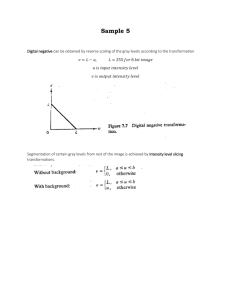
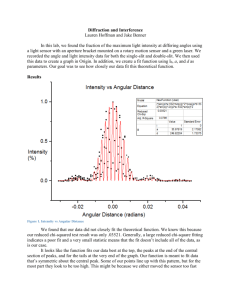
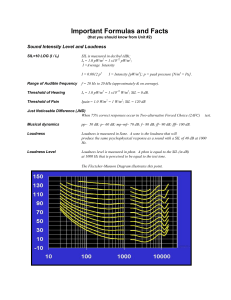
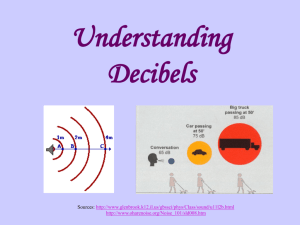
4.3 Wave Intensity - This is defined as the amount of energy per unit
advertisement

4.3 Wave Intensity - This is defined as the amount of energy per unit time flowing through unit area (It is normally measured in W.m-2) If light from a point source spreads out spherically, the intensity at any distance can be found by dividing the power by the surface area of a sphere of radius equal to the distance. The intensity of a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude I α a2 (or I = ka2) 1. A wave of amplitude a has an intensity of 3.0Wm–2. What is the intensity of a wave of the same frequency that has an amplitude 2a? 2. A wave has an amplitude of 0.02 m and an intensity of 2.5 Wm-2. It’s amplitude is increased until its intensity -2 reaches 5 Wm . What is the new amplitude? 3. A light bulb gives out visible light energy at a rate of 60W. What is the intensity at a distance of 5 m from the light bulb (imagine the light spread over a sphere of radius 5m). 4. The sun’s total power output is 3.9 x 1026 W (known as its “luminosity”). What is the intensity of sunlight at the surface of the earth’s atmosphere? (The earth orbits at an average distance of 1.5 x 1011 m from the sun. 5. What power would a light bulb have to have to produce the same intensity as you calculated in question 4 if the light bulb were 3 m away from you. 6. Proxima Centauri (the closest star to the earth after the sun) has a total power output (luminosity) of 6.6 x 1023 W. The distance of Proxima Centauri from the earth is 4.2 light years. Calculate the intensity of light from Proxima Centauri that reaches the earth’s upper atmosphere.