "difficult clinical waste" skip - contact Stores SOLVENTS - storage limited to 50 litres per lab - label with appropriate hazard warning label and segregate flammables from non-flammable stocks. Keep stock list in bin. SURPLUS TOXIC CHEMICALS must be listed and segregated for safe disposal. Contact the Stores Hazardous Waste Coordinator. TIPS –dispose of as sharps U/V LAMP, e.g. gel scanners, must be screened to avoid eye damage. Wear protective goggles. WASTE SOLVENT to be classified as halogenated or non-halogenated, labelled, segregated and stored in Winchesters in bins. WASTE SOLVENT DISPOSALS by arrangement with Stores. WASTE SOLVENT STOCKS count towards lab 50 litre limit - take to Stores. WINCHESTERS must be carried in the appropriate carriers and must not be kept on benches, only in storage bins. 3 CHEMICAL SAFETY PUBLICATIONS The University of Birmingham Health and Safety Unit provide the following publications on the web http://www.bham.ac.uk/SafetyUnit/univ/uhspdocs.html with particular relevance to chemical safety Hazardous Substances Policy - UHSP/15/HS/03 Criteria for Enhanced Good Chemical Practice UHSP/15/HS/03 (Schedule 3.2) Enhanced Good Chemical Practice for Work with Chemical - Schedule 3.3 (Replaces USP/80/CR/2) Enhanced Good Chemical Practice for Work with Cyanides UHSP/15/HS/03 (Schedule 3.4) Enhanced Good Chemical Practice for Work with Hydrogen fluoride and Hydrofluoric Acid UHSP/15/HS/03 (Schedule 3.5) Enhanced Good Chemical Practice for Work with Phenol UHSP/15/HS/03 (Schedule 3.6) Enhanced Good Chemical Practice for Peroxidisable Substances UHSP/15/HS/03 (Schedule 3.7) Arrangements for Keeping and Storage of Hazardous Substances UHSP/15/HS/03 Schedule 5 (Replaces USP/84/SHC/7 ) Good Chemical Practice - UHSP/15/HS/03 (Schedule 3.1) Chemical Hazard and Risk (COSHH) Assessment - UHSP/15/HS/03 Schedule 2 (replaces USP/90/CHRA/16) Out-of-Hours Activities and Unattended Equipment and Apparatus: UHSP/8/SSOHA/96 See also http://www.biosciences.bham.ac.uk/safety/index.htm for COSHH assessment forms and guidelines. Other help and advice can be obtained from the School Safety Office (RoomSG23, tel.46557 s.ward@bham.ac.uk) 4