Text Types Scope and Sequence Prep to Year 6
advertisement

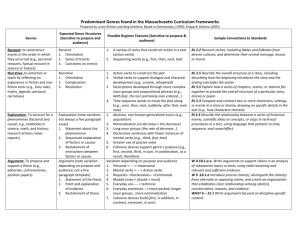
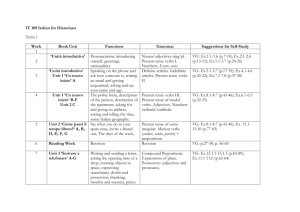
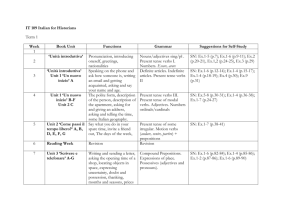
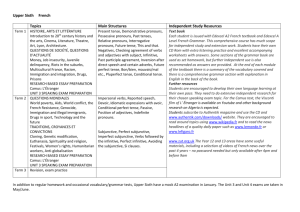
Text Types & Grammar Focuses Recounts- Personal and factual Purpose: To tell what happened Prep Purpose of recounts Recount description Years 1 & 2 Organisation of information in sequence Words/groups of words to denote passing of time Nouns Years 3 & 4 Structure of recount orientation series of events personal comment reorientation Location of who, what, when, where in orientation Past tense Action verbs Pronouns – first and third person Identify how pronouns link to/refer to nouns connectives that refer to time Lesley Wing Jan Adapted Wing Jan , L. Writeways-Modelling Writing Forms, OUP, Melbourne (2001) and Carey Grammar JSK English Program Years 5 & 6 Active and passive voice Varied sentence beginnings Difference between recount and reflection Types of recounts –personal factual imaginative Conjunctions Descriptive details added – use of commas or brackets First, and third person pronouns Paragraphs for major events/points Topic sentences Cohesive devices – ways to organise text so it is cohesive and coherent Types of recount : personal imaginative biography anecdote memoir historical Explanations Purpose: To tell how or why something happens. To describe a process Prep Years 1 & 2 Purpose of explanation- to explain An account of how or why how or why something happens something happens Procedural Texts Purpose: To tell how to do or make something Prep Years 1 & 2 Identify purpose – to tell how to Organisation into a sequence of do or make something actions Use of headings Purpose and function of each section of the structure of a procedure Ways of setting out instructions Years 3 & 4 Types of explanations why how Organisation of explanation statement of phenomenon sequenced explanation of how/shy something occurs Time relationships Action verbs Generalised non human participants (phenomena to be explained) Cause/effect Use of labels, headings, diagrams Purpose of explanation Years 3 & 4 Classes of nouns generalised and specific nouns Action verbs Linking words to do with time General structure of goal, materials and method (can be other words) Diagrams, subheadings, numbers etc.. Purpose of procedural texts Target audience Lesley Wing Jan Adapted Wing Jan , L. Writeways-Modelling Writing Forms, OUP, Melbourne (2001) and Carey Grammar JSK English Program Years 5 & 6 Explanations that explain how can be mechanical technological system natural Explanations that explain why can be as above Cause/effect Passive/active voice Auxiliary verbs Conjunctions Timeless present tense Specialised vocabulary About general rather than specific events Use of definitions & description Adjectives & adjective groups Adverbs & adverb groups Years 5 & 6 Types of instructions Imperatives Use of adverbs/adverb groups how when where Timeless present tense Detailed, factual description of items mentioned Way reader is referred to in general way or not at all eg Cut the string. (You) cut the string Subject specific vocab Use of conjunctions Narratives Purpose: To entertain, teach and inform Prep Purpose of narratives Sequence of actions/events Years 1 & 2 Structure of narrative Nouns Purpose of narratives Reports Purpose: To provide factual information on a topic Prep Years 1 & 2 About general class of things – Sentences containing a fact or rather than specific things series of facts Factual sentences Information in groups Labelled diagrams Years 3 & 4 Organisation of text – structure of narrative Normally past tense Action verbs Use of dialogue Use of adjectives, adverbs to enhance description Direct speech Years 3 & 4 Formal and objective style of writing (no personal pronouns) Use of diagrams, illustrations Labels, captions, subheadings Grouping of information Structure of reports Descriptive language – factual and precise Action verbs Cross sections Labelled diagrams Years 5 & 6 Types of narratives mysteries science fiction choose your own romance horror adventure historical etc.. imaginary & factual Verbal and mental verbs (said, felt) as well as action verbs First, second and third person Change of tense in dialogue Linking words to do with time Direct speech Information Narrative Structure Information woven into plot Descriptive language Years 5 & 6 Lesley Wing Jan Adapted Wing Jan , L. Writeways-Modelling Writing Forms, OUP, Melbourne (2001) and Carey Grammar JSK English Program Use of technical vocabulary Linking verbs Paragraphs Definitions – language for defining Topic sentences Structure of reports opening general statement grouped info about topic – grouped according to characteristic Language of comparison compare/contrast list/describe Timeless present tense Economical language Specialised vocabulary Brackets to explain/clarify Persuasive Texts- Argument. discission and advertisements Purpose: To put forward a point of view. To persuade people to do or think things in line with the author’s/speaker’s point of view Prep Years 1 & 2 Years 3 & 4 Years 5 & 6 State preference/point of view Arguments – state point of view Structure of arguments : Discussions – (debate) structure and justify this usually with and provide reason for this statement of position, arguments – issue, arguments for and “because” Advertisements – state purpose in sequences, restatement of arguments against, conclusion Include only important position Class of text types called information Purpose of arguments : to justify “expositions” which either Arrange information so easily a position, arguing for some sort analyse, interpret or evaluate read of action to take place. Actions are changed into things persuading “that” (nominalisation to make argument persuading “to” sound more objective Use of connectives to order Use of connectives associated arguments with reasoning Identification of “emotive” Use of passive speech terms/words Tense changes according to Identify target audience for stage of text advertisements Removal of personal pronouns Identify and use some devices Organise arguments into for ads eg font size, placement paragraphs of text, use of graphics, colour, Purpose of topic sentences catchy headings, titles, slogans Use of language of persuasion Use logic and evidence to convince reader Use of formalised language Use of abstract and technical terms Compare/contrast Cause/effect Problem/solution Ways of “hiding self” so that writing appears impartial and objective Lesley Wing Jan Adapted Wing Jan , L. Writeways-Modelling Writing Forms, OUP, Melbourne (2001) and Carey Grammar JSK English Program