How Light Effects Plant Growth
advertisement

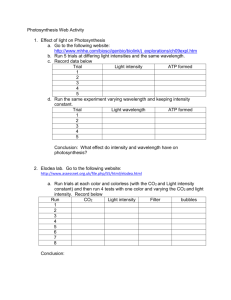
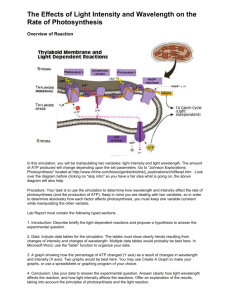
Environmental Factors Plant life depends on light energy for food production through photosynthesis. Plants convert the energy to a form of chemical energy. Three key aspects of light effect plant growth Color Duration Intensity Visible light (light we see) is a small segment of all the radiant energy (rays) given off by the sun. Based on their wavelengths, the rays have been placed on an, Electromagnetic Spectrum.(click) Sunlight contains a blend of visible colors. Each color has a slightly different wavelength < Light quality refers to the color or wavelength reaching the plant surface. Sunlight can be broken up by a prism into respective colors of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. (ROY G BIV) R - Red and blue light have the greatest effect on plant growth. O - Incandescent light is high in the red or orange range but generally produces too much heat to be a valuable light source. Y - Yellow G - Green light is least effective to plants as most plants reflect green light and absorb very little. It is this reflected light that makes them appear green. B - Blue light is primarily responsible for vegetative growth or leaf growth. I - Indigo V - Fluorescent "grow" lights have a mixture of red and blue colors that attempts to imitate sunlight as closely as possible. The light reflected has little affect on the plant. In plants, blue & red have the greatest influence on plant growth. Blue: ◦ Effects photosynthesis Red: ◦ Effects flowering and growth Environmental Factors Plants are responsive to the length of time they are exposed to light. A mechanism in the plant detects the length of the light period. A plant’s response to the length of light is known as, Photoperiodism. Different plants respond differently to the duration of light. Plants are broken into three categories: Short-day plants (Long-nights): Initiate flowering as the night grow longer than 12 hours. Long-day plants (Short-night period): Initiate flowering as the nights grow shorter than 12 hours. Day-neutral plants (unaffected) Are those plants that do not appear to respond to the change of day length. Short Day Plant critical day length 24 hours light dark No Yes No Flowers? light critical day length 24 hours Long Day Plant dark Yes No Yes Flowers? Environmental Factors Involves brightness. Depends largely on the angle of the sun, clouds, and the dust in the atmosphere. Measured in foot candles Light intensity is the greatest in the summer months. All plants have different terms of light intensity. Light intensity can influence plant development for better or for worse. Is the amount of light distributed by a single candle one-foot away. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lgFOnMwo3A&feature=relmfu http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UQ_QqtXo yQw LAB SHEET “How Do I Look in the Light?”